https://github.com/beuth-erdelt/benchmark-experiment-host-manager
This python tool helps managing DBMS benchmarking experiments in a Kubernetes-based HPC cluster environment. It enables users to configure hardware / software setups for easily repeating tests over varying configurations.
https://github.com/beuth-erdelt/benchmark-experiment-host-manager
aws benchmark cluster database dbms k8s kubernetes python tpc-c tpc-h ycsb
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
This python tool helps managing DBMS benchmarking experiments in a Kubernetes-based HPC cluster environment. It enables users to configure hardware / software setups for easily repeating tests over varying configurations.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/beuth-erdelt/benchmark-experiment-host-manager
- Owner: Beuth-Erdelt
- License: agpl-3.0
- Created: 2019-09-14T17:10:12.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-09T14:40:30.000Z (2 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-09T15:43:56.320Z (2 months ago)
- Topics: aws, benchmark, cluster, database, dbms, k8s, kubernetes, python, tpc-c, tpc-h, ycsb
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 69.8 MB
- Stars: 6
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 60
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: docs/CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://GitHub.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/graphs/commit-activity)
[](https://GitHub.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/releases/)
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/bexhoma)
[](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/actions/workflows/draft-pdf.yml)
[](https://snyk.io/advisor/python/bexhoma)
[](https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
# Benchmark Experiment Host Manager (Bexhoma)
## Orchestrating Cloud-Native Benchmarking Experiments with Kubernetes
This Python tools helps **managing benchmark experiments of Database Management Systems (DBMS) in a Kubernetes-based High-Performance-Computing (HPC) cluster environment**.
It enables users to configure hardware / software setups for easily repeating tests over varying configurations.
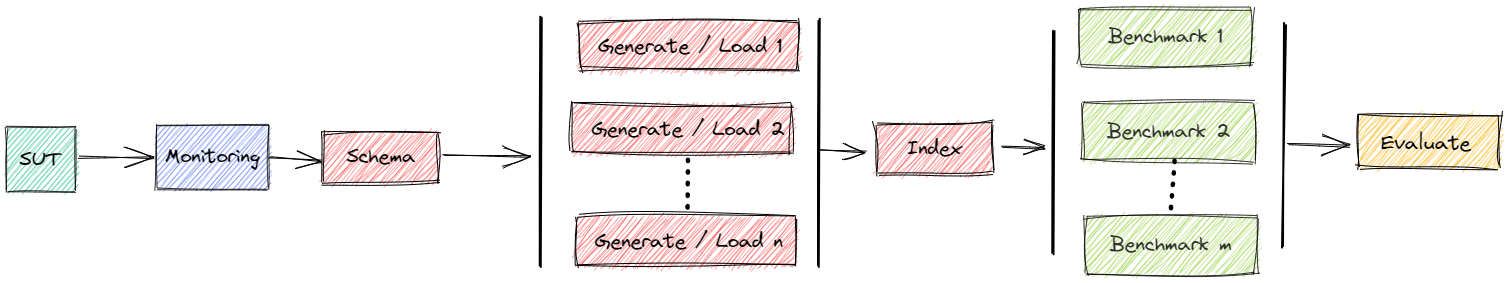
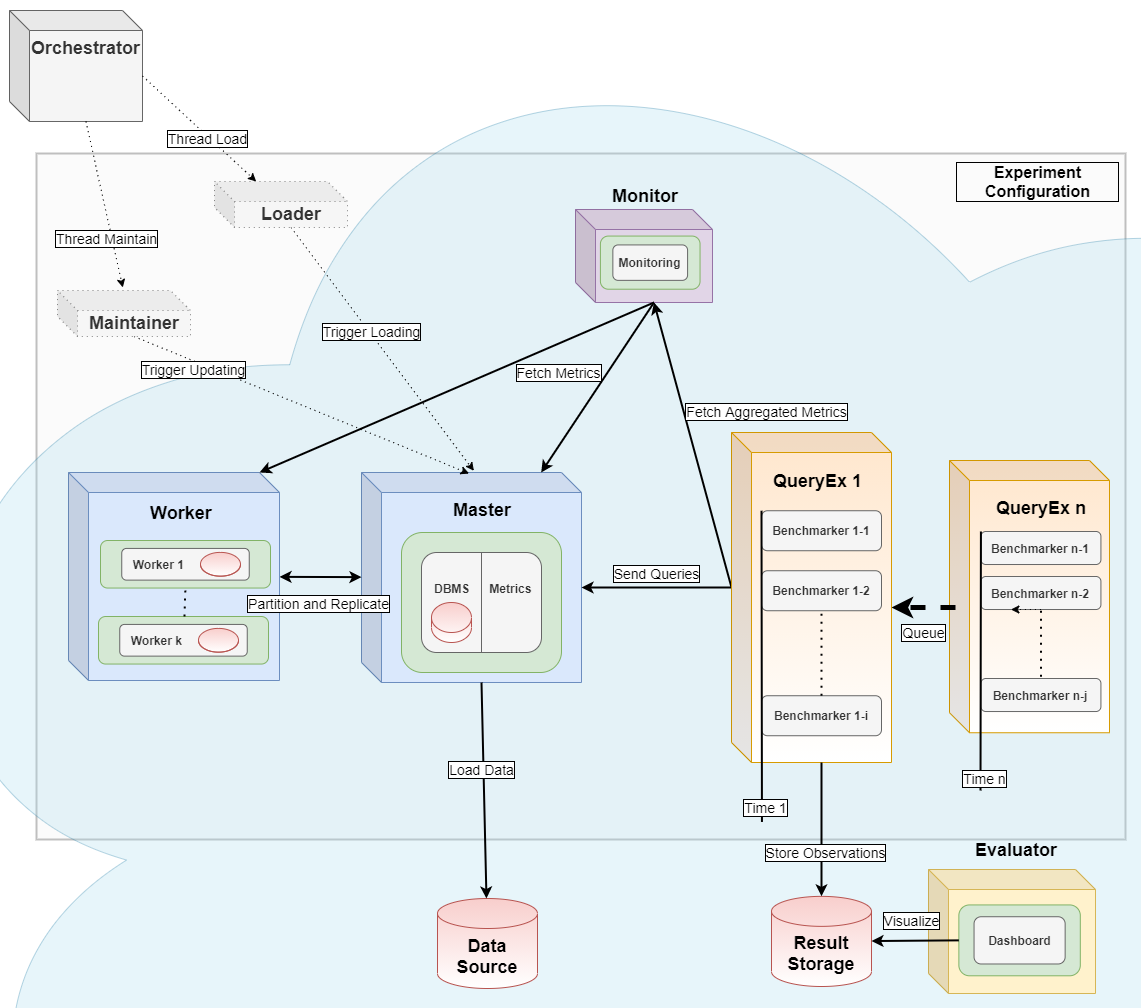
It serves as the **orchestrator** [2] for distributed parallel benchmarking experiments in a Kubernetes Cloud.
This has been tested at Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and at Minikube installations,
running with Citus Data (Hyperscale), Clickhouse, CockroachDB, Exasol, IBM DB2, MariaDB, MariaDB Columnstore, MemSQL (SingleStore), MonetDB, MySQL, OmniSci (HEAVY.AI), Oracle DB, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, SAP HANA, TimescaleDB, Vertica and YugabyteDB.
Benchmarks included are YCSB, TPC-H and TPC-C (HammerDB and Benchbase version).
The basic workflow is [1,2]: start a containerized version of the DBMS, install monitoring software, import data, run benchmarks and shut down everything with a single command.
A more advanced workflow is: Plan a sequence of such experiments, run plan as a batch and join results for comparison.
It is also possible to scale-out drivers for generating and loading data and for benchmarking to simulate cloud-native environments as in [4].
See [example](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/tree/master/TPCTC23) results as presented in [A Cloud-Native Adoption of Classical DBMS Performance Benchmarks and Tools](http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.29866.18880) and how they are generated.
See the [homepage](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager) and the [documentation](https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/stable/).
If you encounter any issues, please report them to our [Github issue tracker](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/issues).
## Installation
1. Download the repository: https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager
1. Install the package `pip install bexhoma`
1. Make sure you have a working `kubectl` installed.
* (Also make sure to have access to a running Kubernetes cluster - for example [Minikube](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/))
* (Also make sure, you can create PV via PVC and dynamic provisioning)
1. Adjust [configuration](https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Config.html)
1. Copy `k8s-cluster.config` to `cluster.config`
1. Set name of context, namespace and name of cluster in that file
2. Make sure the `resultfolder` is set to a folder that exists on your local filesystem
1. Other components like the shared data and result directories, the message queue and the evaluator are installed automatically when you start an experiment. Before that, you might want to adjust
* Result directory: https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/blob/master/k8s/pvc-bexhoma-results.yml
* `storageClassName`: must be an available storage class of type `ReadWriteMany` in your cluster
* `storage`: size of the directory
* Data directory: https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/blob/master/k8s/pvc-bexhoma-data.yml
* `storageClassName`: must be an available storage class of type `ReadWriteMany` in your cluster
* `storage`: size of the directory
## Quickstart
### YCSB
1. Run `python ycsb.py -ms 1 -tr -sf 1 --workload a -dbms PostgreSQL -tb 16384 -nlp 1 -nlt 64 -nlf 4 -nbp 1,8 -nbt 64 -nbf 2,3 run`.
This installs PostgreSQL and runs YCSB workload A with varying target. The driver is monolithic with 64 threads. The experiments runs a second time with the driver scaled out to 8 instances each having 8 threads.
1. You can watch status using `bexperiments status` while running.
1. After benchmarking has finished, you will see a summary.
For further inspecting, you can use a Python interface.
See more details at https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Example-YCSB.html
### HammerDB's TPC-C
1. Run `python hammerdb.py -ms 1 -tr -sf 16 -sd 5 -dbms PostgreSQL -nlt 16 -nbp 1,2 -nbt 16 run`.
This installs PostgreSQL and runs HammerDB's TPC-C with 16 warehouses. The driver is monolithic with 16 threads. The experiments runs a second time with the driver scaled out to 2 instances each having 8 threads.
1. You can watch status using `bexperiments status` while running.
1. After benchmarking has finished, you will see a summary.
For further inspecting, you can use a Python interface.
See more details at https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Example-HammerDB.html
### Benchbase's TPC-C
1. Run `python benchbase.py -ms 1 -tr -sf 16 -sd 5 -dbms PostgreSQL -nbp 1,2 -nbt 16 -nbf 16 -tb 1024 run`.
This installs PostgreSQL and runs Benchbase's TPC-C with 16 warehouses. The driver is monolithic with 16 threads. The experiments runs a second time with the driver scaled out to 2 instances each having 8 threads.
1. You can watch status using `bexperiments status` while running.
1. After benchmarking has finished, you will see a summary.
For further inspecting, you can use a Python interface.
See more details at https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Example-HammerDB.html
### TPC-H
1. Run `python tpch.py -ms 1 -dbms PostgreSQL run`.
This installs PostgreSQL and runs TPC-H at scale factor 1. The driver is monolithic.
1. You can watch status using `bexperiments status` while running.
1. After benchmarking has finished, you will see a summary.
For further inspecting, you can use a Python interface.
See more details at https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Example-TPC-H.html
### TPC-DS
1. Run `python tpcds.py -ms 1 -dbms PostgreSQL run`.
This installs PostgreSQL and runs TPC-DS at scale factor 1. The driver is monolithic.
1. You can watch status using `bexperiments status` while running.
1. After benchmarking has finished, you will see a summary.
For further inspecting, you can use a dashboard or a Python interface.
See more details at https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Example-TPC-DS.html
## More Informations
For full power, use this tool as an orchestrator as in [2]. It also starts a monitoring container using [Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/) and a metrics collector container using [cAdvisor](https://github.com/google/cadvisor). For analytical use cases, the Python package [dbmsbenchmarker](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/DBMS-Benchmarker), [3], is used as query executor and evaluator as in [1,2].
For transactional use cases, HammerDB's TPC-C, Benchbase's TPC-C and YCSB are used as drivers for generating and loading data and for running the workload as in [4].
See the [images](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/tree/master/images/) folder for more details.
## Contributing, Bug Reports
If you have any question or found a bug, please report them to our [Github issue tracker](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/issues).
In any bug report, please let us know:
* Which operating system and hardware (32 bit or 64 bit) you are using
* Python version
* Bexhoma version (or git commit/date)
* Traceback that occurs (the full error message)
We are always looking for people interested in helping with code development, documentation writing, technical administration, and whatever else comes up.
If you wish to contribute, please first read the [contribution section](https://github.com/Beuth-Erdelt/Benchmark-Experiment-Host-Manager/blob/master/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md) or visit the [documentation](https://bexhoma.readthedocs.io/en/latest/CONTRIBUTING.html).
## References
If you use Bexhoma in work contributing to a scientific publication, we kindly ask that you cite our application note [2] or [1]:
[1] [A Framework for Supporting Repetition and Evaluation in the Process of Cloud-Based DBMS Performance Benchmarking](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84924-5_6)
> Erdelt P.K. (2021)
> A Framework for Supporting Repetition and Evaluation in the Process of Cloud-Based DBMS Performance Benchmarking.
> In: Nambiar R., Poess M. (eds) Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. TPCTC 2020.
> Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12752. Springer, Cham.
> https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84924-5_6
[2] [Orchestrating DBMS Benchmarking in the Cloud with Kubernetes](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94437-7_6)
> Erdelt P.K. (2022)
> Orchestrating DBMS Benchmarking in the Cloud with Kubernetes.
> In: Nambiar R., Poess M. (eds) Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. TPCTC 2021.
> Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13169. Springer, Cham.
> https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94437-7_6
[3] [DBMS-Benchmarker: Benchmark and Evaluate DBMS in Python](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.04628)
> Erdelt P.K., Jestel J. (2022).
> DBMS-Benchmarker: Benchmark and Evaluate DBMS in Python.
> Journal of Open Source Software, 7(79), 4628
> https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.04628
[4] [A Cloud-Native Adoption of Classical DBMS Performance Benchmarks and Tools](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68031-1_9)
> Erdelt, P.K. (2024).
> A Cloud-Native Adoption of Classical DBMS Performance Benchmarks and Tools.
> In: Nambiar, R., Poess, M. (eds) Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. TPCTC 2023.
> Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14247. Springer, Cham.
> https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-68031-1_9