https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree
A python library to build Model Trees with Linear Models at the leaves.
https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree
boosting-tree decision-trees linear-models machine-learning model-trees random-forest scikit-learn tree
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
A python library to build Model Trees with Linear Models at the leaves.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree
- Owner: cerlymarco
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-03-27T08:57:48.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-19T04:16:16.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-12T06:31:14.940Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: boosting-tree, decision-trees, linear-models, machine-learning, model-trees, random-forest, scikit-learn, tree
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 5.92 MB
- Stars: 373
- Watchers: 12
- Forks: 56
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# linear-tree
A python library to build Model Trees with Linear Models at the leaves.
linear-tree provides also the implementations of _LinearForest_ and _LinearBoost_ inspired from [these works](https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree#references).
## Overview
**Linear Trees** combine the learning ability of Decision Tree with the predictive and explicative power of Linear Models.
Like in tree-based algorithms, the data are split according to simple decision rules. The goodness of slits is evaluated in gain terms fitting Linear Models in the nodes. This implies that the models in the leaves are linear instead of constant approximations like in classical Decision Trees.
**Linear Forests** generalize the well known Random Forests by combining Linear Models with the same Random Forests. The key idea is to use the strength of Linear Models to improve the nonparametric learning ability of tree-based algorithms. Firstly, a Linear Model is fitted on the whole dataset, then a Random Forest is trained on the same dataset but using the residuals of the previous steps as target. The final predictions are the sum of the raw linear predictions and the residuals modeled by the Random Forest.
**Linear Boosting** is a two stage learning process. Firstly, a linear model is trained on the initial dataset to obtain predictions. Secondly, the residuals of the previous step are modeled with a decision tree using all the available features. The tree identifies the path leading to highest error (i.e. the worst leaf). The leaf contributing to the error the most is used to generate a new binary feature to be used in the first stage. The iterations continue until a certain stopping criterion is met.
**linear-tree is developed to be fully integrable with scikit-learn**. ```LinearTreeRegressor``` and ```LinearTreeClassifier``` are provided as scikit-learn _BaseEstimator_ to build a decision tree using linear estimators. ```LinearForestRegressor``` and ```LinearForestClassifier``` use the _RandomForest_ from sklearn to model residuals. ```LinearBoostRegressor``` and ```LinearBoostClassifier``` are available also as _TransformerMixin_ in order to be integrated, in any pipeline, also for automated features engineering. All the models available in [sklearn.linear_model](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.linear_model) can be used as base learner.
## Installation
```shell
pip install --upgrade linear-tree
```
The module depends on NumPy, SciPy and Scikit-Learn (>=0.24.2). Python 3.6 or above is supported.
## Media
- [Linear Tree: the perfect mix of Linear Model and Decision Tree](https://towardsdatascience.com/linear-tree-the-perfect-mix-of-linear-model-and-decision-tree-2eaed21936b7)
- [Model Tree: handle Data Shifts mixing Linear Model and Decision Tree](https://towardsdatascience.com/model-tree-handle-data-shifts-mixing-linear-model-and-decision-tree-facfd642e42b)
- [Explainable AI with Linear Trees](https://towardsdatascience.com/explainable-ai-with-linear-trees-7e30a6f067d7)
- [Improve Linear Regression for Time Series Forecasting](https://towardsdatascience.com/improve-linear-regression-for-time-series-forecasting-e36f3c3e3534#a80b-b6010ccb1c21)
- [Linear Boosting with Automated Features Engineering](https://towardsdatascience.com/linear-boosting-with-automated-features-engineering-894962c3ba84)
- [Improve Random Forest with Linear Models](https://towardsdatascience.com/improve-random-forest-with-linear-models-1fa789691e18)
## Usage
##### Linear Tree Regression
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from lineartree import LinearTreeRegressor
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_targets=1,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
regr = LinearTreeRegressor(base_estimator=LinearRegression())
regr.fit(X, y)
```
##### Linear Tree Classification
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier
from lineartree import LinearTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_redundant=0,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
clf = LinearTreeClassifier(base_estimator=RidgeClassifier())
clf.fit(X, y)
```
##### Linear Forest Regression
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from lineartree import LinearForestRegressor
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_targets=1,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
regr = LinearForestRegressor(base_estimator=LinearRegression())
regr.fit(X, y)
```
##### Linear Forest Classification
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from lineartree import LinearForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_redundant=0,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
clf = LinearForestClassifier(base_estimator=LinearRegression())
clf.fit(X, y)
```
##### Linear Boosting Regression
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from lineartree import LinearBoostRegressor
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_targets=1,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
regr = LinearBoostRegressor(base_estimator=LinearRegression())
regr.fit(X, y)
```
##### Linear Boosting Classification
```python
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier
from lineartree import LinearBoostClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=4,
n_informative=2, n_redundant=0,
random_state=0, shuffle=False)
clf = LinearBoostClassifier(base_estimator=RidgeClassifier())
clf.fit(X, y)
```
More examples in the [notebooks folder](https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree/tree/main/notebooks).
Check the [API Reference](https://github.com/cerlymarco/linear-tree/blob/main/notebooks/README.md) to see the parameter configurations and the available methods.
## Examples
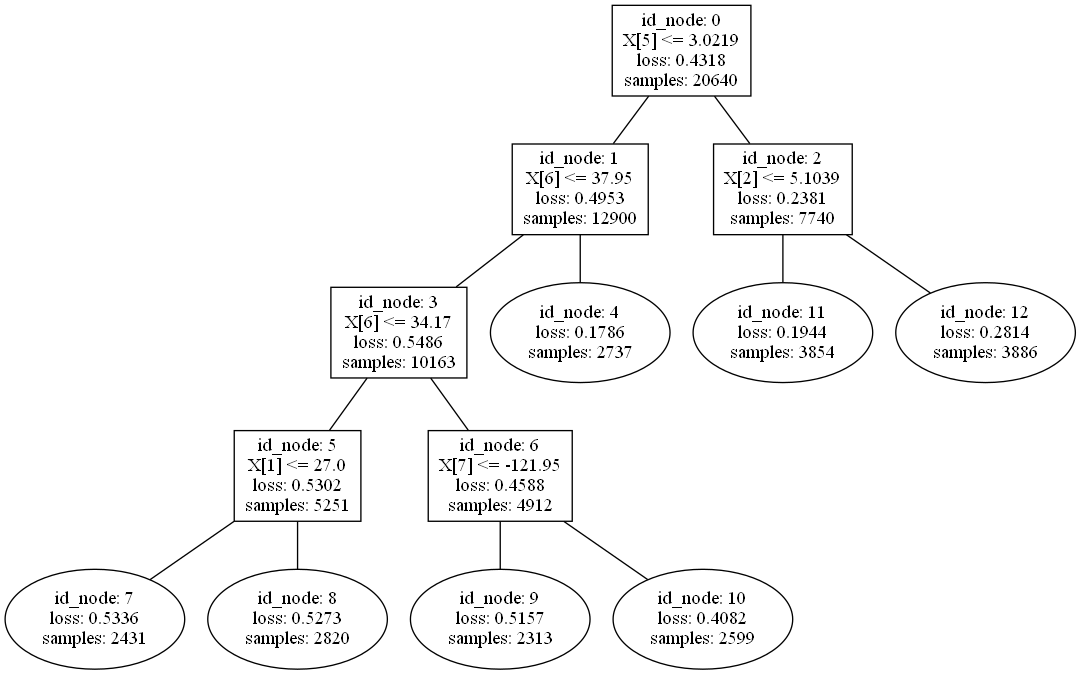
Show the linear tree learning path:
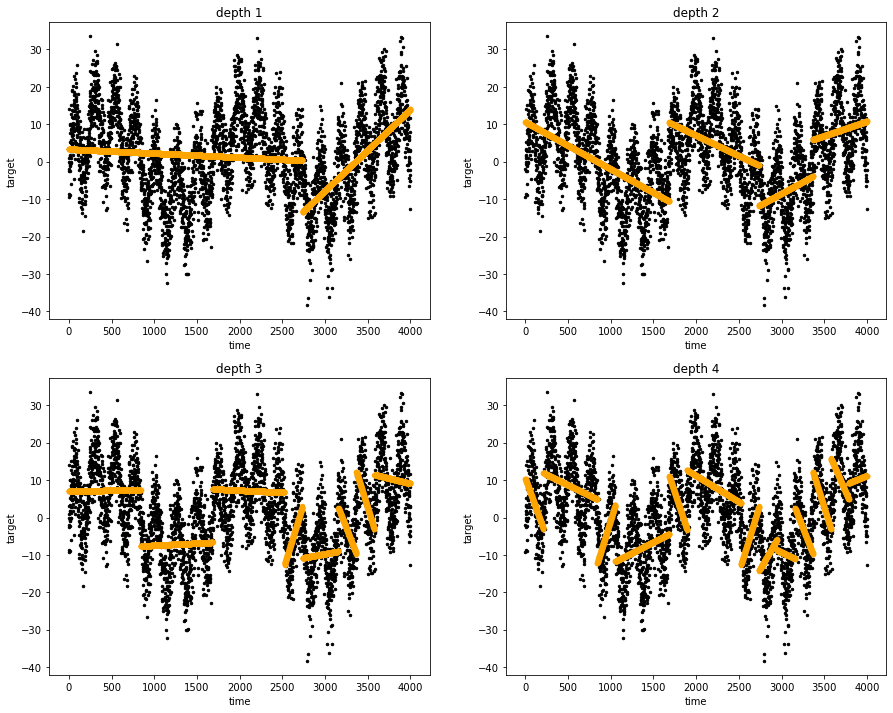
Linear Tree Regressor at work:
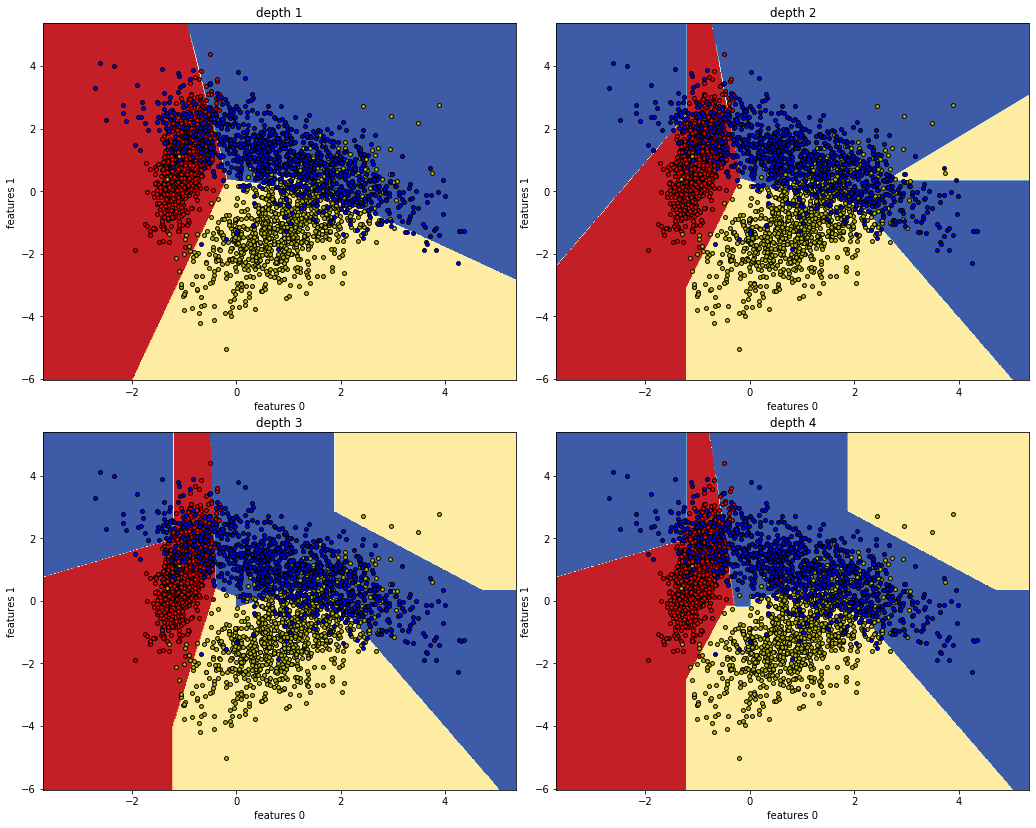
Linear Tree Classifier at work:
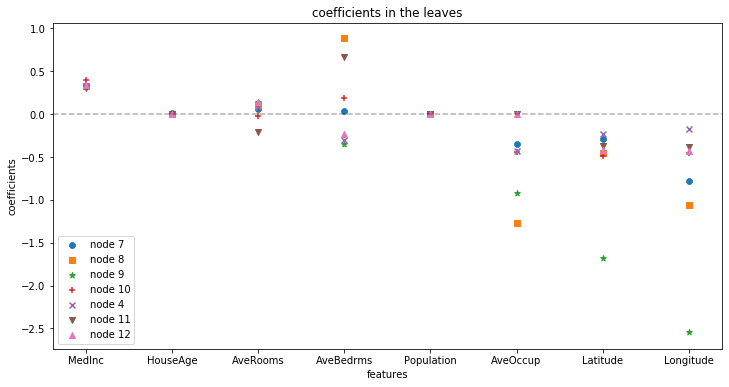
Extract and examine coefficients at the leaves:
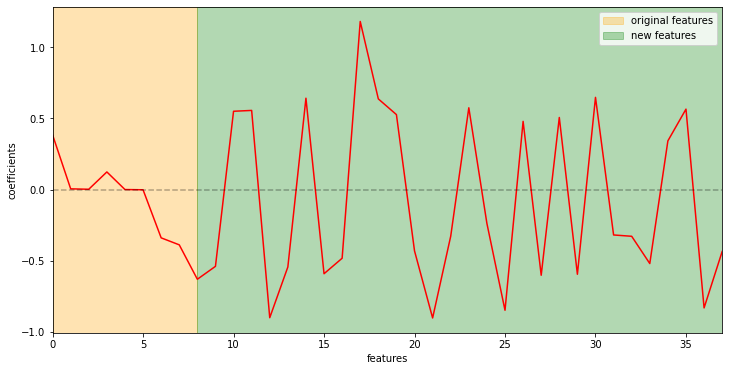
Impact of the features automatically generated with Linear Boosting:
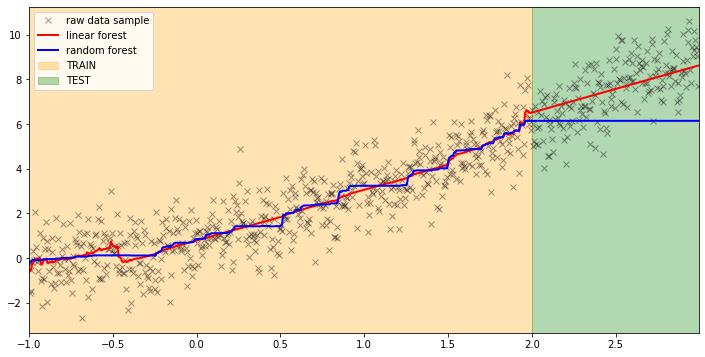
Comparing predictions of Linear Forest and Random Forest:
## References
- Regression-Enhanced Random Forests. Haozhe Zhang, Dan Nettleton, Zhengyuan Zhu.
- Explainable boosted linear regression for time series forecasting. Igor Ilic, Berk Gorgulu, Mucahit Cevik, Mustafa Gokce Baydogan.