Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/budali/jd_nlp
贪心学院 京东nlp
https://github.com/budali/jd_nlp
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
贪心学院 京东nlp
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/budali/jd_nlp
- Owner: budaLi
- Created: 2021-08-25T02:37:07.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-09-10T06:14:05.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-03-05T20:04:56.033Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 3.63 MB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# 贪心学院 NLP
# 2021.8.25
人不能闲下来,闲着就会迷茫...
# 2021.8.25
## 002 训练营介绍,课程体系介绍
介绍了项目开班,课程大概学习的内容
## 003 NLP定义及其歧义性
1. NLP = NLU(语义理解) + NLG(语言生成)
## 004,005 机器翻译
1. 统计机器翻译

传统的机器翻译为;根据语料库里的单词与其翻译一一对应形成词库,翻译时根据对应的词进行直译。
缺点: 速度慢、无语义分析、无上下文环境
2. 中英文翻译
今晚的课程有意思
1) 分词: 今晚| 的| 课程| 有意思
2) 直译 Tongith,of ,the course|interesting
3) 将直译的单词排列组合,通过Language Model(语言模型),可以输出每一组排列组合对应的概率,即
该模型可以判断输入的某一种排列组合更符合语法的概率,最高概率者即为翻译的结果。
上述翻译的问题之一是,当翻译词汇过多时,排列组合的数量呈指数级,通过语言模型预测不太现实,时间复杂度为O(n**2)
分词和翻译过程可以作为translation model,计算概率为langaage model,为了简化,是否可以将二者结合,提出Viterbi 算法。
3.
3.1 语言模型(language model)
给定一句英文e,计算概率P(e)
如果是符合英文语法的,p(e)高,如果是随机语句,p(e)低
3.2 翻译模型(词典)
给定一对,计算p(c|e),c指的是中文,e指的是英文。
语义相似度高则p(c|e)高,语义相似度低则p(c|e)低
3.3 Decoding Algorithm(Viterbi)
给定语言模型,翻译模型和f,找出最优的使得p(e)p(c|e)最大
4. 语言模型
语言模型是需要提前训练好的,对于一个好的语言模型,可以判断出句子是否符合语法,并给出概率:
P(he is studing ai) > P(he studing is ai)
也就是需要给出"he is studing ai"是句子的概率大于"he studing is ai"的概率,那么是如何计算的:
Unigram: P(he is studing ai) = P(he) * P(is) * P(studing) * P(ai) 假设每个单词是独立的
Markov Assumption 马尔科夫假设
Bigram: (he is studing ai) = P(he) * P(is|he) * P(studing|is) * P(ai|studing) 假设当前单词只考虑与前一个单词相关
Trigram: P(he is studing ai) = P(he) * p(is|he) * p(studing|he is) * P(ai| is studing) 假设当前单词与前两个单词相关
N-gram 由Unigram、Bigram、Trigram可以延伸至N-gram,其中前三者是为了简化计算而假设得到的计算
联合概率(joint probability)
p(x1,x2) = p(x1) * p(x2|x1) x1,x2的联合概率p(x1,x2) = 先验概率p(x1) * x1已知时x2的概率
p(x1,x2,x3,x4)
= p(x1)* p (x2|x1)* p(x3|x1,x2) *p(x4|x1,x2,x3) # 为了简化,衍生出Unigram,Bigram,Trigram等 chain rule
= p(x1,x2) * p(x3|x1,x2) * p(x4|x1,x2,x3)
= p(x1,x2,x3) * p(x4|x1,x2,x3)
= p(x1,x2,x3,x4)
## 006 NLP项目实战
1. 问答系统( question answering)
2. 情感分析(sentiment analysis)
股票价格预测、舆情分析、产品评论、事件监测
3. 机器翻译(machine translation)
4. 自动摘要(text summarization)
5. 聊天机器人(charbot) 闲聊形(seq2seq)、任务导向性(意图识别)
6. 信息抽取(information extraction)
## 007 NLP关键技术
Semantic(语义)
Syntax(句子结构)
Morphology(单词)
Phonetics(声音)
1. word segmentation(分词)
今天是自然语言处理训练营第一次课
今天 是 自然语言处理 训练营 第一次 课
2. Part of Speech(词性)
今天是1⽉22⽇,也是我们训练营的第⼀天,暂时课程,以ZOOM的⽅式直播
3. Named Entity Recognition(命名实体识别)
今天是(1⽉22⽇),也是我们(训练营)的第⼀天,暂时课程,以(ZOOM)的⽅式直播
4. Parsing(句法分析)
5. Dependency Parsing (依存分析)
6. Relation Extraction(关系抽取)
## 008 时间复杂度
## 016 P、NP、NP Complete问题
## 017 问答系统
将提问的问题于语料库中的问题进行匹配,包括基于规则的匹配和基于句子相似度的计算。
基于搜索的问答系统核心点:1.文本的表示 2.相似度的计算
知识图谱:1.实体抽取 2.关系抽取

# 2021.8.26
## 020 文本处理的流程
前向最大匹配,后向最大匹配
## 024 维特比算法

分词算法总结
1.基于匹配规则的方法 max matching
2.基于概率统计方法 LM(language model),HMM,CRF
分词可以认为是已经解决的问题
需要掌握:
1.实现max matching 和 Unigram LM方法。
```
# 前向最大匹配
def forward_max_mathcing(mathing_str,dic,max_len):
cur_start= 0
cur_end = max_len
res = []
while cur_end<=len(mathing_str) and cur_start<=cur_end:
cur_str = mathing_str[cur_start:cur_end]
if cur_str not in dic:
cur_end -=1
else:
res.append(cur_str)
cur_start = cur_end
cur_end = min(len(mathing_str),cur_end+max_len)
print(cur_start,cur_end,cur_str,res)
if cur_end!=len(mathing_str)-1:
print("no matching ")
else:
print(res)
dic = ["李","不搭","李不搭","武功","武功盖世","天下","第一","一"]
strs = "李不搭武功盖世天下第一"
max_len = 4
forward_max_mathcing(strs,dic,max_len)
```
输出:
```
0 3 李不搭武 []
3 7 李不搭 ['李不搭']
7 11 武功盖世 ['李不搭', '武功盖世']
7 10 天下第一 ['李不搭', '武功盖世']
7 9 天下第 ['李不搭', '武功盖世']
9 11 天下 ['李不搭', '武功盖世', '天下']
11 11 第一 ['李不搭', '武功盖世', '天下', '第一']
11 10 ['李不搭', '武功盖世', '天下', '第一']
['李不搭', '武功盖世', '天下', '第一']
```
如果只是实现N-gram分词算法的话,意义不是很大,只是一种简单的数据处理方法(窗口取词算法)。
可以基于一定的语料库,利用N-Gram来预计或者评估一个句子是否合理。
可参考:https://www.codenong.com/cs106431277/
# 2021.8.30
## 025 拼写错误纠正(spell correction)
电商、搜索引擎等需要进行拼写纠正,也叫编辑距离。
本质为动态规划。

[拼写纠错](https://github.com/budaLi/Jd_nlp/blob/main/codes/spell_correction.py)
编辑距离 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/comments/

···
class Solution(object):
def minDistance(self, word1, word2):
"""
:type word1: str
:type word2: str
:rtype: int
"""
m = len(word1)
n = len(word2)
# 如果word1或word2为空字符串
# 则编辑距离为长串的长度
if m*n ==0:
return m+n
# 初始化cost
cost = [[0 for i in range(n+1)] for j in range(m+1) ]
print(cost)
# 边界初始化
# word2为空
for i in range(m+1):
cost[i][0] = i
#word1 为空
for j in range(n+1):
cost[0][j] = j
print(cost)
for i in range(1,m+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
if word1[i-1]==word2[j-1]:
cost[i][j] = cost[i-1][j-1]
else:
#因为 cost[i-1][j-1] 与 cost[i-1][j] 以及 cost[i-1][j-1] 与 cost[i][j-1] 的绝对值之差为 1.
# 假设 word1[i-1][j-1] 变换到 word2[i-1][j-1] 需要 k 步,
# 那么 word1[i-1][j-1] 变换到 word[i-1][j] 则需要 k + 1 步,也可能是 k - 1 步。
cost[i][j] = 1+min(cost[i-1][j-1],min(cost[i-1][j],cost[i][j-1]))
return cost[m][n]
S = Solution()
# word1 = "horse"
# word2 = "ros"
word1 = "intention"
word2 = "execution"
# word1 = "a"
# word2 = "b"
cos = S.minDistance(word1,word2)
print(cos)
···
编辑距离的缺点:我们需要把词库中的每一个单词都去和用户输入计算编辑距离,时间复杂度较高,为O(V)*O(mn),
其中V为词库大小,mn为进行编辑距离计算的两个单词的长度。
优化: 用户输入-> 生成与其编辑距离为1,2的字符串 -> 过滤 -> 返回
其中,如何过滤此处不做深究,后续仍需推导

## 028 停用词过滤(Filtering Words),Stemming操作
对应NLP的应用,我们通常先把停用词、出现频率很低的词汇过滤掉,这其实类似于特征筛选的过程。
在英文里,比如"the","an","their"这些都可以作为停用词处理,但是,也要考虑自己的应用场景。
比如在情感分析中,"好","很好"等不能过滤。
词的标准化
Stemming: one way to normalize
went,go,going -> go
fly,flies -> fli
deny,denied,denyig -> denu
"还原的单词不一定为单词,即不能保证还原为有效的原型"
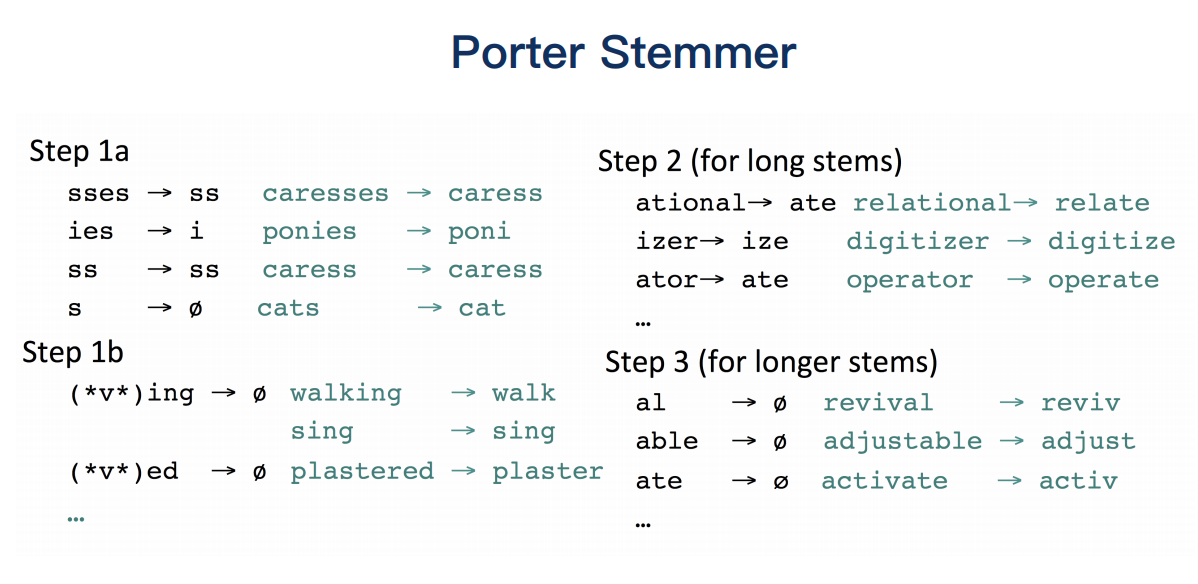
Lemmazation
保证还原的单词一定符合英文语法,比stemming更为严格
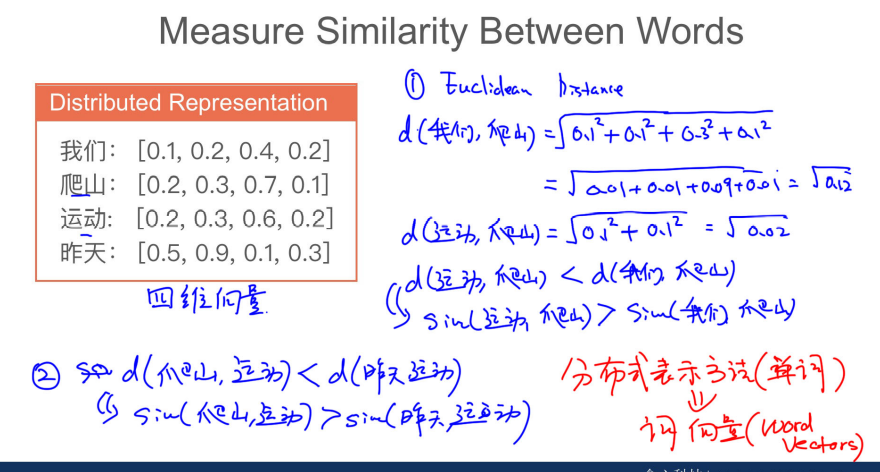
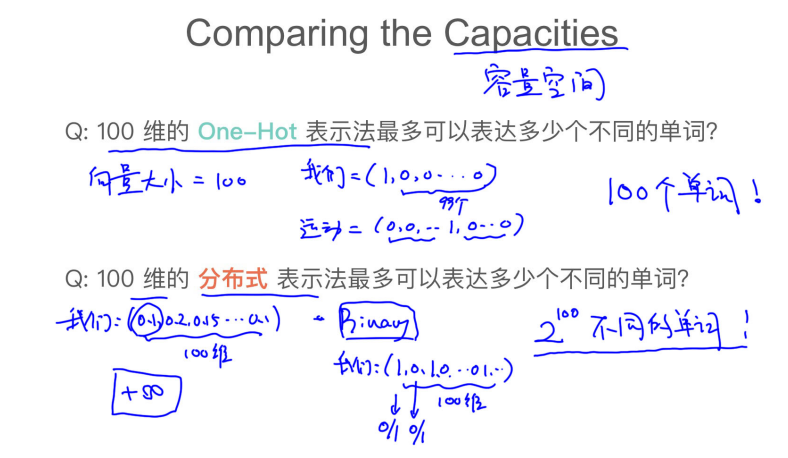
## 029 文本的表示
one-hot
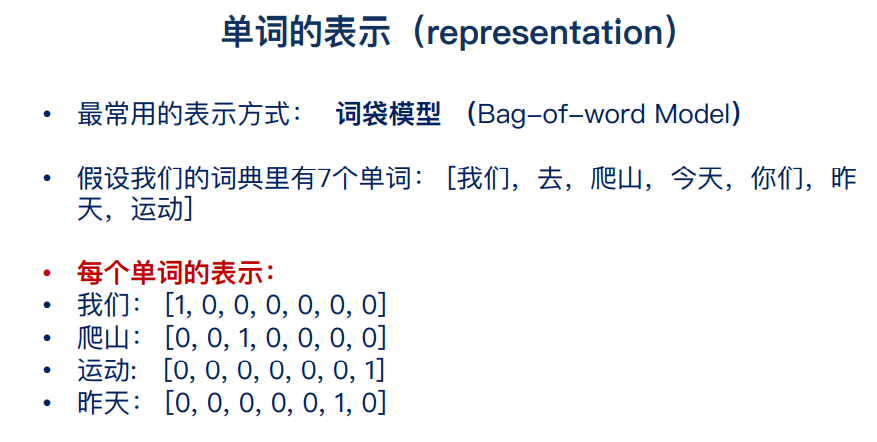


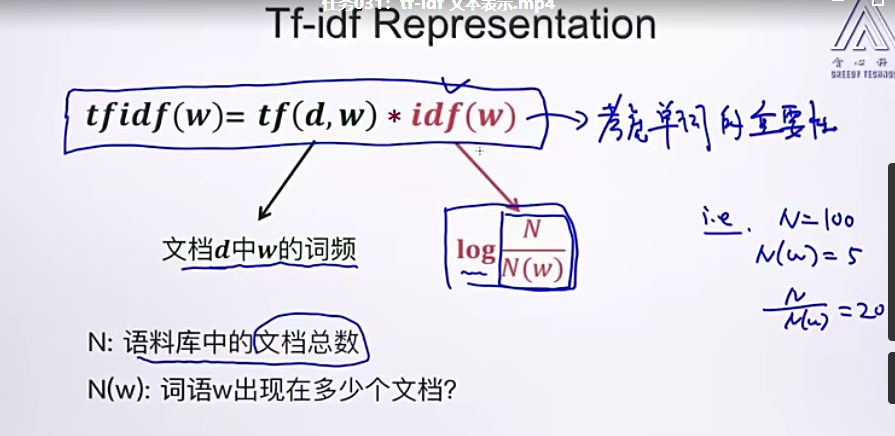
## 031 tf-idf

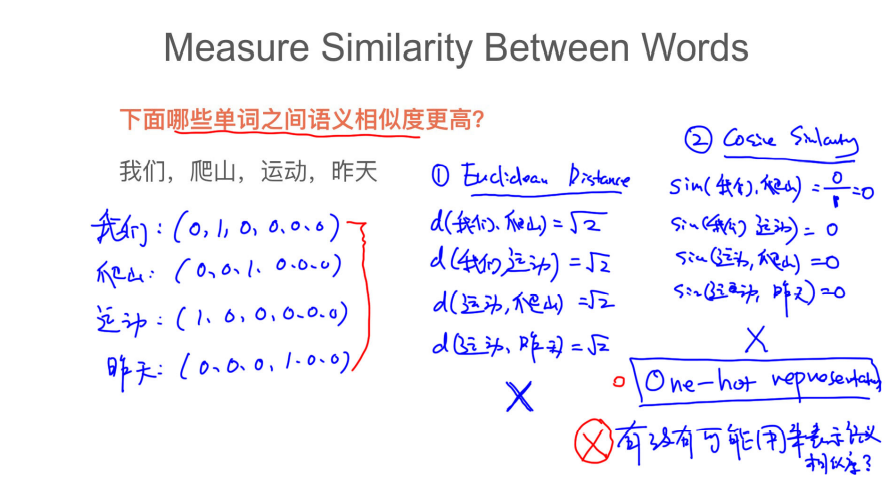

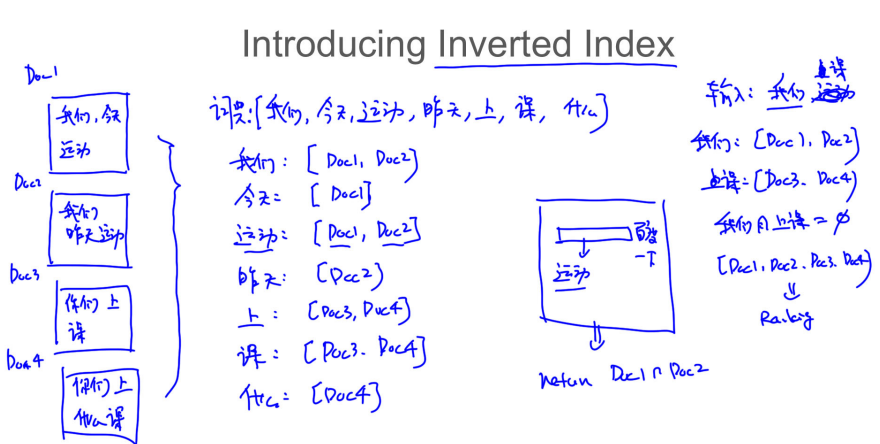
## 034 倒排表
基于检索的问答系统时间复杂度过高,用户的每次输入都要去QA库中计算问题的相似度才能返回。
借鉴搜索引擎的思路,使用倒排索引。
所有优化后的问答系统,可以根据关键词先对问答库进行大部分过滤,再进行相似度匹配。
## 035 Noisy Channel Model
p(text|source) 等比例于 p(source|text)*p(text)
可以理解为,给定一个资源source,需要将其转换为文本的形式,上述公式由贝叶斯得到,
应用场景: 语音识别、机器翻译、拼写纠错、OCR、密码破解 -> 文本


## 036 语言模型
语言模型用来判断一句话是否从语法上通顺。
回顾unigram,bigram,N-gram.
## 050 利用语言模型生成句子
可以利用Unigram model生成句子,生成的过程就是随机从词库中按照词的概率取词,由于Unigram不考虑上下文信息及单词之前的相关性,
所以生成的句子不太符合正常的语言逻辑。
## 055 一些难题
1. 逻辑推理
2. 解决规则冲突
3. 选择最小规则的子集
## 056 机器学习
1. 线性回归
2. 逻辑回归
3. 朴素贝叶斯
4. 神经网络
5. SVM
6. 随机森林
7. Adaboost
8. CNN
无监督学习:
1. K-means
2. PCA
3. ICA
4. MF
5. LSA
6. LDA
# 2021.9.10
工作原因..暂时搁置,后续学习时从词性标注实战开始。