https://github.com/bh90210/simpledbw
(proof of concept) Persistent (key/value) storage library for Android (Badger binding)
https://github.com/bh90210/simpledbw
android badger badgerdb go java key-value library persistent-storage wrapper
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
(proof of concept) Persistent (key/value) storage library for Android (Badger binding)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/bh90210/simpledbw
- Owner: bh90210
- Created: 2019-05-20T11:53:25.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-06-08T14:58:20.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-06-19T05:33:24.753Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: android, badger, badgerdb, go, java, key-value, library, persistent-storage, wrapper
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 248 MB
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# SimpleDBW
A simple to use persistente storage wrapper around [Badger](https://github.com/dgraph-io/badger) for Android.
### Installation
Download (or clone) the repository then use Android Studio to import the library to your project `file > new > import module`
In your app's module `build.gradle` file include
```gradle
repositories {
flatDir {
dirs './simpledbw/libs'
}
}
```
The library uses lifecycle-extensions. So you have to also include this dependacy.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.0.0"
implementation (name:'simpledbw')
}
```
#### initialisation
In your module's main activity onCreate function add this line
```java
ProcessLifecycleOwner.get().getLifecycle().addObserver(new DBWhelper());
```
ie.
```java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// DB init
// Add Lifecycle Observer
ProcessLifecycleOwner.get().getLifecycle().addObserver(new DBWhelper());
```
### Usage
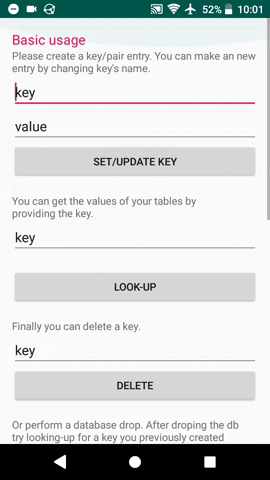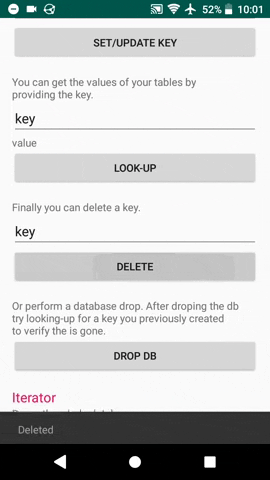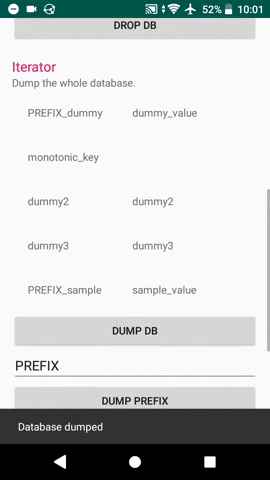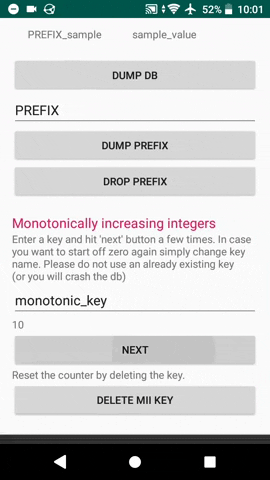
#### Set value
```java
Database db = new Database();
```
The database uses byte[] for both keys and values.
```java
db.Update("key".getBytes(), "value".getBytes());
```
#### Get value
A db.View query returns a byte[] with the requested value. If key does not exist it returns "key does not exist".
```java
byte[] returnedvalue = db.View("key".getBytes());
```
This can be for example converted to string and used with TextView like so
```java
String text = new String(returnedvalue);
exampleTextView.setText(text);
```
#### Delete key
```java
db.Delete("key".getBytes());
```
#### Iterate
##### Prefix
Iterated over the database quering a specific prefix
```java
ArrayMap entries = db.ViewPrefix("prefix".getBytes());
```
and you get an ArrayMap with all the associated keys and values. Please check Android's [documentation](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/v4/util/ArrayMap) for more information and usage.
Delete all keys assosiated with spedific prefix.
```java
db.PrefixDrop("prefix".getBytes());
```
##### Dump returns an ArrayMap with every entry in the database.
```java
ArrayMap entries = db.DumpAll();
```
it can be used for example to inflate a TableLayout
ie.
```java
ArrayMap tables = db.DumpAll();
TableLayout dump = findViewById(R.id.ret_vals);
dump.removeAllViews();
Iterator it = tables.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ArrayMap.Entry pair = (ArrayMap.Entry)it.next();
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) getApplicationContext().getSystemService
(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View row = inflater.inflate(R.layout.row, null);
dump.addView(row);
//View rowID = row.findViewById(R.id.tableraw);
TextView keyfield = row.findViewById(R.id.printkey);
TextView valuefield = row.findViewById(R.id.printvalue);
String key = new String((byte[]) pair.getKey());
String value = new String((byte[]) pair.getValue());
keyfield.setText(key);
valuefield.setText(value);
it.remove(); // avoids a ConcurrentModificationException
}
```
#### Monotonically increasing integers
You can get monotonically increasing integers with strong durability
```java
long nextInt = db.Mii("monotonic_key".getBytes());
```
Reset the count by deleting the key
```java
db.Delete("monotonic_key".getBytes());
```
#### Drop all
```java
db.DropDB();
```
#### Pre-populated entries
Place this on your module's main activity onCreate function. Please note if you drop the DB or delete the key the next time the app starts and opens the database these keys *will* regenerate.
```java
db.PrePopulate("PREFIX_sample".getBytes(), "sample_value".getBytes());
```
ie.
```java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// DB init
// Add Lifecycle Observer
ProcessLifecycleOwner.get().getLifecycle().addObserver(new DBWhelper());
// call the class
Database db = new Database();
// add some dummy pre-populated values
db.PrePopulate("PREFIX_sample".getBytes(), "sample_value".getBytes());
db.PrePopulate("PREFIX_dummy".getBytes(), "dummy_value".getBytes());
```
### Build Go source
Unfortunatly gomobile does not support gomodules at the moment so you have to work within $GOPATH.
First ensure you have gomobile and badger installed. For more information click [here](https://godoc.org/golang.org/x/mobile/cmd/gomobile) and [here](https://github.com/dgraph-io/badger) respectively.
* ```go get github.com/dgraph-io/badger/...```
and
* ```go get golang.org/x/mobile/cmd/gomobile```
* ```gomobile init```
then
* run ```go get https://github.com/bh90210/SimpleDBW```
* and ```gomobile bind -o simpledbw/dbwrapper.aar -target=android $GOPATH/src/github.com/bh90210/SimpleDBW```