Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/blend2d/blend2d-apps
Blend2D interactive demos and benchmarking tool
https://github.com/blend2d/blend2d-apps
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
Blend2D interactive demos and benchmarking tool
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/blend2d/blend2d-apps
- Owner: blend2d
- License: zlib
- Created: 2018-04-30T14:10:17.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-19T16:41:13.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-10T02:10:46.530Z (2 months ago)
- Language: C
- Homepage: https://blend2d.com
- Size: 1.46 MB
- Stars: 51
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 9
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Blend2D Apps
============
This repository provides additional applications that use [Blend2D](https://blend2d.com) rendering engine and optionally other libraries.
At the moment there are two categories of applications:
- `bl_bench` - Blend2D bencharking tool that can be built either standalone or with support for AntiGrain, Cairo, and Qt libraries, for comparison.
- `bl_demos` - Blend2D interactive demos that use Blend2D and Qt toolkit for UI and quality/performance comparison
Blend2D Benchmarking Tool
-------------------------
Blend2D benchmarking tool (`bl_bench`) can be used to test Blend2D performance and compare it with other libraries such as AGG, Cairo, and Qt. Cairo and Qt backends require these libraries to be installed so the CMake script must be able to find them, otherwise these backends will be disabled during the configure step. AGG backend is bundled with `blend2d-apps` so it's always available and built.
The output of `bl_bench` (images rendered) should always be the same regardless of the backend used during benchmarking. The numbers reported by the tool for various backends are comparable. There are some limitations of some backends (like Qt doesn't support reflecting textures, etc) so all tests were designed in a way to use only common features found in all 2D backends available.
Tests provided by `bl_bench`:
- `FillRectA` - Axis aligned rectangle fill. This is one of the most optimized operations in most 2D libraries and it's definitely one of the simplest things to render. The performance of this test can reveal whether solid fills and image blits are well optimized, and the performance of very small fills and blits can reveal how much overhead there is between calling the fill/blit function and the actual pixel filling.
- `FillRectU` - Axis unaligned rectangle fill. Since 2D vector engines work with floating point coordinates it's possible that a renctangle to fill or blit is not axis aligned. In that case it's expected that the corners of such rectangle would be "blurry" (antialiased). Blend2D has a specialized filler for such case and this tests the filler and compares it with other libraries.
- `FillRectRot` - Fills a rotated rectangle. This case generally tests how efficiently the rendering engine can use the rasterizer and rasterize something simple. In many engines filling rotated rectangle means just transforming the coordinates and feeding the rasterizer with the output polygon. In addition, this tests the performance of rotated blits.
- `FillRoundU` - Fills a rounded rectangle (not aligned to a pixel boundary). In general this should benchmark two things - how efficiently a simple path/shape can be rendered and how efficiently the engine flattens such path into a polyline or a set of edges.
- `FillRoundRot` - Fills a rounded rectangle, which is rotated. This should in general be a bit slower than FillRoundU, because the rotation would spread the shape into more scanlines, which means more work for the rasterizer and the pipeline as well. So this test can be used to compare a rendering of a simple shape (FillRoundU) vs the same shape rotated.
- `FillPoly` - Fills a polygon with the specified filling rule (non-zero or even-odd) and with the specified number of vectices. This test should in general reveal the performance of rasterization as polygons do not need flattning (curves do). So the tests can be used to compare the performance of rasterizing polyhons of 10, 20, and 40 vertices with both fill rules. At the moment Blend2D uses a parametrized pipeline so the fill rule doesn't matter, but other libraries may show a difference.
- `FillXXX` - Repeatedly fills the shape from a path at different origins. The geometry can contain lines and curves.
- `StrokeXXX` - Strokes the input. All stroke tests are generally the same just with different inputs. They are complementary to fill tests.
Although the tests may seem simple they really test the raw performance of 2D libraries as all the rendering requests are usually simplified into rectangles or polygons and the question is how fast this can be done and how fast a user call gets into the composition pipeline.
Blend2D Qt Demos
----------------
Interactive Blend2D demos that use Qt GUI toolkit. Some demos are primarily designed to explore Blend2D features and others are designed to compare Blend2D and Qt performance in an interactive way.
Building
--------
Use the following commands to fetch `asmjit`, `blend2d`, and `blend2d-apps` repositories:
```bash
# Download source packages from Git.
$ git clone https://github.com/asmjit/asmjit
$ git clone https://github.com/blend2d/blend2d
$ git clone https://github.com/blend2d/blend2d-apps
```
It can be configured similarly to AsmJit and Blend2D projects:
```bash
$ cd blend2d-apps
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
```
Alternatively you can pick a configure script from `tools` subdirectory if there is a suitable one for your configuration.
CMake should be able to find Qt and other dependencies automatically if they are in your `PATH`, alternatively set `CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH` to tell CMake where Qt and/or other dependencies are installed.
Resources
---------
- `bl_demos/bl-qt-tiger.h` uses a tiger data extracted from [amanithvg](http://www.amanithvg.com/)'s tiger example so this data is not covered by the license
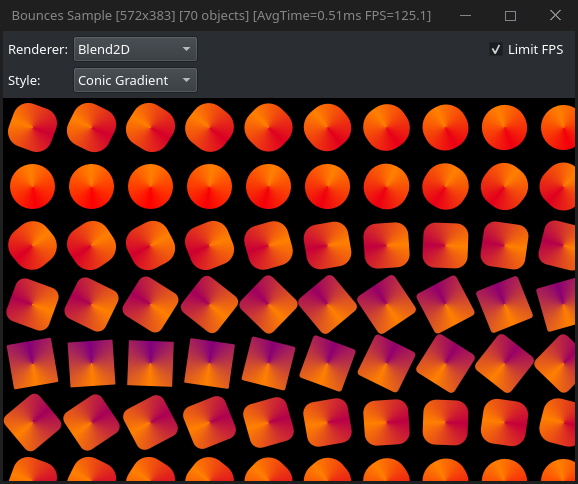
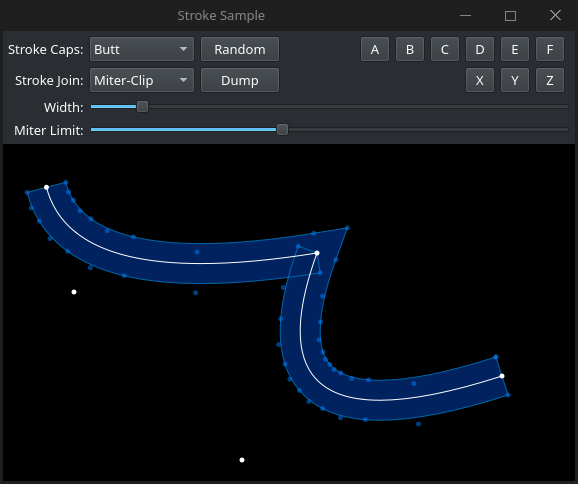
Preview
-------
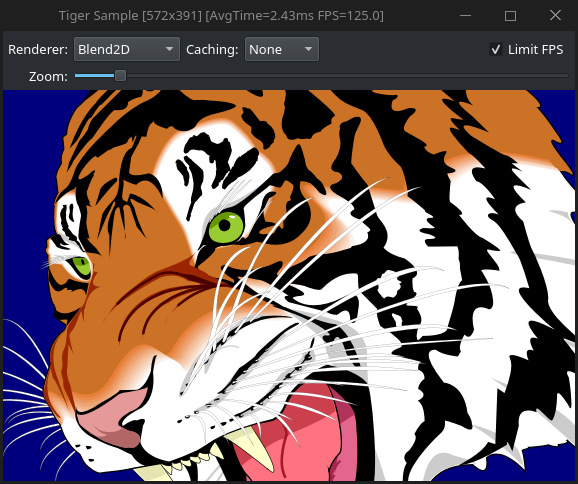 | 
---- | ----
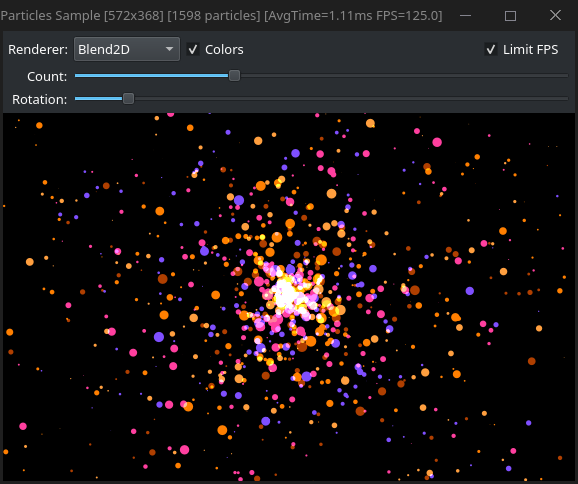 | 
License
-------
All code samples can be distributed under either UNLICENSE (Public Domain) or Zlib license.