https://github.com/bradhowes/joystick
A custom UIView in Swift that presents a simple joystick interface.
https://github.com/bradhowes/joystick
arcade-controller cocoapods ios joystick swift swift-package swift-playgrounds uiimageview
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A custom UIView in Swift that presents a simple joystick interface.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/bradhowes/joystick
- Owner: bradhowes
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-12-03T12:34:37.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-17T23:33:07.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-21T03:45:30.736Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: arcade-controller, cocoapods, ios, joystick, swift, swift-package, swift-playgrounds, uiimageview
- Language: Swift
- Homepage: https://bradhowes.github.io/Joystick/index.html
- Size: 7.59 MB
- Stars: 59
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick)
[](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/.github/workflows/CI.yml)
[](https://swiftpackageindex.com/bradhowes/Joystick)
[](https://swiftpackageindex.com/bradhowes/Joystick)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
# Joystick
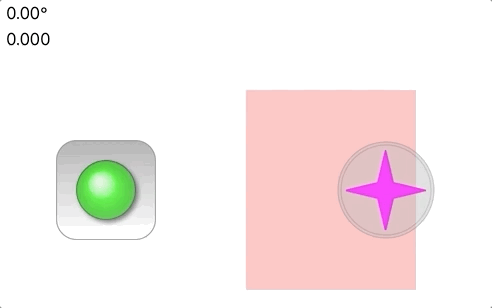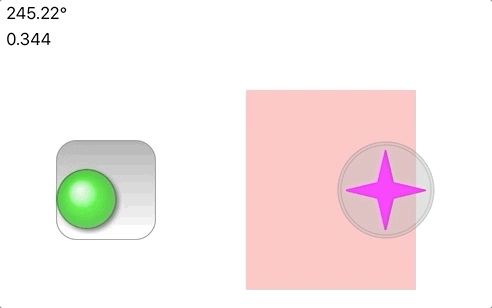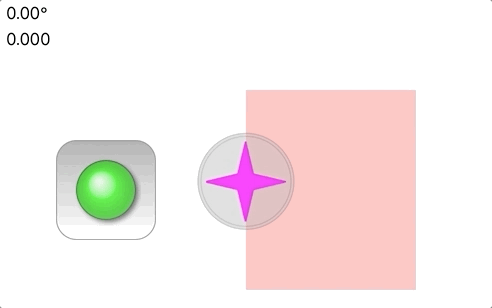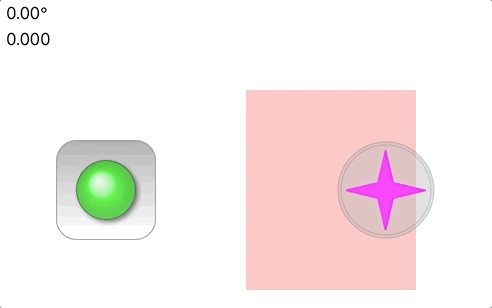
A custom UIView in Swift that presents a simple joystick interface. The custom view consists of two UIImageView
instances, one for the base and one for the handle. When the user moves the handle, it will report out a value
based on its position in relation to the joystick base. The type of information reported depends on the type of
[monitor](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L31) installed:
* [JoyStickViewMonitorKind.polar](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickViewMonitor.swift#L80) -- reports out instances of [JoyStickViewPolarReport](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickViewMonitor.swift#L36) with
* angle -- the direction the handle is point, given in degrees, where north/up is 0° and east/right is 90°
* displacement -- the distance from the center the handle moved, from 0.0 to 1.0 with 1.0.
* [JoyStickViewMonitorKind.xy](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickViewMonitor.swift#L87) -- reports out instances of [JoyStickViewXYReport](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickViewMonitor.swift#L9) with
* x -- horizontal offset from the center of the base, where east/right is positive
* y -- vertical offset from the center of the base, where north/up is positive
```swift
let monitor: JoyStickViewPolarMonitor = {
print("\(String(format: "%.2f°", $0.angle)) \(String(format: "%.3f", $0.displacement))")
}
joystick.monitor = .polar(monitor: monitor2)
```
There is also support (since 3.0.1) for using an Objective-C block as a monitor, with a slight reduction in type
safety. The `setPolarMonitor` and `setXYMonitor` both take a closure that accepts two `CGFloat` arguments and
returns no value. Objective-C blocks can be used as well as Swift closures in these methods. Since 3.1.0, there is also
a `tappedBlock` attribute which one can use to receive a notification when the user just taps on the joystick handle.
The view supports an option ([movable](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L62))
where the view will move when the user moves the handle to a
displacement beyond 1.0. This can be useful when the initial position of the joystick in an app is not ideal for
the user's thumb. Double-tapping on the joystick moves it back to its original position.
In the animation above, there are two joysticks, one green and one magenta. The green is *fixed* and does not
move even when the touch motion would cause a displacement larger than 1.0. The magenta joystick however is
*movable*, with the base following the touch motion. For movable joysticks, the Base motion is optionally
restricted to a `CGRect` in the [movableBounds](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L69) property,
as is the case in the demonstration animation above where the magenta joystick cannot move out of the pink band.
## Additional Properties
Here are some additional configurable features of the JoyStickView:
* [handleConstraint](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L39) -- optional `CGRect` which constrains where the handle can move. See the playground for an example.
* [baseImage](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L116) -- a UIImage to use for the base of the joystick.
* [handleImage](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L119) -- a UIImage to use for the handle of the joystick.
* [baseAlpha](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L83) -- opacity of the base of the joystick.
* [handleAlpha](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L90) -- opacity of the handle of the joystick.
* [handleTintColor](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L96) -- optional tint color applied to the joystick image.
* [handleSizeRatio](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L100) -- scaling applied to the joystick handle's image. Note that default is `0.85` due to
historical reasons.
* [enableDoubleTapForFrameReset](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L123) -- if `movable` is true, allow user to double-tap on view to move base to original
location.
* [handlePositionMode](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/blob/main/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift#L146) -- when set to `.absolute` (default) the handle will move to the initial (constrained) press location. When set to `.relative` the handle will move only after the touch moves.
# Releases
* v3.2.0 -- Offer code as Swift package in addition to CocoaPod packaging
* v3.1.1 -- Added `handlePositionMode` property to control how handle movements are reported. Default behavior
is `.absolute`. New `.relative` mode offers finer control at initial touch (thanks to [Michael Tyson](https://github.com/michaeltyson))
* v3.1.0 -- Added `tappedBlock` property (thanks to [Michael Tyson](https://github.com/michaeltyson))
* v3.0.2 -- Fixed too much scaling in `scaleHandleImageView`
* v3.0.1 -- Added support for Obj-C monitor blocks
* v3.0.0 -- Swift 5 (no code changes, only Xcode configury)
* v2.1.2 -- Swift 4.2
# Code
The Xcode workspace contains three components:
- a framework called [JoyStickView](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/JoyStickView) (when using CocoaPods `import BRHJoyStickView` instead of `import JoyStickView`)
- a simple iOS application called [JoyStickViewApp](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/JoyStickViewApp)
- a playground called [JoyStickView Playground](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/JoyStickView%20Playground.playground/Contents.swift)
Both the playground and the app rely on the framework for the JoyStickView UIView.
> :warning: **NOTE**: due to the plumbing for CocoaPods, when editing in Xcode open the workspace **JoyStickView.xcworkspace** instead of the project **JoyStickView.xcodeproj**.
The Xcode playground code sets up the display environemnt and installs two joysticks, one that is fixed (green)
and the other that is movable (yellow). Both joysticks report out their positions in two labels, one for angles and
the other for displacement.
The [JoyStickView.swift](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift) file defines the joystick view and behavior.
It resides inside the JoyStickView Swift package, and in the BRHJoyStickView framework in CocoaPods. There you will also find a file called
[CoreGraphics+Additions.swift](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/Sources/JoyStickView/CoreGraphics+Additions.swift) that contains various
extensions to some CoreGraphics structs that allow for some simplified mathematical expressions in the [JoyStickView](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick) code.
By default the [JoyStickView](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/Sources/JoyStickView/JoyStickView.swift) class uses two image assets found in the
[Assets](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/Sources/JoyStickView/Resources/Assets.xcassets) container.
folder:
* DefaultBase — the image to use for the base of the joystick
* DefaultHandle — the image to use for the handle of the joystick. **Note**: this will be tinted with the `handleTintColor` setting
Both exist in three resolutions for the various iOS devices out today. They were generated using the great [Opacity](http://likethought.com/opacity/) app. The
Opacity documents are included in this repository in the [Resources](https://github.com/bradhowes/Joystick/tree/master/JoyStickViewApp/Resources) directory for
the `JoyStickViewApp` demonstration app.
To use your own images, simple set `baseImage` and/or `handleImage` attributes with the `UIImage` you wish to use.
# Documentation
Please see the [code documentation](https://bradhowes.github.io/Joystick/) for additional information.
# CocoaPods
There is a simple [CocoaPods](https://cocoapods.org) spec file available so you can add the code and resources
by adding "BRHJoyStickView" to your `Podfile` file and import with `import BRHJoyStickView`. Currently everything more or less works, except for the fact
that pointing to image resources via Interface Builder (IB) will result in invalid UImage results because the files won't be
found where IB was able to find them. The only solution is to manually locate those files and set them in your
view loading code. Something like the following should help:
```swift
extension Bundle {
/**
Locate an inner Bundle generated from CocoaPod packaging.
- parameter name: the name of the inner resource bundle. This should match the "s.resource_bundle" key or
one of the "s.resoruce_bundles" keys from the podspec file that defines the CocoPod.
- returns: the resource Bundle or `self` if resource bundle was not found
*/
func podResource(name: String) -> Bundle {
guard let bundleUrl = self.url(forResource: name, withExtension: "bundle") else { return self }
return Bundle(url: bundleUrl) ?? self
}
}
```
In your setup code, you then will need to do something like so:
```swift
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let bundle = Bundle(for: JoyStickView.self).podResource(name: "BRHJoyStickView")
joystick.baseImage = UIImage(named: "FancyBase", in: bundle, compatibleWith: nil)
joystick.handleImage = UIImage(named: "FancyHandle", in: bundle, compatibleWith: nil)
}
```
The `podResource` method attempts to locate a named inner bundle, defaulting to the original bundle if not found. The
`viewDidLoad` code will then use the right `bundle` object in the UIImage constructors.