https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata
Quality control tool on metagenomic and metatranscriptomic sequencing data, especially data from microbiome experiments.
https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata
biobakery bowtie2 kneaddata public quality-control tools
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Quality control tool on metagenomic and metatranscriptomic sequencing data, especially data from microbiome experiments.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata
- Owner: biobakery
- License: other
- Created: 2020-04-07T17:53:23.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-20T16:47:29.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-29T01:09:49.435Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: biobakery, bowtie2, kneaddata, public, quality-control, tools
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 978 KB
- Stars: 116
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 31
- Open Issues: 13
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
- Changelog: history.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# ***ATTENTION***
Before opening a new issue here, please check the appropriate help channel on the [KneadData bioBakery Support Forum](https://forum.biobakery.org/c/infrastructure-and-utilities/kneaddata/8) and consider opening or commenting on a thread there.
For additional information, visit the [KneadData Tutorial](https://github.com/biobakery/biobakery/wiki/kneaddata).
----
# KneadData User Manual #
KneadData is a tool designed to perform quality control on metagenomic and
metatranscriptomic sequencing data, especially data from microbiome experiments.
In these experiments, samples are typically taken from a host in hopes of
learning something about the microbial community on the host. However,
sequencing data from such experiments will often contain a high ratio of host to
bacterial reads. This tool aims to perform principled *in silico* separation of
bacterial reads from these "contaminant" reads, be they from the host, from
bacterial 16S sequences, or other user-defined sources. Additionally, KneadData
can be used for other filtering tasks. For example, if one is trying to clean
data derived from a human sequencing experiment, KneadData can be used to
separate the human and the non-human reads.
**If you use the KneadData software, please cite our manuscript: TBA**
## Contents ##
- [Requirements](#requirements)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Create a Custom Database](#create-a-custom-database)
- [How to Run](#how-to-run)
- [Single End Run](#single-end-run)
- [Paired End Run](#paired-end-run)
- [Demo Run](#demo-run)
- [Sequencer Source for trimming Adapter Contents](#sequencer-source-for-trimming-adapter-contents)
- [Trim Overrepresented/Repetitive sequences](#trim-overrepresentedrepetitive-sequences)
- [Additional Arguments](#additional-arguments)
- [Complete Option List](#complete-option-list)
## Requirements ##
1. [Trimmomatic](http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic) (version == 0.33) (automatically installed)
2. [Bowtie2](http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/bowtie2/index.shtml) (version >= 2.2) (automatically installed)
3. [Python](http://www.python.org/) (version >= 2.7)
4. [Java Runtime Environment](http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jre7-downloads-1880261.html)
5. [TRF](https://tandem.bu.edu/trf/trf.html) (optional)
6. [Fastqc](http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/) (optional)
7. [SAMTools](https://github.com/samtools/samtools) (only required if input file is in BAM format)
8. Memory (>= 4 Gb if using Bowtie2, >= 8 Gb if using BMTagger)
9. Operating system (Linux or Mac)
Optionally, [BMTagger](ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/agarwala/bmtagger/) can be used instead of Bowtie2.
The executables for the required software packages should be installed in your $PATH. Alternatively, you can provide the location of the Bowtie2 install ($BOWTIE2_DIR) with the following KneadData option “--bowtie2 $BOWTIE2_DIR”.
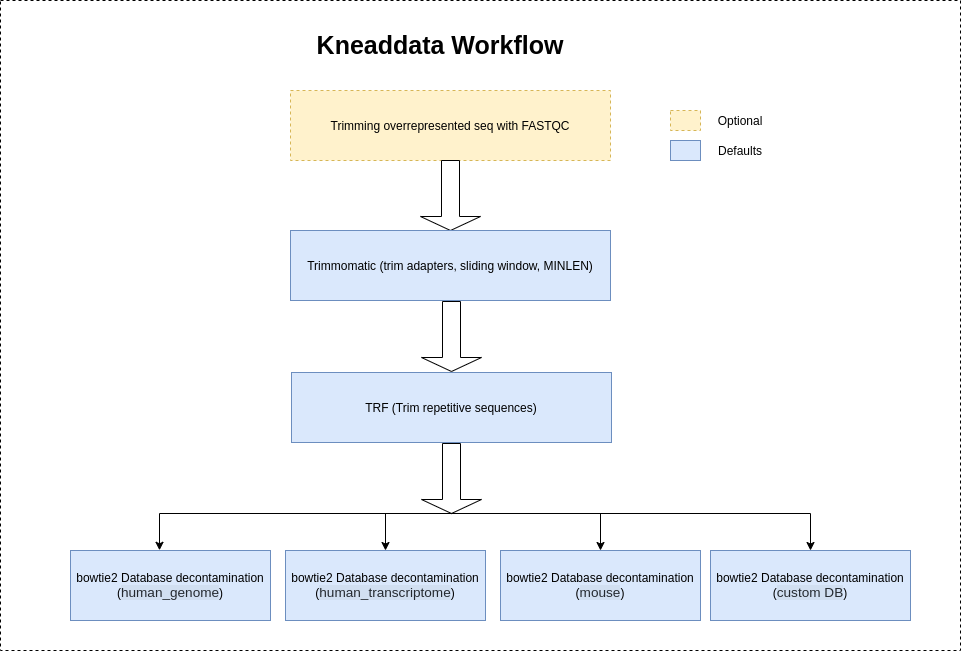
## Installation ##
Before installing KneadData, please install the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). First [download](http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jre7-downloads-1880261.html) the JRE for your platform. Then follow the instructions for your platform: [Linux 64-bit](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/install/linux_jre.html#CFHIEGAA) or [Mac OS](http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/install/mac_jre.html#jre_8u40_osx). At the end of the installation, add the location of the java executable to your $PATH.
## Download KneadData ###
You can download the latest KneadData release or the development version. The source contains example files. If installing with pip, it is optional to first download the KneadData source.
Option 1: Latest Release (Recommended)
* Download [kneaddata.tar.gz](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/kneaddata) and unpack the latest release of KneadData.
Option 2: Development Version
* Create a clone of the repository:
`` $ git clone https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata.git ``
Note: Creating a clone of the repository requires [Git](https://git-scm.com/) to be installed.
## Install KneadData ###
#### Install with pip ####
* `` $ pip install kneaddata ``
* This command will automatically install Trimmomatic and Bowtie2. To bypass the install of dependencies, add the option "--install-option='--bypass-dependencies-install'".
* If you do not have write permissions to '/usr/lib/', then add the option "--user" to the install command. This will install the python package into subdirectories of '$HOME/.local'. Please note when using the "--user" install option on some platforms, you might need to add '$HOME/.local/bin/' to your $PATH as it might not be included by default. You will know if it needs to be added if you see the following message ``kneaddata: command not found`` when trying to run KneadData after installing with the "--user" option.
#### Install from source ####
1. Follow the instructions to download KneadData
2. Move to the KneadData source directory: ``$ cd kneaddata``
3. Install KneadData
* ``$ python setup.py install``
* This command will automatically install Trimmomatic and Bowtie2. To bypass the install of dependencies, add the option "--bypass-dependencies-install".
* If you do not have write permissions to '/usr/lib/', then add the option "--user" to the install command. This will install the python package into subdirectories of '$HOME/.local'. Please note when using the "--user" install option on some platforms, you might need to add '$HOME/.local/bin/' to your $PATH as it might not be included by default. You will know if it needs to be added if you see the following message ``kneaddata: command not found`` when trying to run KneadData after installing with the "--user" option.
### Download the database ###
It is recommended that you download the human ([Homo_sapiens_hg39_T2T_Bowtie2_v0.1.tar.gz](https://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/kneadData_databases/Homo_sapiens_hg39_T2T_Bowtie2_v0.1.tar.gz) - [source](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCF_009914755.1/) ) reference database (approx. size = 3.6 GB). However, this step is not required if you are using your own custom reference database or if you will not be running with a reference database.
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download human_genome bowtie2 $DIR ``
* When running this command, $DIR should be replaced with the full path to the directory you have selected to store the database.
If you are running with bmtagger instead of bowtie2, then download the bmtagger database instead of the bowtie2 database with the following command.
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download human_genome bmtagger $DIR ``
* When running this command, $DIR should be replaced with the full path to the directory you have selected to store the database.
The human transcriptome (hg38) reference database is also available for download (approx. size = 254 MB).
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download human_transcriptome bowtie2 $DIR ``
The SILVA Ribosomal RNA reference database is also available for download (approx. size = 11 GB).
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download ribosomal_RNA bowtie2 $DIR ``
The mouse (C57BL) reference database is also available for download (approx. size = 3 GB).
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download mouse_C57BL bowtie2 $DIR ``
The dog reference database is also available for download (approx. size = 1.4 GB). This database is based on the genomic DNA sequences for the [Canis familiaris (domestic dog) assembly version ROS_Cfam_1.0.](https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/014/441/545/GCF_014441545.1_ROS_Cfam_1.0/GCF_014441545.1_ROS_Cfam_1.0_genomic.fna.gz) This file includes the nucleotide sequences of the assembled chromosomes and unplaced scaffolds.
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download dog_genome bowtie2 $DIR ``
The cat reference database is available for download (approx. size = 3.7 GB). This database is based on the genomic DNA sequences for the [Felis catus (domestic cat)](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/GCF_018350175.1/) This link includes the nucleotide sequences of the assembled chromosomes and unplaced scaffolds.
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download cat_genome bowtie2 $DIR ``
## Create a Custom Database ##
A reference database can be downloaded to use when running KneadData. Alternatively, you can create your own custom reference database.
### Select Reference Sequences ###
First you must select reference sequences for the contamination you are trying to
remove. Say you wish to filter reads from a particular "host." Broadly
defined, the host can be an organism, or a set of organisms, or just a set of
sequences. Then, you simply must generate a reference database for KneadData from a
[FASTA](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTA_format) file containing these
sequences. Usually, researchers want to remove reads from the human genome, the
human transcriptome, or ribosomal RNA. You can access some of these FASTA files
using the resources below:
- Ribosomal RNA: [Silva](http://www.arb-silva.de/) provides a comprehensive
database for ribosomal RNA sequences spanning all three domains of life
(*Bacteria*, *Archaea*, and *Eukarya*).
- Human Genome & Transcriptome: Information about the newest assembly of human
genomic data can be found at the [NCBI project
page](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/genome/assembly/grc/human/). USCS
provides a convenient [website](http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/downloads.html#human) to download
this data.
### Generating KneadData Databases ###
KneadData requires that your reference sequences (FASTA files) be indexed to
form KneadData databases beforehand. This only needs to be done once per
reference sequence.
For certain common databases, we provide indexed files. If you use these, you
can skip the manual build steps below. Alternatively if you would like to bypass
the reference alignment portion of the workflow, a database does not need to be
provided when running KneadData.
To download the indexed human reference database, run the following command:
* `` $ kneaddata_database --download human bowtie2 $DIR ``
* When running this command, $DIR should be replaced with the full path to the directory you have selected to store the database.
### Creating a Bowtie2 Database #####
Simply run the `bowtie2-build` indexer included with Bowtie2 as follows:
``$ bowtie2-build ``
Where `` is the reference FASTA file, and `` is the name you
wish to call your Bowtie2 database. For more details, refer
to the [bowtie2-build-documentation](http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/bowtie2/manual.shtml#the-bowtie2-build-indexer)
##### **Note: Creating SILVA ribosomal_RNA Database**
Creating the **SILVA ribosomal_RNA** database requires one additional step. Run the following python program before `bowtie2-build` command which converts the "U"s to "T"s in the fasta sequences.
Script link: [modify_RNA_to_DNA.py](https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata/blob/master/kneaddata/db_preprocessing/modify_RNA_to_DNA.py)
``$ python -u modify_RNA_to_DNA.py input.fasta output.fa``
### Creating a BMTagger Database #####
KneadData includes `kneaddata_build_database`, an executable that
will automatically generate these databases for BMTagger. Simply run
``$ kneaddata_build_database reference.fasta``
By default, this will generate the reference databases, whose names are prefixed
with `reference.fasta`.
A note on PATH: The above command will fail if the tools in the BMTagger suite
(specifically, bmtool and srprism) and the NCBI BLAST executables are not in
your PATH. If this is the case, you can specify a path to these tools using the
`-b`, `-s`, and `-m` options. Run
``$ kneaddata_build_database --help``
for more details.
#### Example Custom Database Build #####
Say you want to remove human reads from your metagenomic sequencing data.
You downloaded the human genome in a file called `Homo_sapiens.fasta`.
Then, you can generate the KneadData database by executing:
``$ bowtie2-build Homo_sapiens.fasta -o Homo_sapiens_db``
for Bowtie2, or
``$ kneaddata_build_database Homo_sapiens.fasta -o Homo_sapiens_db``
All of the required KneadData database files will have file names prefixed by
`Homo_sapiens_db` and have various file extensions.
### **Note**: For creating SILVA ribosomal_RNA database
Run the following python program before `bowtie2-build` command which converts the "U"s to "T"s in the fasta sequences for creating SILVA ribosomal_RNA database.
Script link: [modify_RNA_to_DNA.py](https://github.com/biobakery/kneaddata/blob/master/kneaddata/db_preprocessing/modify_RNA_to_DNA.py)
``$ python -u modify_RNA_to_DNA.py input.fasta output.fa``
## How to Run ###
After downloading or generating your database file, you can start to remove contaminant reads.
As input, KneadData requires FASTQ files. It supports both single end and paired
end reads. KneadData uses either Bowtie2 (default) or BMTagger to identify the
contaminant reads.
## Single End Run ####
To run KneadData in single end mode, run
` $ kneaddata --unpaired seq.fastq --reference-db $DATABASE --output kneaddata_output `
This will create files in the folder `kneaddata_output` named
+ `seq_kneaddata_$DATABASE_bowtie2_contam.fastq`: FASTQ file containing reads that were
identified as contaminants from the database (named $DATABASE).
+ `seq_kneaddata.fastq`: This file includes reads that were not in the reference database.
+ `seq_kneaddata.trimmed.fastq`: This file has trimmed reads.
+ `seq_kneaddata.log`
To run KneadData in single end mode with BMTagger, run
` $ kneaddata --unpaired seq.fastq --reference-db $DATABASE --run-bmtagger`
By default, this will create the same four files as running with bowtie2. The only differences are the contaminants file will have "bmtagger" in the name instead of "bowtie2" and the included $DATABASE name would differ.
If you wanted to use BMTagger and the BMTagger executable was located at
`$HOME/bmtagger/bmtagger.sh` which is not in your $PATH you would add the option "--bmtagger $HOME/bmtagger/bmtagger.sh" to the command.
If you wanted to select the basenames of the output files, you would add the option "--output-prefix $NAME", replacing $NAME with the name you would like used.
## Paired End Run ####
To run KneadData in paired end mode with Bowtie2, run
` $ kneaddata --input1 seq1.fastq --input2 seq2.fastq -db $DATABASE --output kneaddata_output`
To run KneadData in paired end mode with BMTagger, run
` $ kneaddata --input seq1.fastq --input seq2.fastq -db $DATABASE --run-bmtagger --output kneaddata_output `
+ `seq1.fastq`: Your input FASTQ file, first mate
+ `seq2.fastq`: Your input FASTQ file, second mate
+ `$DATABASE`: Prefix for the KneadData database.
+ `kneaddata_output`: The folder to write the output files.
The outputs depend on what happens during the quality filtering and trimming
part of the pipeline.
When performing quality filtering and trimming for paired end files, three things
can happen:
1. Both reads in the pair pass.
2. The read in the first mate passes, and the one in the second does not pass.
3. The read in the second mate passes, and the one in the first does not pass.
The number of outputs are a function of the read quality.
KneadData + Bowtie2 (or BMTagger) Outputs: There can be up to 8 outputs per reference
database, plus up to 5 aggregate outputs.
Instead of single end reads, say you have paired end reads and you want to
separate the reads that came from bacterial mRNA, bacterial rRNA, and human RNA.
You have two databases, one prefixed `bact_rrna_db` and the other prefixed
`human_rna_db`, and your sequence files are `seq1.fastq` and `seq2.fastq`. To
run with Bowtie2, execute
`$ kneaddata --input1 seq1.fastq --input2 seq2.fastq -db bact_rrna_db -db human_rna_db --output seq_out `
This will output files in the folder `seq_out` named:
Files for just the `bact_rrna_db` database:
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_contam_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as belonging to the `bact_rrna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_contam_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as belonging to the `bact_rrna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_clean_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`bact_rrna_db` database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_clean_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`bact_rrna_db` database.
Depending on the input FASTQ, one or more of the following may be output:
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_1_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_contam.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as belonging to the `bact_rrna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_1_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_clean.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`bact_rrna_db` database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_2_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_contam.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (3) above that were identified as belonging to the `bact_rrna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_2_bact_rrna_db_bowtie2_clean.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (3) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`bact_rrna_db` database.
Files for just the `human_rna_db` database:
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_human_rna_db_bowtie2_contam_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as belonging to the `human_rna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_human_rna_db_bowtie2_contam_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as belonging to the `human_rna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_human_rna_db_bowtie2_clean_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`human_rna_db` database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_human_rna_db_bowtie2_clean_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (1) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`human_rna_db` database.
Depending on the input FASTQ, one or more of the following may be output:
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_1_human_rna_db_bowtie2_contam.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as belonging to the `human_rna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_1_human_rna_db_bowtie2_clean.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`human_rna_db` database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_2_human_rna_db_bowtie2_contam.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as belonging to the `human_rna_db`
database.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_2_human_rna_db_bowtie2_clean.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in
situation (2) above that were identified as NOT belonging to the
`human_rna_db` database.
Note, the files named "*_clean.fastq" will only be written if running with the option "--store-temp-output".
Aggregated files:
+ `seq_kneaddata.log`: Log file containing statistics about the run.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in situation (1) identified as
NOT belonging to any of the reference databases.
+ `seq_kneaddata_paired_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in situation (1) identified as
NOT belonging to any of the reference databases.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_1.fastq`: Reads from the first mate in situation (2) identified as
NOT belonging to any of the reference databases.
+ `seq_kneaddata_unmatched_2.fastq`: Reads from the second mate in situation (3) identified as
NOT belonging to any of the reference databases.
## Demo Run ####
The examples folder contains a demo input file. This file is a single read, fastq format.
`` $ kneaddata --unpaired examples/demo.fastq --reference-db examples/demo_db --output kneaddata_demo_output ``
This will create four output files:
1. `` kneaddata_demo_output/demo_kneaddata.fastq ``
2. `` kneaddata_demo_output/demo_kneaddata_demo_db_bowtie2_contam.fastq ``
3. `` kneaddata_demo_output/demo_kneaddata.log ``
3. `` kneaddata_demo_output/demo_kneaddata.trimmed.fastq ``
## Sequencer Source for trimming Adapter Contents ####
Kneaddata will use **"NexteraPE"** adapters provided by trimomatic to trim the adapter contents `by default`.
The other available options are: `["NexteraPE", "TruSeq2", "TruSeq3","none"]`. Based on the source of the sequencer and the FASTQC report, it is **highly reccommended**
to choose the correct sequencer source to ensure the removal of adapter contents by Kneaddata.
###### Example: Trimmming adapter sequence using **TruSeq3** sequencer adapters in the workflow:
```
kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq -db demo_db -o kneaddata_output --sequencer-source TruSeq3 --fastqc FastQC
```
###### Example: Skipping adapter trimming in the workflow:
```
kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq -db demo_db -o kneaddata_output --sequencer-source none --fastqc FastQC
```
## Trim Overrepresented/Repetitive sequences ####
It is highly recommeded to use **--run-trim-repetitive** flag for **Shotgun sequences (Metatranscriptomics-MTX, Metagenomics-MGX)** to trim the overrepresented sequences if shown in FASTQC reports.
However, Kneaddata will **not** trim the overrepresented sequences **by default** as **Amplicon sequences** usually have a large number of repetitive reads resulting in depletion of the read count.
###### Example: Trimming overrepresented sequences using the Fastqc reports:
```
kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq -db demo_db -o kneaddata_output --run-trim-repetitive --fastqc FastQC
```
###### Example: Trimming overrepresented sequences and TruSeq3 adapters:
```
kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq -db demo_db -o kneaddata_output --run-trim-repetitive --sequencer-source TruSeq3 --fastqc FastQC
```
## Additional Arguments ####
If you want to specify additional arguments for Bowtie2 using the
`--bowtie2-options` flag, you will need to use the equals sign along with quotes. Add additional flags for each option.
For example:
`$ kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq --output kneaddata_output --reference-db database_folder --bowtie2-options="--very-fast" --bowtie2-options="-p 2"`
A similar approach is used to specify additional arguments for Trimmomatic:
`$ kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq --output kneaddata_output --reference-db database_folder --trimmomatic-options="LEADING:3" --trimmomatic-options="TRAILING:3"`
*NOTE*: Manually specifying additional arguments will completely override the defaults.
Also more than one database can be provided for each run. The database argument can contain the folder that includes the database or the prefix of the database files.
For example:
`$ kneaddata --unpaired demo.fastq --output kneaddata_output --reference-db database_folder --reference-db database_folder2/demo`
## Contributions ##
Thanks go to these wonderful people:
- weichi weichi.syu@atgenomix.com
- TRF parallel run bug fix
## Complete Option List ##
All options can be accessed with `$ kneaddata --help`.
```
usage: kneaddata [-h] [--version] [-v] [-i1 INPUT1] [-i2 INPUT2]
[-un UNPAIRED] -o OUTPUT_DIR
[-db REFERENCE_DB] [--bypass-trim] [--run-trim-repetitive]
[--output-prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX] [-t <1>] [-p <1>]
[-q {phred33,phred64}] [--run-bmtagger]
[--run-fastqc-start] [--run-fastqc-end] [--store-temp-output]
[--cat-final-output]
[--log-level {DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR,CRITICAL}] [--log LOG]
[--trimmomatic TRIMMOMATIC_PATH] [--max-memory MAX_MEMORY]
[--trimmomatic-options TRIMMOMATIC_OPTIONS]
[--bowtie2 BOWTIE2_PATH] [--bowtie2-options BOWTIE2_OPTIONS]
[--bmtagger BMTAGGER_PATH] [--trf TRF_PATH] [--match MATCH]
[--mismatch MISMATCH] [--delta DELTA] [--pm PM] [--pi PI]
[--minscore MINSCORE] [--maxperiod MAXPERIOD]
[--fastqc FASTQC_PATH]
KneadData
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose additional output is printed
global options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-i INPUT, --input INPUT
input FASTQ file (add a second argument instance to run with paired input files)
-o OUTPUT_DIR, --output OUTPUT_DIR
directory to write output files
-db REFERENCE_DB, --reference-db REFERENCE_DB
location of reference database (additional arguments add databases)
--run-trim-repetitive Option to trim repetitive/overrepresented sequences generated by FASTQC reports
--bypass-trim bypass the trim step
--output-prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX
prefix for all output files
[ DEFAULT : $SAMPLE_kneaddata ]
-t <1>, --threads <1>
number of threads
[ Default : 1 ]
-p <1>, --processes <1>
number of processes
[ Default : 1 ]
-q {phred33,phred64}, --quality-scores {phred33,phred64}
quality scores
[ DEFAULT : phred33 ]
--run-bmtagger run BMTagger instead of Bowtie2 to identify contaminant reads
--bypass-trf option to bypass the removal of tandem repeats
--run-fastqc-start run fastqc at the beginning of the workflow
--run-fastqc-end run fastqc at the end of the workflow
--store-temp-output store temp output files
[ DEFAULT : temp output files are removed ]
--cat-final-output concatenate all final output files
[ DEFAULT : final output is not concatenated ]
--log-level {DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR,CRITICAL}
level of log messages
[ DEFAULT : DEBUG ]
--log LOG log file
[ DEFAULT : $OUTPUT_DIR/$SAMPLE_kneaddata.log ]
trimmomatic arguments:
--trimmomatic TRIMMOMATIC_PATH
path to trimmomatic
[ DEFAULT : $PATH ]
--max-memory MAX_MEMORY
max amount of memory
[ DEFAULT : 500m ]
--trimmomatic-options TRIMMOMATIC_OPTIONS
options for trimmomatic
[ DEFAULT : SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:50 ]
MINLEN is set to 50 percent of total input read length. The user can alternatively specify a length (in bases) for MINLEN.
--sequencer-source options for sequencer-source
[ DEFAULT: NexteraPE]
Available sequencers: ["NexteraPE","TruSeq2","TruSeq3"]
bowtie2 arguments:
--bowtie2 BOWTIE2_PATH
path to bowtie2
[ DEFAULT : $PATH ]
--bowtie2-options BOWTIE2_OPTIONS
options for bowtie2
[ DEFAULT : --very-sensitive ]
bmtagger arguments:
--bmtagger BMTAGGER_PATH
path to BMTagger
[ DEFAULT : $PATH ]
trf arguments:
--bypass-trf bypass the TRF step
--trf TRF_PATH path to TRF
[ DEFAULT : $PATH ]
--match MATCH matching weight
[ DEFAULT : 2 ]
--mismatch MISMATCH mismatching penalty
[ DEFAULT : 7 ]
--delta DELTA indel penalty
[ DEFAULT : 7 ]
--pm PM match probability
[ DEFAULT : 80 ]
--pi PI indel probability
[ DEFAULT : 10 ]
--minscore MINSCORE minimum alignment score to report
[ DEFAULT : 50 ]
--maxperiod MAXPERIOD
maximum period size to report
[ DEFAULT : 500 ]
fastqc arguments:
--fastqc FASTQC_PATH path to fastqc
[ DEFAULT : $PATH ]
```