Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/bwconrad/flexivit
PyTorch reimplementation of FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes
https://github.com/bwconrad/flexivit
computer-vision pytorch transformer vision-transformer
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
PyTorch reimplementation of FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/bwconrad/flexivit
- Owner: bwconrad
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-02-24T18:47:01.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-05T14:15:10.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-09-28T13:22:24.638Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: computer-vision, pytorch, transformer, vision-transformer
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 452 KB
- Stars: 45
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
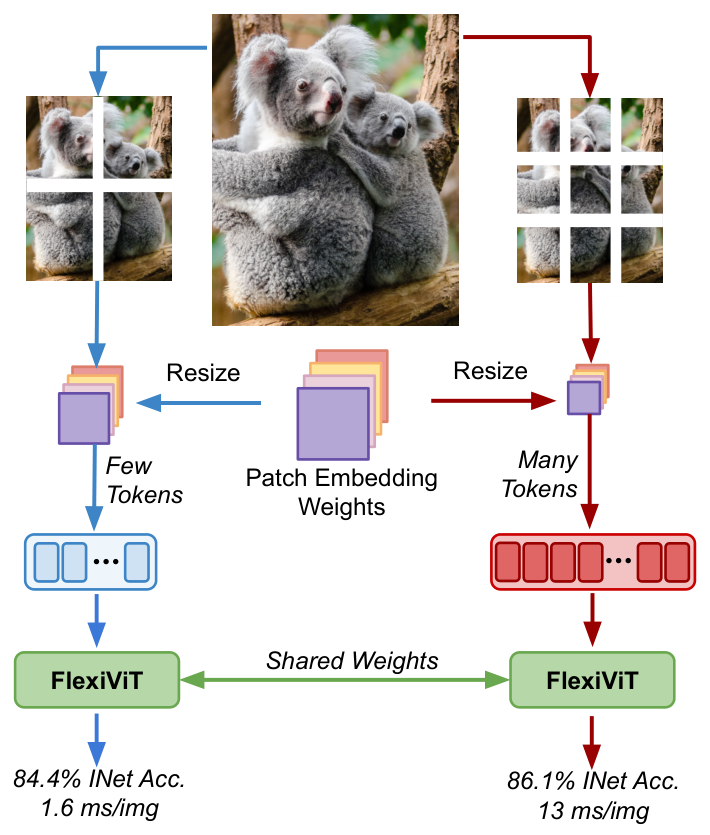
# FlexiViT
PyTorch reimplementation of ["FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.08013).
## Installation
```
pip install flexivit-pytorch
```
Or install the entire repo with:
```
git clone https://github.com/bwconrad/flexivit
cd flexivit/
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Usage
#### Basic Usage
```python
import torch
from flexivit_pytorch import FlexiVisionTransformer
net = FlexiVisionTransformer(
img_size=240,
base_patch_size=32,
patch_size_seq=(8, 10, 12, 15, 16, 20, 14, 30, 40, 48),
base_pos_embed_size=7,
num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
mlp_ratio=4,
)
img = torch.randn(1, 3, 240, 240)
preds = net(img)
```
You can also initialize default network configurations:
```python
from flexivit_pytorch import (flexivit_base, flexivit_huge, flexivit_large,
flexivit_small, flexivit_tiny)
net = flexivit_tiny()
net = flexivit_small()
net = flexivit_base()
net = flexivit_large()
net = flexivit_huge()
```
#### Resizing Pretrained Model Weights
The patch embedding layer of a standard pretrained vision transformer can be resized to any patch size using the `pi_resize_patch_embed()` function. A example
doing this with the `timm` library is the following:
```python
from timm import create_model
from timm.layers.pos_embed import resample_abs_pos_embed
from flexivit_pytorch import pi_resize_patch_embed
# Load the pretrained model's state_dict
state_dict = create_model("vit_base_patch16_224", pretrained=True).state_dict()
# Resize the patch embedding
new_patch_size = (32, 32)
state_dict["patch_embed.proj.weight"] = pi_resize_patch_embed(
patch_embed=state_dict["patch_embed.proj.weight"], new_patch_size=new_patch_size
)
# Interpolate the position embedding size
image_size = 224
grid_size = image_size // new_patch_size[0]
state_dict["pos_embed"] = resample_abs_pos_embed(
posemb=state_dict["pos_embed"], new_size=[grid_size, grid_size]
)
# Load the new weights into a model with the target image and patch sizes
net = create_model(
"vit_base_patch16_224", img_size=image_size, patch_size=new_patch_size
)
net.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=True)
```
##### Conversion Script
`convert_patch_embed.py` can similarity do the resizing on any local model checkpoint file. For example, to resize to a patch size of 20:
```
python convert_patch_embed.py -i vit-16.pt -o vit-20.pt -n patch_embed.proj.weight -ps 20
```
or to a patch size of height 10 and width 15:
```
python convert_patch_embed.py -i vit-16.pt -o vit-10-15.pt -n patch_embed.proj.weight -ps 10 15
```
- The `-n` argument should correspond to the name of the patch embedding weights in the checkpoint's state dict.
### Evaluating at Different Patch Sizes
`eval.py` can be used to evaluate pretrained Vision Transformer models at different patch sizes. For example, to evaluate a ViT-B/16 at a patch size of 20 on the ImageNet-1k validation set, you can run:
```
python eval.py --accelerator gpu --devices 1 --precision 16 --model.resize_type pi
--model.weights vit_base_patch16_224.augreg_in21k_ft_in1k --data.root path/to/val/data/
--data.num_classes 1000 --model.patch_size 20 --data.size 224 --data.crop_pct 0.9
--data.mean "[0.5,0.5,0.5]" --data.std "[0.5,0.5,0.5]" --data.batch_size 256
```
- `--model.weights` should correspond to a `timm` model name.
- The `--data.root` directory should be organized in the [TorchVision ImageFolder](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/generated/torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder.html) structure. Alternatively, an LMDB file can be used by setting `--data.is_lmdb True` and having `--data.root` point to the `.lmdb` file.
- To accurately compare to `timm`'s [baseline results](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-image-models/blob/main/results/results-imagenet.csv), make sure that
`--data.size`, `--data.crop_pct`, `--data.interpolation` (all listed [here](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-image-models/blob/main/results/results-imagenet.csv)), `--data.mean`, and `--data.std` (in general found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-image-models/blob/main/timm/models/vision_transformer.py#L861)) are correct for the model. `--data.mean imagenet` and `--data.mean clip` can be set to use the respective default values (same for `--data.std`).
- Run `python eval.py --help` for a list and descriptions for all arguments.
## Experiments
The following experiments test using PI-resizing to change the patch size of standard ViT models during evaluation. All models have been fine-tuned on ImageNet-1k with a fixed patch size and are evaluated with different patch sizes.
#### Adjusting patch size and freezing image size to 224
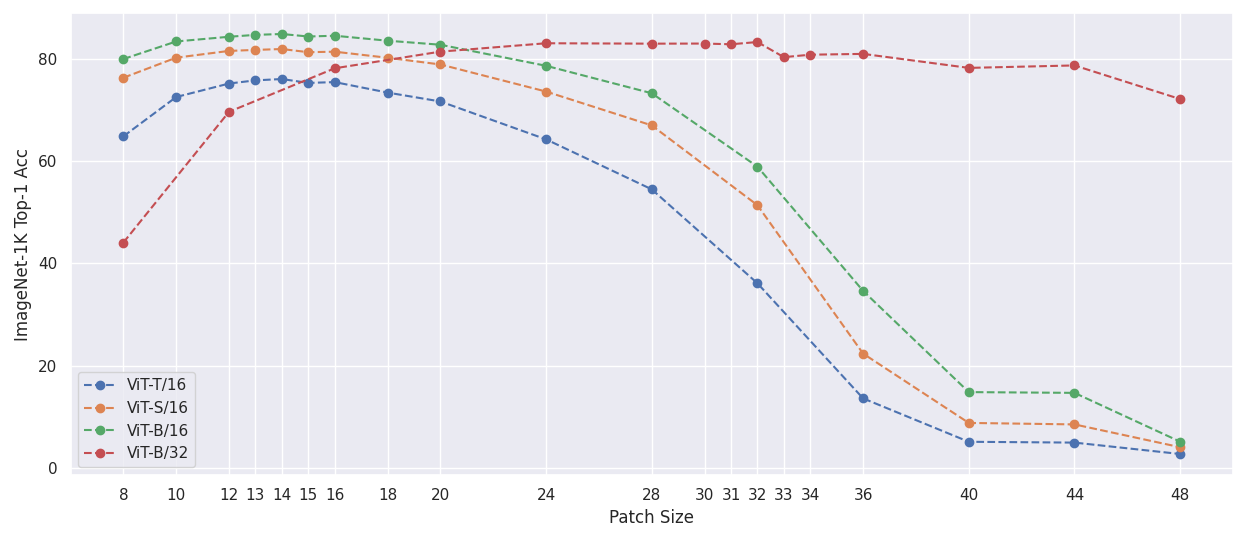
Numerical Results
| Patch Size | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 |
|:----------:|-------|-------|-------|-------|-----------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|------|
| ViT-T/16 | 64.84 | 72.54 | 75.18 | 75.80 | __76.06__ | 75.30 | 75.46 | 73.41 | 71.67 | 64.26 | 54.48 | 36.10 | 13.58 | 5.09 | 4.93 | 2.70 |
| ViT-S/16 | 76.31 | 80.24 | 81.56 | 81.76 | __81.93__ | 81.31 | 81.41 | 80.22 | 78.91 | 73.61 | 66.99 | 51.38 | 22.34 | 8.78 | 8.49 | 4.03 |
| ViT-B/16 | 79.97 | 83.41 | 84.33 | 84.70 | __84.87__ | 84.38 | 84.53 | 83.56 | 82.77 | 78.65 | 73.28 | 58.92 | 34.61 | 14.81 | 14.66 | 5.11 |
| Patch Size | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 |
|:----------:|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-----------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|-------|
| ViT-B/32 | 44.06 | 69.65 | 78.16 | 81.42 | 83.06 | 82.98 | 83.00 | 82.86 | __83.30__ | 80.34 | 80.82 | 80.98 | 78.24 | 78.72 | 72.14 |
#### Adjusting patch and image size
- Maintaining the same number of tokens as during training
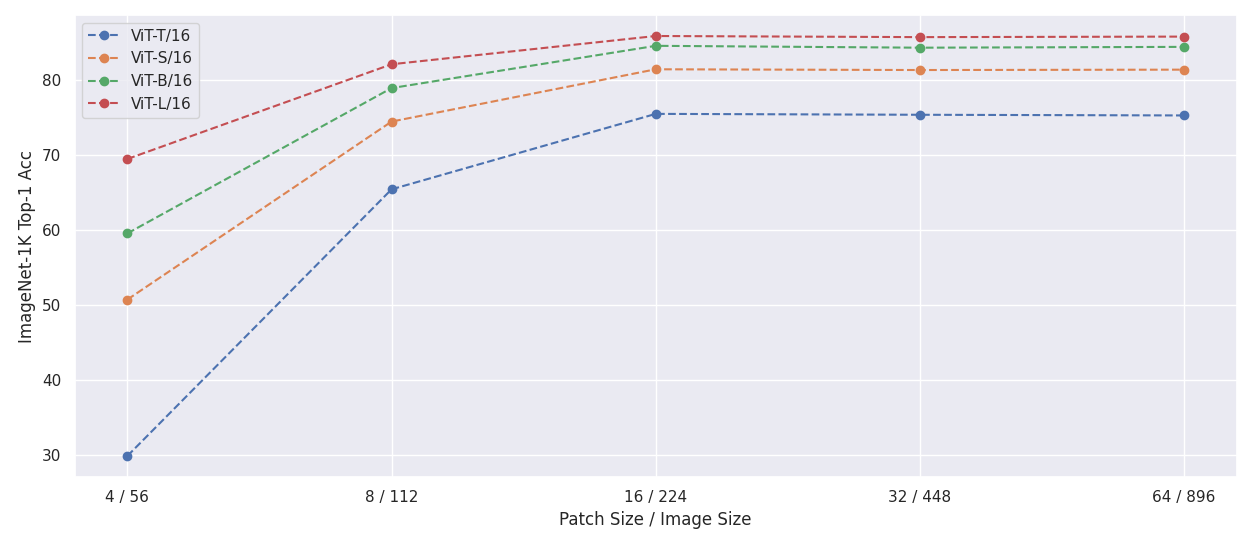
Numerical Results
| Patch Size / Image Size | 4 / 56 | 8 / 112 | 16 / 224 | 32 / 224 | 64 / 896 |
|:-----------------------:|--------|---------|----------|----------|----------|
| ViT-T/16 | 29.81 | 65.39 | 75.46 | 75.34 | 75.25 |
| ViT-S/16 | 50.68 | 74.43 | 81.41 | 81.31 | 81.36 |
| ViT-B/16 | 59.51 | 78.90 | 84.54 | 84.29 | 84.40 |
| ViT-L/16 | 69.44 | 82.08 | 85.85 | 85.70 | 85.77 |
## Citation
```bibtex
@article{beyer2022flexivit,
title={FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes},
author={Beyer, Lucas and Izmailov, Pavel and Kolesnikov, Alexander and Caron, Mathilde and Kornblith, Simon and Zhai, Xiaohua and Minderer, Matthias and Tschannen, Michael and Alabdulmohsin, Ibrahim and Pavetic, Filip},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.08013},
year={2022}
}
```