https://github.com/cafebazaar/async-actions
A more efficient way of handling async actions and loading/error states without code duplications in Vue.
https://github.com/cafebazaar/async-actions
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
A more efficient way of handling async actions and loading/error states without code duplications in Vue.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cafebazaar/async-actions
- Owner: cafebazaar
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-09-15T06:59:56.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-03-05T12:27:59.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-08T18:13:21.705Z (about 2 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://www.npmjs.com/package/@cafebazaar/async-actions
- Size: 1.24 MB
- Stars: 20
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

## Overview
Handling async actions(like API calls) is so tedious. Showing loading state and handling options like debouncing needs a lot of code duplications.
Async-Actions proposes a more efficient way of handling those actions without code duplications.
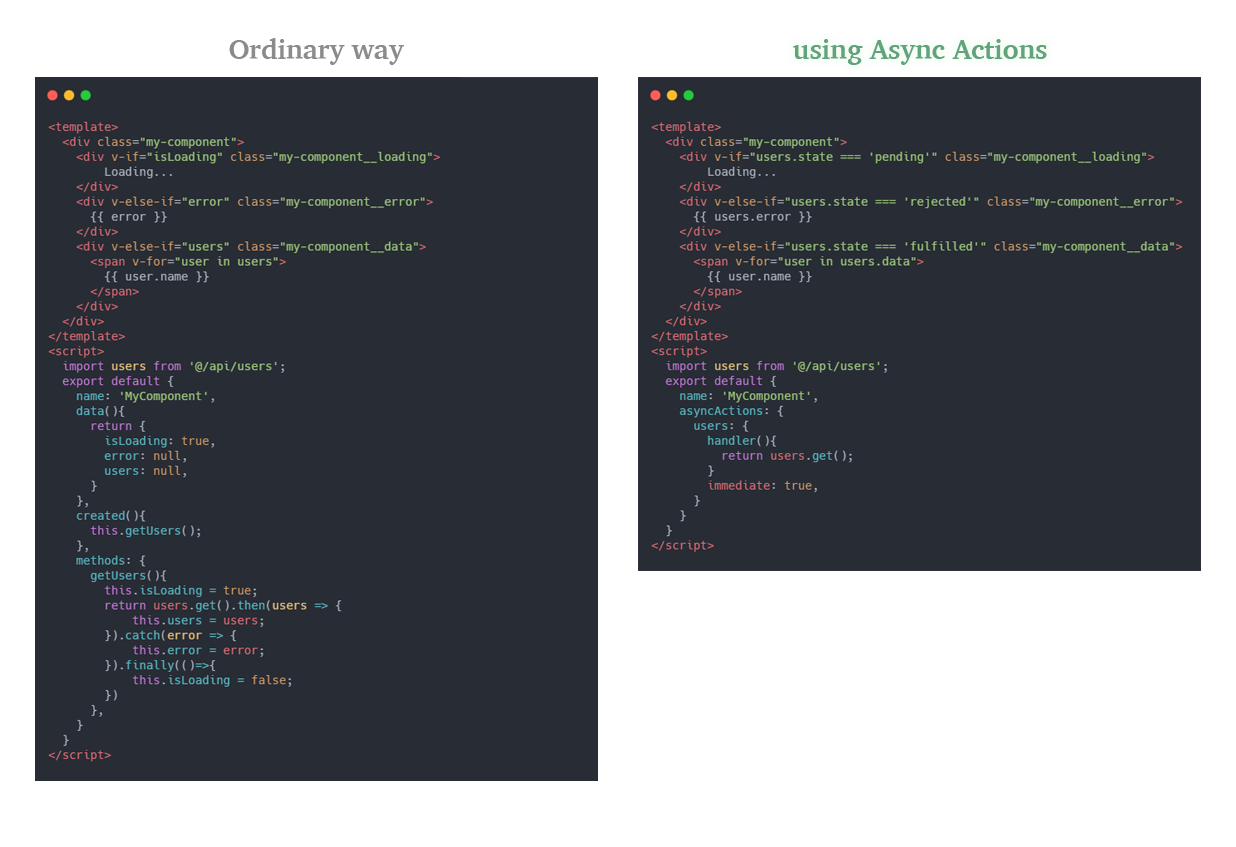
## How It Works
Actions are just simple functions. Async-Actions adds `state`, `error`, `pending` and `data` properties to your functions and dynamically updates these properties.
#### Action lifecycle and possible values of the `state` property
| Value | Description |
| ------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| notInitiated | Action has not been called yet. |
| pending | Action has been called, but it has not been completed yet. |
| fulfilled | Action has been completed successfully, and the result value is accessible using the `data` property. |
| rejected | Action has been rejected with an error which is accessible using `error` property. |
For checking if an action is in the **pending** status or not, you can also use the `pending` property on the action, which is more convenient.
## Installation
You can install Async-Actions with NPM or Yarn.
```bash
npm install @cafebazaar/async-actions --save
```
or
```bash
yarn add @cafebazaar/async-actions
```
## Usage
You can use Async-Actions in [pure JS](#pure-js). Also there are built in extensions for [Vue.js](#vuejs) and [Svelte](#svelte).
### Vue.js
`Vue.observable` provided by default as the observable function in the Vue version, and you don't need to pass it. There are two ways to use Async-Actions in a Vue.js project.
#### 1. Define actions in component options
For declaring async-actions in this way, you need to import the plugin and `use` it as a Vue plugin to enable the functionality globally on all components.
```javascript
import Vue from 'vue';
import AsyncActions from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/vue';
Vue.use(AsyncActions);
```
Then, you can define async-actions in all components using `asyncActions` property.
```javascript
Fetching Users List. Please Wait...
Oops. Somthing Went Wrong :(
-
{{ user.name }}
export default {
name: 'UsersList',
asyncActions: {
getUsers: {
handler() {
return someApiCall();
},
immediate: true,
initialData: [],
// other options...
},
},
};
```
The List of all options is available [here](#options).
If an action does not need any options, you can define it as a function for the sake of simplicity.
```javascript
import { loginApi } from './api';
export default {
name: 'Login',
asyncActions: {
login() {
return loginApi();
}
},
};
```
#### Options
| Property | Description | type | Required | Default |
| ----------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------- | -------- | ------- |
| handler | action's handler | function | true | |
| immediate | determines handler function should be called immediately after creation | boolean | false | false |
| debounce | debounce time in miliseconds | number | false | 0 |
| initialData | initial value of `data` property of action | any | false | null |
#### 2. Create asyncActions outside of components
In this way, you can create asyncActions anywhere and use them as regular functions.
```javascript
// usersActions.js
import { asyncAction } from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/vue';
import { someApiCall } from './api';
export const getUsers = asyncAction(() => someApiCall(), {
initialData: [],
});
```
And after that, you can import and use it inside Vue components:
```javascript
Fetching Users List. Please Wait...
Oops. Somthing Went Wrong :(
-
{{ user.name }}
import { getUsers } from './usersActions';
export default {
name: 'UsersList',
computed: {
getUsersAction(){
return getUsers;
}
},
created(){
getUsers();
}
};
```
### Svelte
In the Svelte version, `Store.writable` is used for every observable prop(`state`, `data`, and `error`) and, you don't need to provide `observableFn`. You can simply do:
```html
<script>
import asyncAction from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/src/svelte';
let myPromise = asyncAction(function () {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('My Data!!'), 5000);
});
}, options);
let { state, data, error } = myPromise;
// execute async function
myPromise();
- Status: {$state}
- Data: {$data}
- Error: {$error}
```
The List of all options is available [here](#options).
You can use asyncAction outside of svelte file and import it and use it directly inside DOM.
### Pure JS
You can define an async-action using `asyncAction` method which gets a handler function and configuration options as its parameters. When using the pure version, you must provide an observable function which used for updating action properties.
```javascript
import { asyncAction } from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/pure';
import customObservable from 'utils/observable';
const myAsyncAction = asyncAction(
Promise.resolve('Hello'),
options,
customObservable
);
```
List of all options are available [here](#options).
## License
[MIT](https://github.com/cafebazaar/async-actions/blob/master/LICENSE)