https://github.com/chinmaykunkikar/vide-amplify
VOD platform built using ReactJS and managed on AWS. An HLS Adaptive Bitrate stack is encoded using FFMPEG.
https://github.com/chinmaykunkikar/vide-amplify
adaptive-bitrate aws-amplify aws-cognito aws-dynamodb aws-lambda aws-s3 create-react-app ffmpeg graphql hls material-ui reactjs
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
VOD platform built using ReactJS and managed on AWS. An HLS Adaptive Bitrate stack is encoded using FFMPEG.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/chinmaykunkikar/vide-amplify
- Owner: chinmaykunkikar
- Created: 2021-05-05T14:35:11.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-22T10:32:38.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-28T20:11:57.309Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: adaptive-bitrate, aws-amplify, aws-cognito, aws-dynamodb, aws-lambda, aws-s3, create-react-app, ffmpeg, graphql, hls, material-ui, reactjs
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://master.d1j0u94s8l7oc.amplifyapp.com/
- Size: 87.6 MB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 16
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Vide - A Video on Demand Platform
- [Vide - A Video on Demand Platform](#vide---a-video-on-demand-platform)
- [Concepts](#concepts)
- [Video on Demand](#video-on-demand)
- [Adaptie Bitrate Streaming](#adaptie-bitrate-streaming)
- [HLS](#hls)
- [Transcoding and FFmpeg](#transcoding-and-ffmpeg)
- [Architecture Diagrams](#architecture-diagrams)
- [Setup](#local-setup)
- [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- [Install and configure the Amplify CLI](#install-and-configure-the-amplify-cli)
- [Clone GitHub repository and add dependencies](#clone-github-repository-and-add-dependencies)
- [Initialize Amplify project](#initialize-amplify-project)
- [Deploy the services to AWS](#deploy-the-services-to-aws)
- [Run the project](#run-the-project)
## Concepts
### Video on Demand
Video on Demand (VoD) is a technology for delivering video content, such as movies and television shows, directly to individual customers for immediate viewing, regardless of broadcast schedules. Examples include, among others, Amazon Prime Video, Netflix and YouTube.
### Adaptie Bitrate Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming, abbreviated as ABR, basically refers to the ability of a video player to adjust the quality of a video dynamically according to the available bandwidth, network conditions, and user’s device performance.
The idea behind this is to segment a whole media file into two distinct dimensions: time and resolution. You take an hour-long video and splice it into several X seconds segments, and you also create multiple resolutions (e.g. 256x144, 640x360, 1280x720, etc), also known as renditions.
When the device is not able to handle a media, due to its current context, it can dynamically adapt. For instance, while the network is facing a hard time to download a high resolution content, the player can pick a lower resolution of a video.
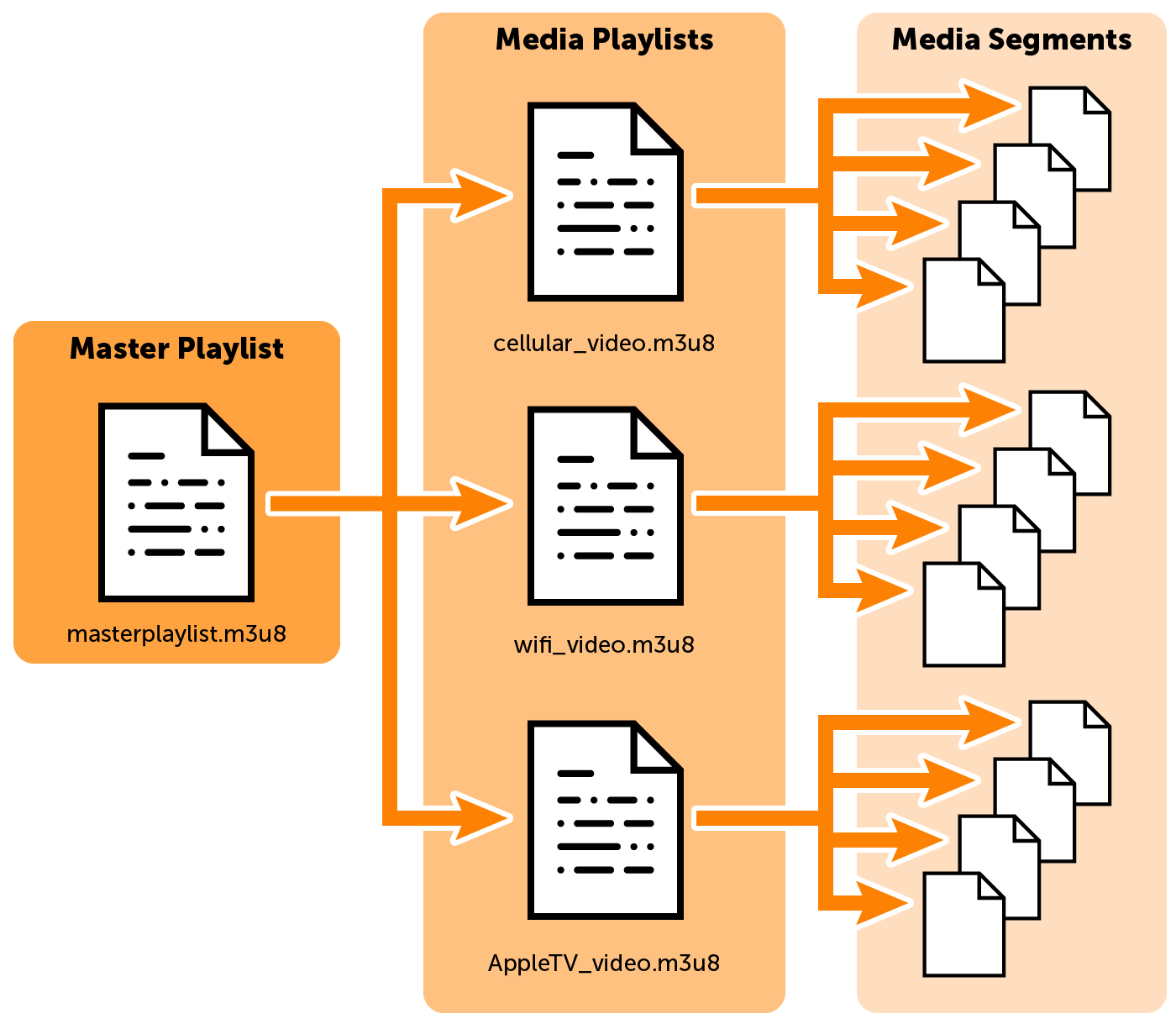
But now we have another problem, how will the player acknowledge this protocol? How many renditions do we own? or how many segments does the media have? To answer these questions a text file format is introduced, known as a manifest, which contains all the information for the player to make decisions.

The whole process of creating multiple renditions, segmenting media by time, and creating a manifest describing this scheme is known as packaging. HLS is one such packaging format.[^1]
### HLS
Developed by Apple, HLS is a protocol for streaming live video content over the internet. HLS is short for HTTP Live Streaming.
You take one big video file and break it up into small segments that can be anywhere from 2-12 seconds. So if you have a two-hour-long video, broken up into 10-second segments, you would have 720 segments.
Each segment is a file that ends with `.ts`. They are usually numbered sequentially so you get a directory that looks like this:
```plaintext
segments/
00001.ts
00002.ts
00003.ts
00004.ts
```
The player will download and play each segment as the user is streaming. And the player will keep a buffer of segments in case it loses network connection later.[^2]
### Transcoding and FFmpeg
To optimize the viewing experience across a variety of devices and connection speeds, you’ll need a transcoder built using `ffmpeg`.
Transcoding allows you to create multiple files from a single source through the process of transrating, transizing and trasmuxing.
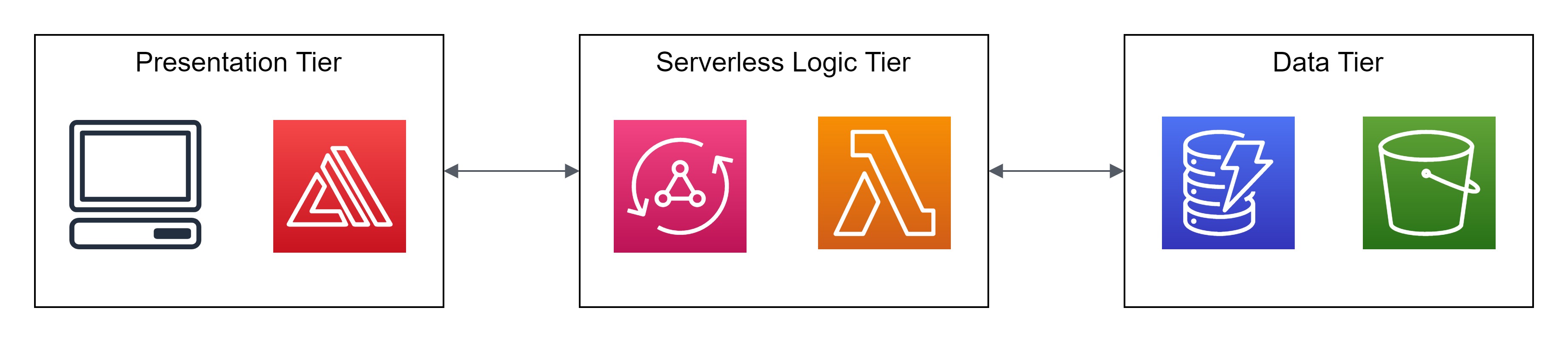
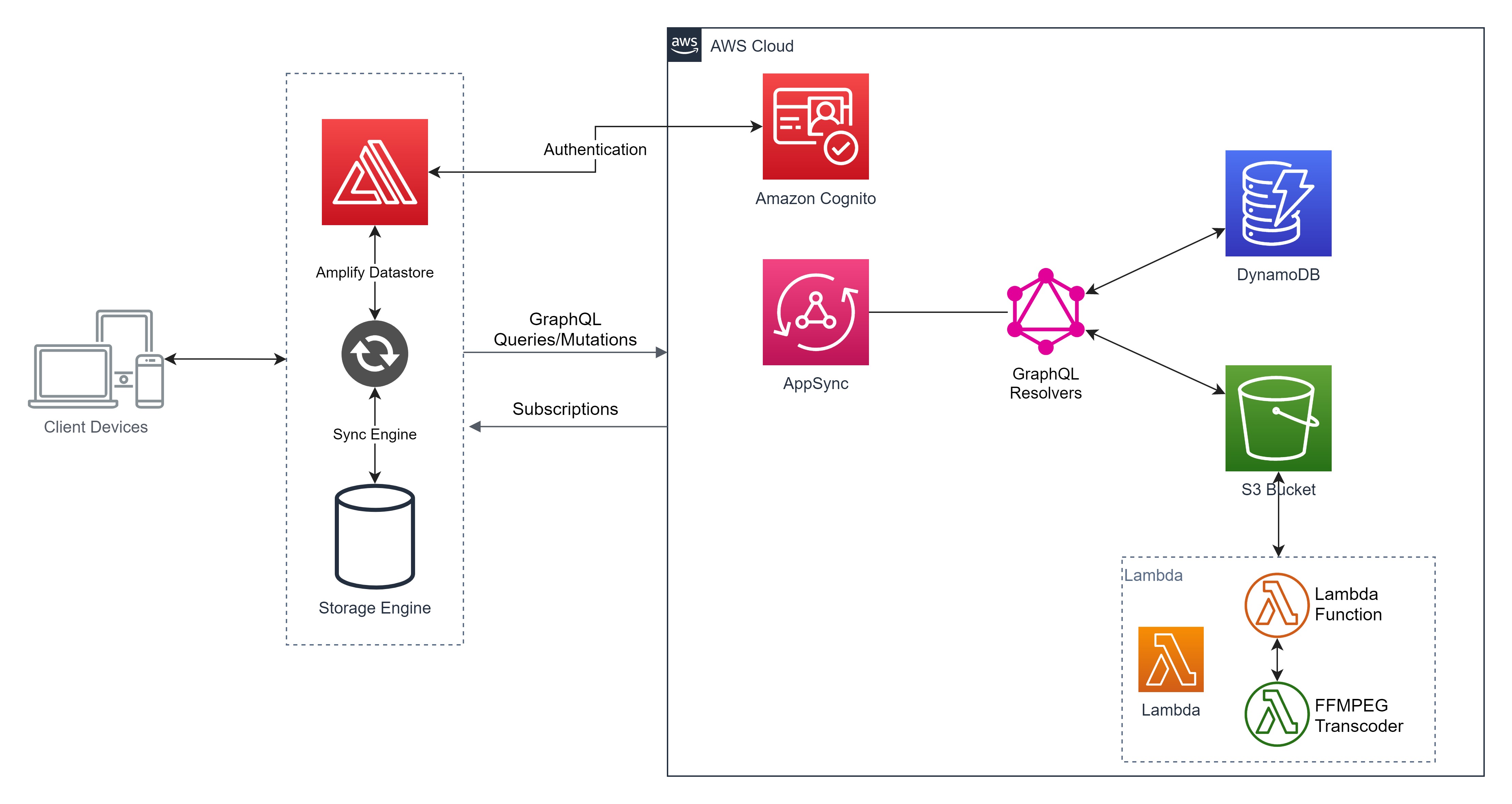
## Architecture Diagrams
---
## Setup
### Prerequisites
- An activated AWS account
- ReactJS ^17.0.2
- NodeJS ^14.0
- npm ^7.0
- Git ^2.22
- Python ^3.8
- FFmpeg
### Install and configure the Amplify CLI
```bash
npm install -g @aws-amplify/cli
amplify configure
```
For complete configuration instructions, refer official Amplify Framework Docs[^3].
### Clone GitHub repository and add dependencies
```bash
git clone https://github.com/chinmaykunkikar/vide-amplify.git
cd vide-amplify
npm install
```
### Initialize Amplify project
```bash
amplify init
```
Output
Note: It is recommended to run this command from the root of your app directory
? Do you want to use an existing environment? Yes
? Choose the environment you would like to use: master
? Choose your default editor: Visual Studio Code
Using default provider awscloudformation
? Select the authentication method you want to use: AWS profile
? Please choose the profile you want to use: default
√ Initialized provider successfully.
### Deploy the services to AWS
```bash
amplify push
```
Once all the resources are deployed to the cloud, make sure the `src/aws-exports.js` file is generated.
To view deployed services, go to amplify console by running the following command: `amplify console` and select ~~_Amplify Admin UI_~~ _Amplify Studio_.
### Run the project
```bash
npm start
```
Open [localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) on your browser.
[^1]: https://howvideo.works/#packaging
[^2]: https://howvideo.works/#hls
[^3]: https://docs.amplify.aws/