https://github.com/biocore/qurro
Visualize differentially ranked features (taxa, metabolites, ...) and their log-ratios across samples
https://github.com/biocore/qurro
bioinformatics microbiome qiime visualization
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Visualize differentially ranked features (taxa, metabolites, ...) and their log-ratios across samples
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/biocore/qurro
- Owner: biocore
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2018-11-19T18:14:53.000Z (about 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-13T21:15:06.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-02T05:08:04.748Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: bioinformatics, microbiome, qiime, visualization
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://biocore.github.io/qurro
- Size: 80.7 MB
- Stars: 33
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 10
- Open Issues: 124
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Qurro: Quantitative Rank/Ratio Observations
## What does this tool do?
Lots of tools for analyzing " 'omic" datasets can produce
__feature rankings__. These rankings can be used as a guide to look at the __log-ratios__ of certain features in a dataset. Qurro is a tool for visualizing and exploring both of these types of data.
### What are feature rankings?
The term "feature rankings" includes __differentials__, which we define as the estimated log-fold changes for features' abundances across different sample types. You can get this sort of output from lots of "differential abundance" tools, including but definitely not limited to [ALDEx2](https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/ALDEx2.html), [Songbird](https://github.com/biocore/songbird/), [Corncob](https://github.com/bryandmartin/corncob/), [DESeq2](https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html), [edgeR](https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/edgeR.html), etc.
The term "feature rankings" also includes __feature loadings__ in a [biplot](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biplot) (see [Aitchison and Greenacre 2002](https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1467-9876.00275)); you can get biplots from running [DEICODE](https://github.com/biocore/DEICODE),
which is a tool that works well with microbiome datasets, or from a variety of other methods.
Differentials and feature loadings alike can be interpreted as rankings -- you
can sort them numerically to "rank" features based on their association with
some sort of variation in your dataset.
### What can we do with feature rankings?
A common use of these rankings is examining the __log-ratios__ of
particularly high- or low-ranked features across the samples in your dataset,
and seeing how these log-ratios relate to your sample metadata (e.g. "does
this log-ratio differ between 'healthy' and 'sick' samples?"). For
details as to why this approach is useful, check out
[this open access paper](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-10656-5).
### How does this tool help?
__Qurro is an interactive web application for visualizing feature rankings
and log-ratios.__ It does this
using a two-plot interface: on the left side of the screen, a "rank plot" shows
how features are ranked for a selected ranking, and on the right side of the
screen a "sample plot" shows the log-ratios of selected features' abundances
within samples. There are a variety of controls available for selecting
features for a log-ratio, and changing the selected log-ratio updates both the
rank plot (highlighting selected features) and the sample plot (changing the
y-axis value of each sample to match the selected log-ratio).
**A paper describing Qurro is now available at NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics
[here](https://academic.oup.com/nargab/article/2/2/lqaa023/5826153).**
### How do I use this tool?
Qurro can be used standalone (as a Python 3 script that generates a
folder containing a HTML/JS/CSS visualization) or as a
[QIIME 2](https://qiime2.org/) plugin (that generates a QZV file that can be
visualized at [view.qiime2.org](https://view.qiime2.org/) or by using
`qiime tools view`).
Qurro is still being developed, so backwards-incompatible changes might
occur. If you have any bug reports, feature requests, questions, or if you just
want to yell at me, then feel free to
[open an issue](https://github.com/biocore/qurro/issues) in this repository!
## Demos
See the Qurro website for a list of
interactive demos using real datasets.
### Screenshot: Visualizing KEGG orthologs in metagenomic data from the Red Sea
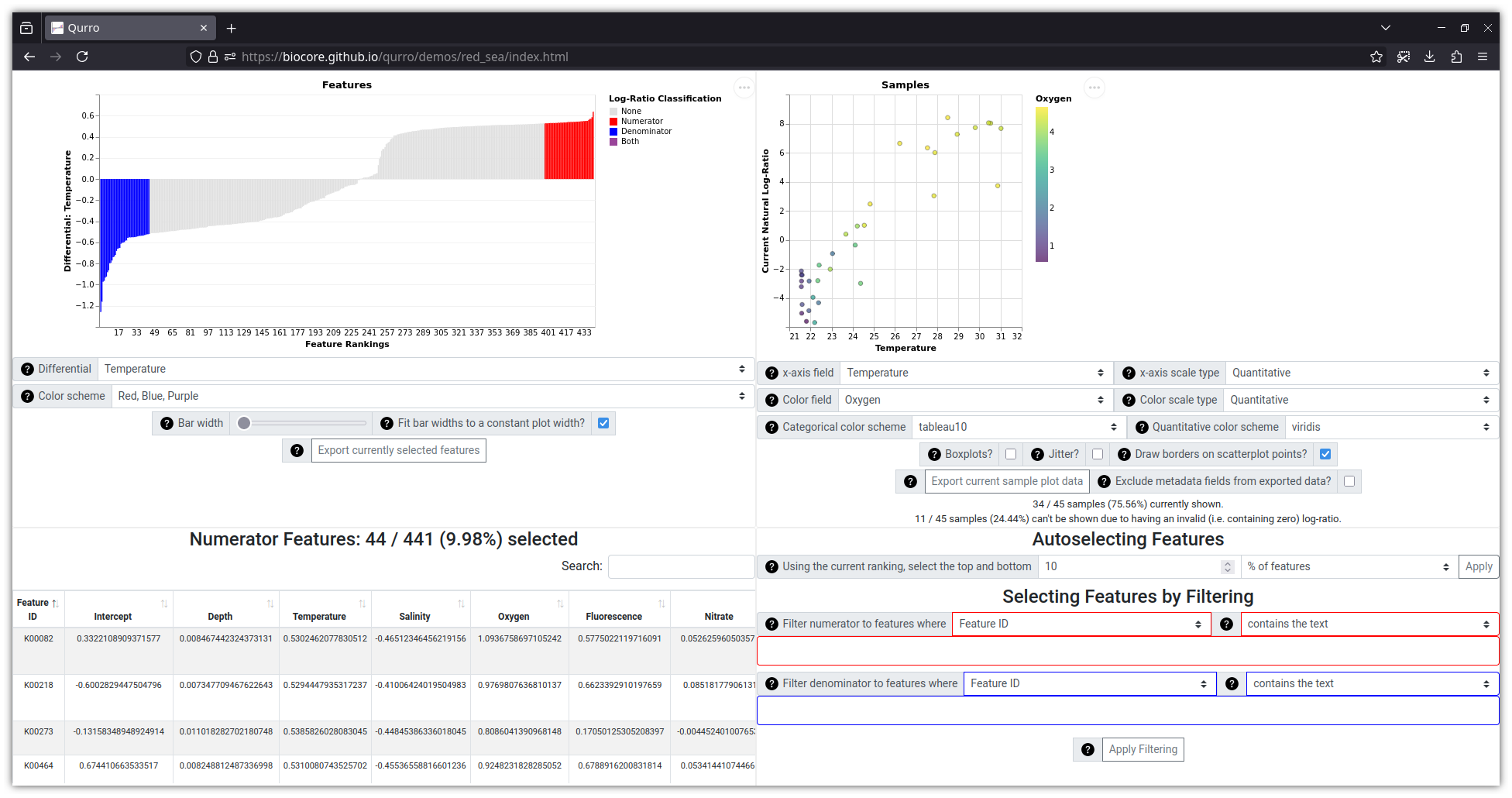
This visualization (which uses data from
[this study](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315489/), with
differentials generated by [Songbird](https://github.com/biocore/songbird/))
can be viewed online [here](https://biocore.github.io/qurro/demos/red_sea/index.html).
## Installation and Usage
You can install Qurro using [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/)
or [conda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/).
### System requirements
**If you're using Qurro within QIIME 2,** you will need a QIIME 2 version of at
least 2020.11. It has been tested with QIIME 2 versions up through the most recent
release, as of writing (QIIME 2 2024.10).
**If you're using Qurro outside of QIIME 2,** you will need a Python version of
at least 3.6.
In either case, Qurro should work with most modern web browsers; Firefox or Chrome are
recommended.
### Installing with `pip`
```bash
pip install cython "numpy >= 1.12.0"
pip install qurro
```
### Installing with `conda`
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge qurro
```
### Slight field name adjustments
Certain characters in column names in the sample metadata, feature metadata (if passed), and feature differentials (if passed) will be replaced with similar characters or just removed entirely:
| Old Character(s) | New Character |
| ------------- | ------------- |
| `.` | `_` |
| `:` | `;` |
| `]` | `)` |
| `[` | `(` |
| `\ ` | \| |
| `'` or `"` | Nothing |
This is due to some downstream issues with handling these sorts of characters
in field names. See [this issue](https://github.com/biocore/qurro/issues/66)
for context.
## Tutorials
### In-depth tutorials
These tutorials are all good places to start, depending on what sort of data and
feature rankings you have.
- [Color Composition tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/color_compositions/color_example.ipynb)
- **Data Summary:** Color composition data from abstract paintings
- Feature rankings: Feature loadings in an arbitrary compositional biplot
- Qurro used through QIIME 2 or standalone?: Standalone
- ["Moving Pictures" tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/moving_pictures/moving_pictures.ipynb)
- **Data Summary:** Microbiome 16S rRNA marker gene sequencing data from four types of body site samples
- Feature rankings: Feature loadings in a [DEICODE](https://github.com/biocore/DEICODE) biplot
- Qurro used through QIIME 2 or standalone?: QIIME 2
- [Transcriptomics tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/ALDEx2_TCGA_LUSC/transcriptomic_example.ipynb)
- **Data Summary:** Gene expression ("RNA-Seq") data from TCGA tumor and "solid tissue normal" samples
- Feature rankings: [ALDEx2](https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/ALDEx2.html) differentials
- Qurro used through QIIME 2 or standalone?: Standalone
### Selection tutorial
There are a lot of different ways to select features in Qurro, and the
interface can be difficult to get used to. This document describes all of these
methods, and provides some examples of where they could be useful in practice.
- [Selection tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/selection/selection.ipynb)
### Basic command-line tutorials
These tutorials show examples of using Qurro in identical ways both inside and
outside of QIIME 2.
- [Sleep Apnea tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/DEICODE_sleep_apnea/deicode_example.ipynb)
- Feature rankings: feature loadings in a [DEICODE](https://github.com/biocore/DEICODE) biplot
- [Red Sea tutorial](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/songbird_red_sea/songbird_example.ipynb)
- Feature rankings: [Songbird](https://github.com/biocore/songbird/) differentials
## Qarcoal
**Qarcoal** (pronounced "charcoal") is a new part of Qurro that lets you
compute log-ratios based on taxonomic searching directly from the command-line.
This can be useful for a variety of reasons.
Currently, Qarcoal is only available through Qurro's QIIME 2 plugin interface.
Please see [**`qarcoal_example.ipynb`**](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/biocore/qurro/blob/master/example_notebooks/qarcoal/qarcoal_example.ipynb)
for a demonstration of using Qarcoal.
## Poster
We presented [this poster](https://biocore.github.io/qurro/CRISP-poster.pdf) on Qurro at the
[2019 CRISP Annual Review](https://crisp.engineering.virginia.edu/2019-crisp-annual-review).
The data shown here is already slightly outdated compared to the actual Qurro paper (e.g. the differentials are slightly different), but feel free to check out the poster anyway!
## Acknowledgements
### Dependencies
Code files for the following projects are distributed within
`qurro/support_files/vendor/`.
See the `qurro/dependency_licenses/` directory for copies of these software projects'
licenses (each of which includes a respective copyright notice).
- [Vega](https://vega.github.io/vega/)
- [Vega-Lite](https://vega.github.io/vega-lite/)
- [Vega-Embed](https://github.com/vega/vega-embed)
- [jQuery](https://jquery.com/)
- [DataTables](https://datatables.net/)
- [RequireJS](https://requirejs.org/)
- [Bootstrap](https://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.3/getting-started/introduction/)
- [Bootstrap Icons](https://icons.getbootstrap.com/)
- We make use of the "Question fill" icon's SVG, as well as some example code
for embedding this or other icons in CSS.
- [Popper.js](https://popper.js.org/) (included within the Bootstrap JS "bundle" file)
The following software projects are required for Qurro's python code
to function, although they are not distributed with Qurro (and are
instead installed alongside Qurro).
- [Altair](https://altair-viz.github.io/)
- [biom-format](http://biom-format.org/)
- [click](https://palletsprojects.com/p/click/)
- [NumPy](https://www.numpy.org/)
- [pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/)
- [scikit-bio](http://scikit-bio.org/)
### Testing Dependencies
For python testing/style checking, Qurro uses
[pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/),
[pytest-cov](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-cov),
[flake8](http://flake8.pycqa.org/en/latest/), and
[black](https://github.com/ambv/black). You'll also need to have QIIME 2
installed to run most of the python tests (note that, due to click vs. black
vs. QIIME 2 dependency issues, you should use a QIIME 2 environment of at least
2022.8; see
[`CONTRIBUTING.md`](https://github.com/biocore/qurro/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
for details).
For JavaScript testing/style checking, Qurro uses
[Mocha](https://mochajs.org/), [Chai](https://www.chaijs.com/),
[mocha-headless-chrome](https://github.com/direct-adv-interfaces/mocha-headless-chrome),
[nyc](https://github.com/istanbuljs/nyc), [jshint](https://jshint.com/),
and [prettier](https://prettier.io/).
Qurro also uses [GitHub Actions](https://github.com/features/actions) and
[Codecov](https://codecov.io/).
The Jupyter notebooks in Qurro's `example_notebooks/` folder are automatically
rerun using [nbconvert](https://nbconvert.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html),
also.
### Data Sources
The test data located in `qurro/tests/input/mackerel/` were exported from
QIIME 2 artifacts in [this repository](https://github.com/knightlab-analyses/qurro-mackerel-analysis). These data are from Minich et al. 2020 [1].
The test data located in `qurro/tests/input/byrd/` are from
[this repository](https://github.com/knightlab-analyses/reference-frames).
These data, in turn, originate from Byrd et al.'s 2017 study on atopic
dermatitis [2].
The test data located in `qurro/tests/input/sleep_apnea/`
(and in `example_notebooks/DEICODE_sleep_apnea/input/`)
are from [this Qiita study](https://qiita.ucsd.edu/study/description/10422),
which is associated with Tripathi et al.'s 2018 study on sleep apnea [4].
The test data located in `qurro/tests/input/moving_pictures/` (and in
`example_notebooks/moving_pictures/data/`)
are from [the QIIME 2 moving pictures tutorial](https://docs.qiime2.org/2019.1/tutorials/moving-pictures/).
The `ordination` files in these folders were computed based on the
[DEICODE moving pictures tutorial](https://library.qiime2.org/plugins/deicode/19/).
These data (sans the DEICODE ordination) are associated with Caporaso et al. 2011 [5].
Lastly, the data located in `qurro/tests/input/red_sea`
(and in `example_notebooks/songbird_red_sea/input/`, and shown in the
screenshot above) were taken from Songbird's GitHub repository in its
[`data/redsea/`](https://github.com/biocore/songbird/tree/master/data/redsea)
folder, and are associated with Thompson et al. 2017 [3].
### Logo
Qurro's logo was created using the [Lalezar](https://github.com/BornaIz/Lalezar) font.
Also, shout out to [this gist](https://gist.github.com/DavidWells/7d2e0e1bc78f4ac59a123ddf8b74932d) for showing how to center images in GitHub markdown files (which is more of a hassle than it sounds).
### Special Thanks
The design of Qurro was strongly inspired by
[EMPeror](https://github.com/biocore/emperor) and
[q2-emperor](https://github.com/qiime2/q2-emperor/), along with
[DEICODE](https://github.com/biocore/DEICODE). A big shoutout to
Yoshiki Vázquez-Baeza for his help in planning this project, as well as to
Cameron Martino for a ton of work on getting the code in a distributable state
(and making it work with QIIME 2). Thanks also to Jamie Morton, who wrote the
original code for producing rank and sample plots from which this is derived.
And thanks to a bunch of the Knight Lab for helping name the tool :)
## Citing Qurro
If you use Qurro in your research, please cite it!
The preferred citation for Qurro is [this manuscript at NAR Genomics and
Bioinformatics](https://academic.oup.com/nargab/article/2/2/lqaa023/5826153).
Here's the BibTeX:
```
@article {fedarko2020,
author = {Fedarko, Marcus W and Martino, Cameron and Morton, James T and González, Antonio and Rahman, Gibraan and Marotz, Clarisse A and Minich, Jeremiah J and Allen, Eric E and Knight, Rob},
title = "{Visualizing ’omic feature rankings and log-ratios using Qurro}",
journal = {NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
year = {2020},
month = {04},
issn = {2631-9268},
doi = {10.1093/nargab/lqaa023},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1093/nargab/lqaa023},
note = {lqaa023},
eprint = {https://academic.oup.com/nargab/article-pdf/2/2/lqaa023/33137933/lqaa023.pdf},
}
```
## References
[1] Minich, J. J., Petrus, S., Michael, J. D., Michael, T. P., Knight, R., &
Allen, E. E. (2020). Temporal, environmental, and biological drivers of the
mucosal microbiome in a wild marine fish, Scomber japonicus. _mSphere, 5_(3),
e00401-20. [Link](https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/mSphere.00401-20).
[2] Byrd, A. L., Deming, C., Cassidy, S. K., Harrison, O. J., Ng, W. I., Conlan, S., ... & NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. (2017). Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strain diversity underlying pediatric atopic dermatitis. _Science Translational Medicine, 9_(397), eaal4651.
[Link](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28679656).
[3] Thompson, L. R., Williams, G. J., Haroon, M. F., Shibl, A., Larsen, P.,
Shorenstein, J., ... & Stingl, U. (2017). Metagenomic covariation along densely
sampled environmental gradients in the Red Sea. _The ISME Journal, 11_(1), 138.
[Link](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27420030).
[4] Tripathi, A., Melnik, A. V., Xue, J., Poulsen, O., Meehan, M. J., Humphrey, G., ... & Haddad, G. (2018). Intermittent hypoxia and hypercapnia, a hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea, alters the gut microbiome and metabolome. _mSystems, 3_(3), e00020-18.
[Link](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29896566).
[5] Caporaso, J. G., Lauber, C. L., Costello, E. K., Berg-Lyons, D., Gonzalez, A., Stombaugh, J., ... & Gordon, J. I. (2011). Moving pictures of the human microbiome. _Genome Biology, 12_(5), R50.
[Link](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21624126).
## License
This tool is licensed under the [BSD 3-clause license](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD_licenses#3-clause_license_(%22BSD_License_2.0%22,_%22Revised_BSD_License%22,_%22New_BSD_License%22,_or_%22Modified_BSD_License%22)).
Our particular version of the license is based on [scikit-bio](https://github.com/biocore/scikit-bio)'s [license](https://github.com/biocore/scikit-bio/blob/master/COPYING.txt).

