https://github.com/cekdahl/jSoupLink
HTML parser for Mathematica/Wolfram Language
https://github.com/cekdahl/jSoupLink
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
HTML parser for Mathematica/Wolfram Language
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cekdahl/jSoupLink
- Owner: cekdahl
- Created: 2015-02-14T23:58:46.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-24T20:43:42.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-05T09:11:37.212Z (11 months ago)
- Language: Mathematica
- Size: 1.07 MB
- Stars: 42
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-wolfram-language - jSoupLink
README
# jsoupLink
Created by Calle Ekdahl.
GPL-2.0+ licensed.
Current version: 1.0
## Introduction
[jsoup](http://jsoup.org) is an open-source library written in Java, which excels at parsing HTML and manipulating the DOM. jsoupLink is a package written for Mathematica in Wolfram Language which aims to provide an interface to jsoup that feels natural for Mathematica users.
While traditionally HTML has been worked on in Mathematica by importing it as symbolic XML and painstakingly transforming it with pattern matching, jsoupLink introduces the concept of HTML element objects, which make it super easy to traverse the DOM tree and to modify it.
The most common application for jsoupLink is to extract information from websites, for example table data.
## Installing jsoupLink
`jsoupLink` is distributed in the form of a paclet. Download the latest version of the paclet from [the releases page](https://github.com/cekdahl/jsoupLink/releases) and install it using the the `PacletManager` package (which you already have because it comes with Mathematica):
Needs["PacletManager`"]
PacletInstall["~/Downloads/jSoupLink-1.0.0.paclet"]
Use `Needs` to load jsoupLink:
Needs["jsoupLink`"]
## Importing and Exporting Documents
It is easy to import and export HTML using jsoupLink, with the built-in `Import` and `Export` commands. Specify `HTMLDOM` as the file format.

The returned value is an HTML element object. It has properties that can be used to access information about itself or its children. It also has properties that can modify itself or its children. Having modified the object, exporting it back to HTML is equally simple:

## HTML Elements
HTML is but a bunch of nested elements. `
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
` is made up of a `div` element and two `p` elements, the `div` being the parent to its two children `p`, and the `p`s being siblings. The idea of jsoup is to assign one object to each element, and to relate the objects to each other through properties. The property `Children` of the object corresponding to `div` would list the two objects corresponding to the `p` elements, the property `Parent` on either of the `p` elements would list the object `div`, and the `Siblings` property of either of the `p` elements would list the other `p` element. Furthermore other properties would retrieve other types of information. The `InnerHTML` property of `div` would return `Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
` as a string, whereas the `OuterHTML` property of the first `p` would return `Paragraph 1
`.
jsoupLink provides direct access to all of these objects and their properties. In a notebook, these objects have a distinctive display:

Starting with the object corresponding to the outermost element, `html`, various properties can be used to find all other elements of interest. Properties can be retrieved as subvalues of the objects, as in the image.
In difference to normal Wolfram Language expressions, objects representing elements are mutable, and there are several properties that can modify elements. Most properties can be accessed as `obj["property"]`, some take several arguments, e.g. `obj["Attribute", "attributeName"]`, or `obj["Attribute", "key", "value"]`, which will set the attribute `key` to the value `value`. Since setting attributes is a common task, the shorthand notation `obj[key] = val` is also provided. Attributes can also be retrieved with `obj[attr]` if `attr` is not one of the properties listed by `obj["Properties"]`.
## Properties
Throughout this list, objects representing HTML elements will be referred to simply as elements. Elements are arranged in a tree structure, called the DOM tree. Whenever descriptions such as "the same level" or "topmost", or "beneath" are used in the following text, it refers to this tree structure. (See also the first paragraph of the preceding section.)
This is a complete listing of all the properties, available to all elements:
- `element["TagName"]`
Tag name.
Example: link elements return `a`, paragraph elements return `p`.
- `element["TagName", "tag"]`
Set element tag name.
Example: Use to convert an`h1` element into an `h2` element.
- `element["Root"]`
Topmost element, usually `html`.
- `element["Parent"]`
Immediate ancestor of `element`.
Example: the parent to `body` is `html`.
- `element["Children"]`
All elements that lie directly under `element`.
Example: `li` elements are usually children of a `ul`.
- `element["Siblings"]`
All elements on the same level as `element`.
Example: The siblings of an `
- `element["Select", "selector"]`
All elements from anywhere beneath `element`, that match the CSS selector "selector". More information about valid syntax: [Use selector syntax to find elements](https://jsoup.org/cookbook/extracting-data/selector-syntax).
- `element["AllElements"]`
All elements beneath `element`.
- `element["InnerHTML"]`
HTML corresponding to the offspring of `element`.
Example: the inner HTML of `
- `element["OuterHTML"]`
HTML corresponding to `element` and all offspring.
Example: the outer HTML of `
- `element["OwnText"]`
Text which resides directly under `element`.
Example: the `OwnText` of `
text more text
` is `text`. The `OwnText` of the `b` element is `more text`. - `element["AllText"]`
All text beneath `element`.
Example: `AllText` of the `html` element returns all text in the document.
- `element["AllText", "text"]`
Remove existing elements and text beneath `element` and replace with `"text"`.
- `element["ID"]`
The `ID` attribute.
- `element["ClassNames"]`
List of classes in the class attribute.
- `element["Value"]`
The `value` attribute, if the element has it.
- `element["HasAttribute", "attr"]`
`True` if the attribute `attr` is given, and `False` otherwise.
- `element["Attribute", "attr"]`
Value of the attribute `attr`.
- `element["Attribute", "attr", "val"]`
Set attribute `attr` to the value `val`.
- `element["Attribute", "attr", True | False]`
Set attribute `attr` to `""` if `True`, remove `attr` if `False`.
- `element["Attribute", "assoc"]`
Set all attributes as given by the association `assoc`.
- `element["Attributes"]`
Association with all attributes and their values.
- `element["RemoveAttribute", "attr"]`
Remove the attribute `attr`.
- `element["IsBlock"]`
`True` if `element` is a block level element, `False` otherwise.
- `element["HasText"]`
`True` if `element["AllText"]` is not equal to `""`, `False` if it is.
- `element["BaseURI"]`
The base URI of the document.
- `element["BaseURI", "uri"]`
Set the base URI of the document.
- `element["HasClass", "class"]`
`True` if `class` appears in `element`'s class attribute, `False` otherwise.
- `element["AddClass", "class"]`
Add `class` to `element`'s class attribute.
- `element["RemoveClass", "class"]`
Remove `class` from `element`'s class attribute.
- `element["ToggleClass", "class"]`
Add `class` to `element`'s class attribute if it doesn't have it, and remove it if it is already there.
- `element["Before", "html"]`
Parse `html` and insert the resulting object before `element`.
- `element["Before", el]`
Insert element `el` before `element`.
- `element["After", "html"]`
Parse `html` and insert the resulting object after `element`.
- `element["After", el]`
Insert element `el` after `element`.
- `element["Prepend", "html"]`
Parse `html` and prepend the resulting object to `element`'s children.
- `element["Prepend", el]`
Prepend element `el` to `element`'s children.
- `element["Append", "html"]`
Parse `html` and append the resulting object to `element`'s children.
- `element["Append", el]`
Append element `el` to `element`'s children.
- `element["ReplaceWith", el]`
Replace `element` with element `el`.
- `element["Remove"]`
Remove `element`.
- `element["Wrap", "html"]`
Make `element` a child of the object resulting from parsing `html`.
- `element["Unwrap"]`
Remove `element` but keep its children, essentially moving them up one level.
- `element["Clean"]`
Run `element` and all its offspring through a whitelist. Used to e.g. prevent XSS attacks.
- `element["DeepCopy"]`
Return a copy of `element`, such that modifications done to the copy do not affect `element`.
- `element["Properties"]`
List all properties.
- `element["DOMTree"]`
Display the DOM tree. Details below.
## DOM Tree Interface
`element["DOMTree"]` opens an interface to view the DOM tree with `element` as root:
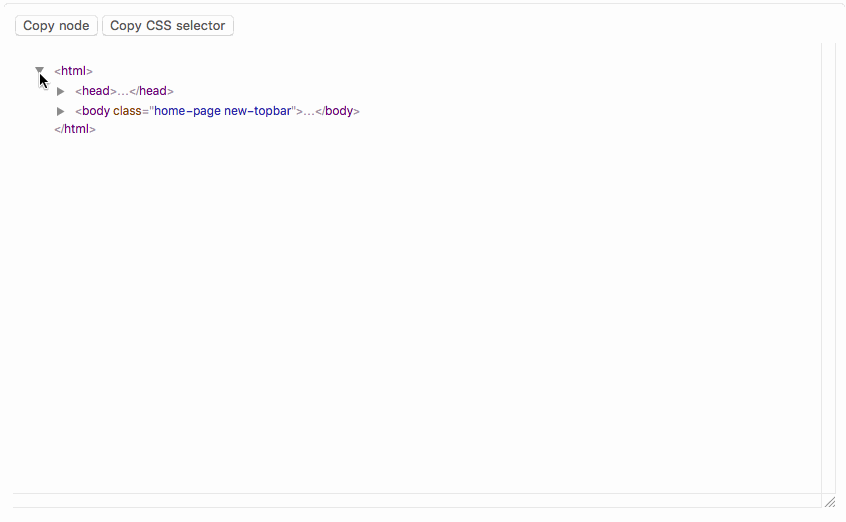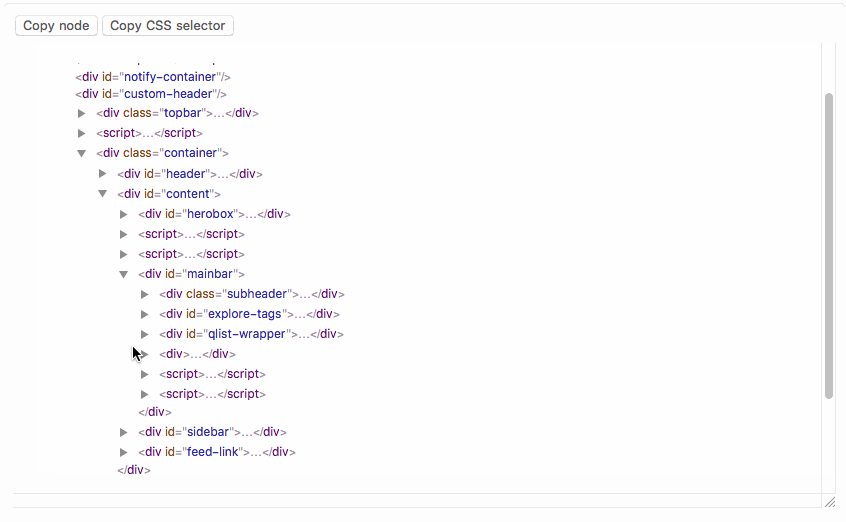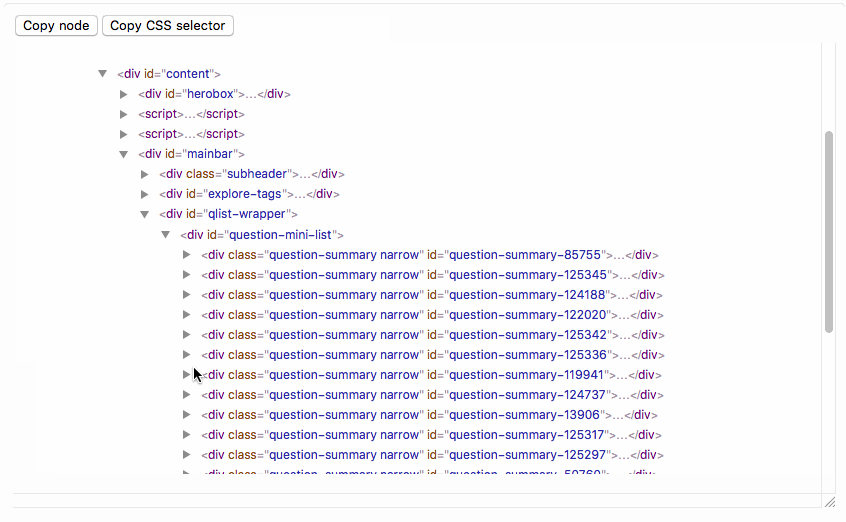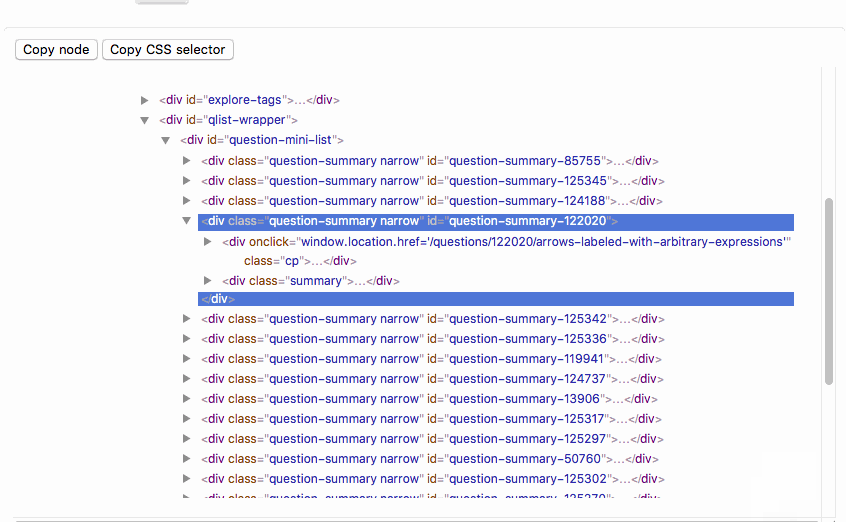
Elements can be selected by clicking on them. The "copy node" button writes the corresponding element to the clipboard, so that it can be pasted into a notebook. "Copy CSS selector" writes a CSS selector that uniquely identifies the selected element to the clipboard.
## Retrieving absolute URLs
If you are having problem retrieving absolute URLs from links, you may try to retrieve the `abs:href` attribute instead of the `href` attribute.