https://github.com/cbailiss/basictabler
Construct Rich Tables for Output to HTML/Excel
https://github.com/cbailiss/basictabler
html htmlwidget r tables visualization
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Construct Rich Tables for Output to HTML/Excel
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cbailiss/basictabler
- Owner: cbailiss
- Created: 2017-09-21T14:39:37.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-26T14:06:29.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-07-12T16:47:16.016Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: html, htmlwidget, r, tables, visualization
- Language: R
- Homepage:
- Size: 2.06 MB
- Stars: 36
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.Rmd
- Changelog: NEWS.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- jimsghstars - cbailiss/basictabler - Construct Rich Tables for Output to HTML/Excel (R)
- awesome-shiny-extensions - basictabler - Construct rich tables for output to HTML/Excel. (UI Components / Table)
README
---
title: "basictabler"
output: github_document
---
```{r setup, include=FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(echo = TRUE)
```
[](https://github.com/cbailiss/basictabler/actions)
[](https://cran.r-project.org/package=basictabler)
The `basictabler` package enables rich tables to be created and rendered/exported with just a few lines of R.
The `basictabler` package:
- Provides an easy way of creating basic tables, especially from data frames and matrices.
- Provides flexibility so that the structure/content of the table can be easily built/modified.
- Provides formatting options to simplify rendering/exporting data.
- Provides styling options so the tables can be themed/branded as needed.
The tables are rendered as htmlwidgets or plain text. The HTML/text can be exported for use outside of R.
The tables can also be exported to Excel, including the styling/formatting. The formatting/styling is specified once and can then be used when rendering to both HTML and Excel - i.e. it is not necessary to specify the formatting/styling separately for each output format.
Using the `flextabler` package it is also possible to output tables to Word and PowerPoint.
`basictabler` is a companion package to the `pivottabler` package. `pivottabler` is focussed on generating pivot tables and can aggregate data. `basictabler` does not aggregate data but offers more control of table structure.
For more information see http://www.basictabler.org.uk/.
### Installation
You can install:
* the latest released version from CRAN with
```{r eval=FALSE}
install.packages("basictabler")
```
* the latest development version from github with
```{r eval=FALSE}
devtools::install_github("cbailiss/basictabler", build_vignettes = TRUE)
```
### Examples
#### Trivial Example
Creating a tiny HTML table from a data frame and immediately rendering it as a htmlwidget:
```{r, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, eval=FALSE, comment=""}
library(basictabler)
qhtbl(data.frame(a=1:2, b=3:4))
```
#### Another Example
Creating a table from a data frame, specifying column names and value formats:
```{r eval=FALSE}
# aggregate the sample data to make a small data frame
library(basictabler)
library(dplyr)
tocsummary <- bhmsummary %>%
group_by(TOC) %>%
summarise(OnTimeArrivals=sum(OnTimeArrivals),
OnTimeDepartures=sum(OnTimeDepartures),
TotalTrains=sum(TrainCount)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
mutate(OnTimeArrivalPercent=OnTimeArrivals/TotalTrains*100,
OnTimeDeparturePercent=OnTimeDepartures/TotalTrains*100) %>%
arrange(TOC)
# To specify formatting, a list is created which contains one element for each column in
# the data frame, i.e. tocsummary contains six columns so the columnFormats list has six elements.
# The values in the first column in the data frame won't be formatted since NULL has been specified.
# The values in the 2nd, 3rd and 4th columns will be formatted using format(value, big.mark=",")
# The values in the 5th and 6th columns will be formatted using sprintf(value, "%.1f")
columnFormats=list(NULL, list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), "%.1f", "%.1f")
# render the table directly as a html widget
qhtbl(tocsummary, firstColumnAsRowHeaders=TRUE,
explicitColumnHeaders=c("TOC", "On-Time Arrivals", "On-Time Departures",
"Total Trains", "On-Time Arrival %", "On-Time Departure %"),
columnFormats=columnFormats)
```
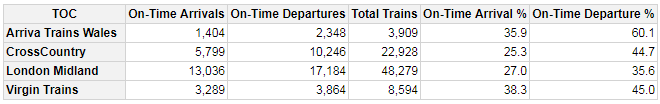
In the example above, the `qhtbl()` functions returns a html widget that is rendered immediately in the R-Studio viewer window. An alternative is to use the `qtbl()` function which returns a BasicTable object that can be further manipulated. The styling example further below demonstrates this.
#### Changing a Table Example
Tables can also be built row-by-row, column-by-column and cell-by-cell. Once built tables can be modified (adding/removing rows columns and cells, merging cells and changing styling). The following example shows more granular ways of building and changing a table:
```{r eval=FALSE}
# data for the table
saleIds <- c(5334, 5336, 5338)
items <- c("Apple", "Orange", "Banana")
quantities <- c(5, 8, 6)
prices <- c(0.34452354, 0.4732543, 1.3443243)
# construct a table column by column
library(basictabler)
tbl <- BasicTable$new()
tbl$cells$setCell(1, 1, cellType="root", rawValue="Sale ID")
tbl$cells$setCell(1, 2, cellType="columnHeader", rawValue="Item")
tbl$cells$setCell(1, 3, cellType="columnHeader", rawValue="Quantity")
tbl$cells$setCell(1, 4, cellType="columnHeader", rawValue="Price")
tbl$cells$setColumn(1, cellTypes="rowHeader", rawValues=saleIds)
tbl$cells$setColumn(2, cellTypes="cell", rawValues=items)
tbl$cells$setColumn(3, cellTypes="cell", rawValues=quantities)
tbl$cells$setColumn(4, cellTypes="cell", rawValues=prices,
formats=list("%.2f"))
# example of changing the table - appending a row
formats <- list(NULL, NULL, NULL, "%.2f")
cellTypes=c("rowHeader", "cell", "cell", "cell")
tbl$cells$setRow(5, cellTypes=cellTypes, formats=formats,
rawValues=list(5343, "Pear", 2, 1.0213424))
# example of changing the table - inserting a row
tbl$cells$insertRow(1)
tbl$cells$setRow(1, cellTypes="columnHeader",
rawValues=list("Sale ID", "Sale Details", "", ""))
# example of changing the table - merging some cells
tbl$mergeCells(rFrom=1, cFrom=1, rSpan=2, cSpan=1)
tbl$mergeCells(rFrom=1, cFrom=2, rSpan=1, cSpan=3)
# render the final table
tbl$renderTable()
```
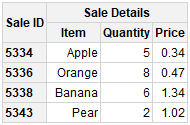
#### Styling Example
Styling can be specified when creating tables:
```{r eval=FALSE}
# aggregate the sample data to make a small data frame
library(basictabler)
library(dplyr)
tocsummary <- bhmsummary %>%
group_by(TOC) %>%
summarise(OnTimeArrivals=sum(OnTimeArrivals),
OnTimeDepartures=sum(OnTimeDepartures),
TotalTrains=sum(TrainCount)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
mutate(OnTimeArrivalPercent=OnTimeArrivals/TotalTrains*100,
OnTimeDeparturePercent=OnTimeDepartures/TotalTrains*100) %>%
arrange(TOC)
# column formats
columnFormats=list(NULL, list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), "%.1f", "%.1f")
# create the table
tbl <- qtbl(tocsummary, firstColumnAsRowHeaders=FALSE,
explicitColumnHeaders=c("TOC", "On-Time Arrivals", "On-Time Departures",
"Total Trains", "On-Time Arrival %", "On-Time Departure %"),
columnFormats=columnFormats,
tableStyle=list("border-color"="maroon"),
headingStyle=list("color"="cornsilk", "background-color"="maroon",
"font-style"="italic", "border-color"="maroon"),
cellStyle=list("color"="maroon", "background-color"="cornsilk",
"border-color"="maroon"))
# set column alignment of first column
# the arguments are (rFrom, cFrom, rTo, cTo, declarations)
tbl$setStyling(2, 1, 5, 1, declarations=list("text-align"="left"))
# render table
tbl$renderTable()
```
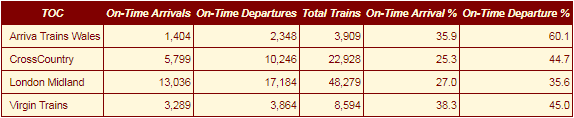
#### Excel Output
The same styling/formatting used for the HTML output is also used when outputting to Excel - greatly reducing the amount of script that needs to be written to create Excel output. The only additional formatting that typically needs applying is the Excel cell format strings.
```{r eval=FALSE}
# aggregate the sample data to make a small data frame
library(basictabler)
library(dplyr)
tocsummary <- bhmsummary %>%
group_by(TOC) %>%
summarise(OnTimeArrivals=sum(OnTimeArrivals),
OnTimeDepartures=sum(OnTimeDepartures),
TotalTrains=sum(TrainCount)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
mutate(OnTimeArrivalPercent=OnTimeArrivals/TotalTrains*100,
OnTimeDeparturePercent=OnTimeDepartures/TotalTrains*100) %>%
arrange(TOC)
columnFormats=list(NULL, list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), list(big.mark=","), "%.1f", "%.1f")
# create the table
tbl <- qtbl(tocsummary, firstColumnAsRowHeaders=TRUE,
explicitColumnHeaders=c("TOC", "On-Time Arrivals", "On-Time Departures",
"Total Trains", "On-Time Arrival %", "On-Time Departure %"),
columnFormats=columnFormats)
# set the styling on the count cells
# the arguments are (rFrom, cFrom, rTo, cTo, declarations)
tbl$setStyling(2, 2, 5, 4, declarations=list("xl-value-format"="#,##0"))
# set the styling on the average delay cells
tbl$setStyling(2, 5, 5, 6, declarations=list("xl-value-format"="##0.0"))
# render the table to an Excel workbook
library(openxlsx)
wb <- createWorkbook(creator = Sys.getenv("USERNAME"))
addWorksheet(wb, "Data")
tbl$writeToExcelWorksheet(wb=wb, wsName="Data",
topRowNumber=2, leftMostColumnNumber=2, applyStyles=TRUE)
saveWorkbook(wb, file="C:\\test.xlsx", overwrite = TRUE)
```
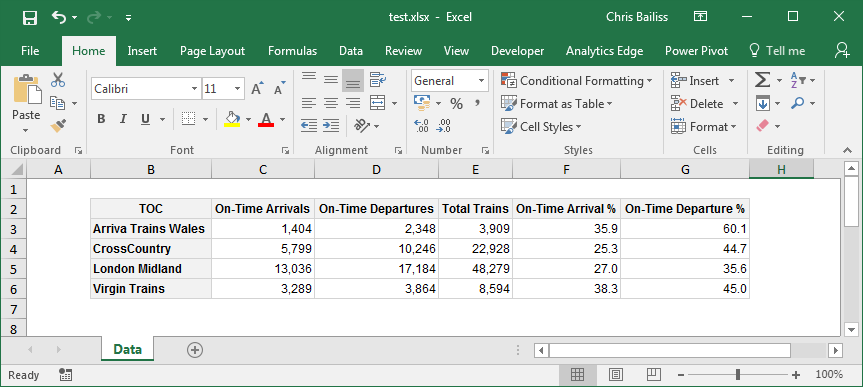
In the screenshot above, Gridlines have been made invisible to make the styling easier to see (by clearing the checkbox on the 'View' ribbon). Columns were also auto-sized - though the widths of columns could also be manually specified from R. See the Excel Export vignette for more details.
### More Information
It is possible to create tables from data frames, matrices, row-by-row, column-by-column and/or cell-by-cell.
Tables can be further manipulated once created, including adding/removing cells/rows/columns and merging cells.
Styling and formatting can be specified for individual cells and ranges of cells.
See the package vignettes for more information:
```{r eval=FALSE}
# to see a list of available package vignettes:
vignette(package="basictabler")
# to open a specific vignette
vignette(topic="v01-introduction", package="basictabler")
```
The vignettes can also be read on CRAN at:
https://cran.r-project.org/package=basictabler