https://github.com/chltjdrhd777/gitip
⚙️ CLI tool for easy GitHub workflow
https://github.com/chltjdrhd777/gitip
github github-api typescript-library
Last synced: about 13 hours ago
JSON representation
⚙️ CLI tool for easy GitHub workflow
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/chltjdrhd777/gitip
- Owner: chltjdrhd777
- Created: 2024-06-03T22:28:51.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-07-19T12:33:43.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-10-29T05:23:21.895Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: github, github-api, typescript-library
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://www.npmjs.com/package/gitip
- Size: 722 KB
- Stars: 7
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# 🌟 **gitip** 🌟
✨ A handy CLI tool to manage GitHub issues & pull requests with ease ✨
## 🚀 **Getting Started**
### Installation
```sh
# Install globally
npm install gitip -g
gitip
# Or run directly with npx
npx gitip
```
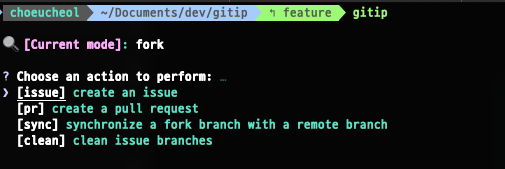
### Usage
```sh
1. Selection mode
gitip
2. Quick command mode
gitip i # or gitip issue
gitip p # or gitip pr
gitip s # or gitip sync
gitip c # or gitip clean
```
## 📋 **Environment Setup**
### 1. Environment Configuration
By default, this tool operates in the **fork repo system** mode. ✨
If you prefer to use the **origin repo system** mode, simply include the `ORIGIN_REPO_OWNER` variable in your `.env` file. When `ORIGIN_REPO_OWNER` is detected, the tool will automatically switch to **origin repo system** mode, allowing you to interact directly with the original repository. 🚀
> - `fork repo system` = manage issues and pull requests in a **forked repository**
> - `origin repo system` = manage issues and pull requests directly in the **original repository**
---
## 🔧 Example Configurations
### 🔄 Environment Priority Loading
This tool determines which `.env` file to load based on the following priority order:
1. `.env.local`
2. `.env.test`
3. `.env.development`
4. `.env.production`
5. Any other `.env.*` file (e.g., `.env.staging`, `.env.custom`)
6. `.env`
If multiple `.env` files are present, the file with the highest priority will be loaded.
> 💡 If you want to initialize the environment variables required, It is recommended to use the `init` command.
Please refer to the [**Commands**](#commands) section for more information.
---
### 🔄 Fork Repo System Configuration
Use the following setup for working with a **forked repository**:
```env
GIT_ACCESS_TOKEN=your-github-access-token
FORK_REPO_OWNER=fork-repo-owner-name
UPSTREAM_REPO_OWNER=upstream-repo-owner-name
REPO_NAME=repository-name
DEFAULT_BRANCH_NAME=default-branch-name
TEMPLATE_TITLE_PLACEHOLDER=(optional) issue template title placeholder
```
---
### 🔗 Origin Repo System Configuration
Use the following setup for working directly with the **original repository**:
```env
GIT_ACCESS_TOKEN=your-github-access-token
ORIGIN_REPO_OWNER=origin-repo-owner-name
REPO_NAME=repository-name
DEFAULT_BRANCH_NAME=default-branch-name
TEMPLATE_TITLE_PLACEHOLDER=(optional) issue template title placeholder
```
---
## 📝 Notes
- ✅ If the `ORIGIN_REPO_OWNER` variable is present in the `.env` file, **gitip automatically switches to origin repo system mode**.
- 🚫 If `ORIGIN_REPO_OWNER` is missing, the tool defaults to **fork repo system mode**.
- 🔍 The tool checks for `.env` files in the current directory and loads them based on the priority described above.
- ⚠️ Ensure all required variables are included in the selected `.env` file to avoid runtime errors.
### 3. Issue Templates
This tool uses GitHub issue templates. If a template isn't available, the default template will be used. To use a specific template, set the `TEMPLATE_TITLE_PLACEHOLDER` variable in your `.env` file.

## ✨ **Features**
### 🖊️ 1. Create an Issue
- Easily create GitHub issues with just a few steps.


### 📑 2. Create a Pull Request
[Prerequisite]
1. Commit your changes.
2. Select "Create a pull request."
- The pull request title is automatically suggested based on your latest commit message. However, only commits with conventional prefixes (like `feat:`, `test:`, `fix:`, etc.) will be extracted. For commits without these prefixes, you'll need to enter the title manually.
- Related issues are automatically closed when the pull request is merged (if the base branch is the default branch).

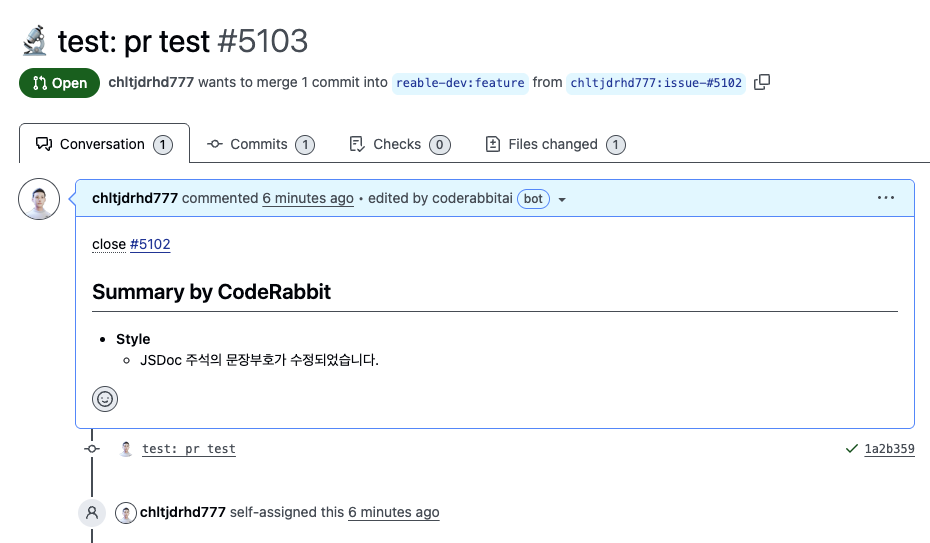
> [!NOTE]
> To use the "close" keyword for related issues, the base branch must be the default branch.

### 🔄 3. Synchronize Fork with Origin
Keep your fork updated with the origin branch effortlessly.
**😭 Manual Method (Not Recommended)**:

**☺️ Recommended Method (with gitip sync)**

### 🗑️ 4. Clean Up Unused Issue Branches
Remove unused branches locally and remotely with ease.
#### 1. Local Debris:

#### 2. Fork Debris:

#### 3. Cleaned State:


## 📜 **CLI Commands**
### General Options:
- **`-o, --origin`**: Use origin repository (default is fork).
- **`-v, --version`**: Display the current version.
- **`-h, --help`**: Show help message.
### Commands:
#### **`init`**
- Initialize default `.env` file with required environment variables.
- This command will create or update the `env` file in your current directory.
- **Usage**: `gitip init`
#### **`issue` | `i`**
- Manage GitHub issues: Create, update, or retrieve issues.
- **Usage**: `gitip i`
#### **`pr` | `p`**
- Manage GitHub pull requests: Create, update, or list pull requests.
- **Usage**: `gitip p`
#### **`sync` | `s`**
- Synchronize your fork with the origin repository.
- **Usage**: `gitip s`
#### **`clean` | `c`**
- Remove unused branches locally or remotely.
- **Usage**: `gitip c`
## 💡 **Pro Tips**
- Use the `TEMPLATE_TITLE_PLACEHOLDER` environment variable to customize your issue titles.
- Keep your `.env` files updated for both fork and origin systems.
Enjoy managing your GitHub repositories with **gitip**! 😊