https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop
Probabilistic programming framework that facilitates objective model selection for time-varying parameter models.
https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop
anomaly-detection bayesian-inference model-selection probabilistic-programming time-series-analysis
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Probabilistic programming framework that facilitates objective model selection for time-varying parameter models.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop
- Owner: christophmark
- License: mit
- Created: 2015-08-27T08:11:41.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-19T16:42:44.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-30T14:11:21.482Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: anomaly-detection, bayesian-inference, model-selection, probabilistic-programming, time-series-analysis
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://bayesloop.com
- Size: 11.1 MB
- Stars: 157
- Watchers: 12
- Forks: 28
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-python-data-science - bayesloop - Probabilistic programming framework that facilitates objective model selection for time-varying parameter models. (Time Series / NLP)
- awesome-meteo - bayesloop - varying parameters and model selection based on Bayesian inference. (Uncategorized / Uncategorized)
- fintech-awesome-libraries - bayesloop - Probabilistic programming framework that facilitates objective model selection for time-varying parameter models. (Date and Time / Automatic Plotting)
- awesome-python-data-science - bayesloop - Probabilistic programming framework that facilitates objective model selection for time-varying parameter models. (Time Series / Others)
README
[](http://bayesloop.com)
[](https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop/actions/workflows/test.yml)
[](http://docs.bayesloop.com)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/christophmark/bayesloop)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/41474112)
Time series analysis today is an important cornerstone of quantitative science in many disciplines, including natural and life sciences as well as economics and social sciences. Regarding diverse phenomena like tumor cell migration, brain activity and stock trading, a similarity of these complex systems becomes apparent: the observable data we measure – cell migration paths, neuron spike rates and stock prices – are the result of a multitude of underlying processes that act over a broad range of spatial and temporal scales. It is thus to expect that the statistical properties of these systems are not constant, but themselves show stochastic or deterministic dynamics of their own. Time series models used to understand the dynamics of complex systems therefore have to account for temporal changes of the models' parameters.
*bayesloop* is a python module that focuses on fitting time series models with time-varying parameters and model selection based on [Bayesian inference](https://cocosci.berkeley.edu/tom/papers/tutorial.pdf). Instead of relying on [MCMC methods](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~arnaud/andrieu_defreitas_doucet_jordan_intromontecarlomachinelearning.pdf), *bayesloop* uses a grid-based approach to evaluate probability distributions, allowing for an efficient approximation of the [marginal likelihood (evidence)](http://alumni.media.mit.edu/~tpminka/statlearn/demo/). The marginal likelihood represents a powerful tool to objectively compare different models and/or optimize the hyper-parameters of hierarchical models. To avoid the [curse of dimensionality](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curse_of_dimensionality) when analyzing time series models with time-varying parameters, *bayesloop* employs a sequential inference algorithm that is based on the [forward-backward-algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forward%E2%80%93backward_algorithm) used in [Hidden Markov models](http://www.cs.sjsu.edu/~stamp/RUA/HMM.pdf). Here, the relevant parameter spaces are kept low-dimensional by processing time series data step by step. The module covers a large class of time series models and is easily extensible.
*bayesloop* has been successfully employed in cancer research (studying the migration paths of invasive tumor cells), financial risk assessment, climate research and accident analysis. For a detailed description of these applications, see the following articles:
**Bayesian model selection for complex dynamic systems**
Mark C., Metzner C., Lautscham L., Strissel P.L., Strick R. and Fabry B.
[*Nature Communications 9:1803 (2018)*](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-04241-5)
**Superstatistical analysis and modelling of heterogeneous random walks**
Metzner C., Mark C., Steinwachs J., Lautscham L., Stadler F. and Fabry B.
[*Nature Communications 6:7516 (2015)*](https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms8516)
## Features
* infer time-varying parameters from time series data
* compare hypotheses about parameter dynamics (model evidence)
* create custom models based on SymPy and SciPy
* straight-forward handling of missing data points
* predict future parameter values
* detect change-points and structural breaks in time series data
* employ model selection to online data streams
## Getting started
For a comprehensive introduction and overview of the main features that *bayesloop* provides, see the [documentation](http://docs.bayesloop.com).
The following code provides a minimal example of an analysis carried out using *bayesloop*. The data here consists of the number of coal mining disasters in the UK per year from 1851 to 1962 (see this [article](http://www.dima.unige.it/~riccomag/Teaching/ProcessiStocastici/coal-mining-disaster-original%20paper.pdf) for further information).
```python
import bayesloop as bl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
S = bl.HyperStudy() # start new data study
S.loadExampleData() # load data array
# observed number of disasters is modeled by Poisson distribution
L = bl.om.Poisson('rate')
# disaster rate itself may change gradually over time
T = bl.tm.GaussianRandomWalk('sigma', bl.cint(0, 1.0, 20), target='rate')
S.set(L, T)
S.fit() # inference
# plot data together with inferred parameter evolution
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
plt.subplot2grid((1, 3), (0, 0), colspan=2)
plt.xlim([1852, 1961])
plt.bar(S.rawTimestamps, S.rawData, align='center', facecolor='r', alpha=.5)
S.plot('rate')
plt.xlabel('year')
# plot hyper-parameter distribution
plt.subplot2grid((1, 3), (0, 2))
plt.xlim([0, 1])
S.plot('sigma', facecolor='g', alpha=0.7, lw=1, edgecolor='k')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
```
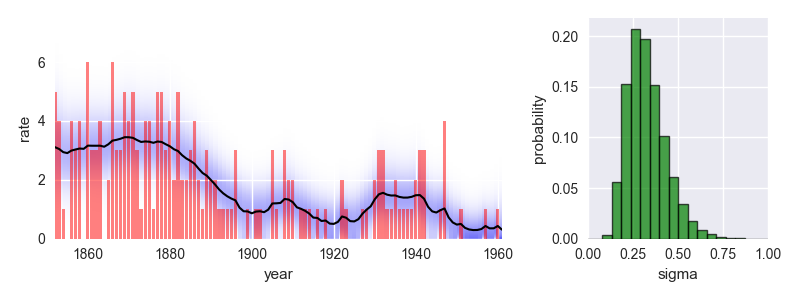
This analysis indicates a significant improvement of safety conditions between 1880 and 1900. Check out the [documentation](http://docs.bayesloop.com) for further insights!
## Installation
The easiest way to install the latest release version of *bayesloop* is via `pip`:
```
pip install bayesloop
```
Alternatively, a zipped version can be downloaded [here](https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop/releases). The module is installed by calling `python setup.py install`.
### Development version
The latest development version of *bayesloop* can be installed from the master branch using pip (requires git):
```
pip install git+https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop
```
Alternatively, use this [zipped version](https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop/zipball/master) or clone the repository.
## Dependencies
*bayesloop* is tested on Python 3.8. It depends on NumPy, SciPy, SymPy, matplotlib, tqdm and cloudpickle. All except the last two are already included in the [Anaconda distribution](https://www.continuum.io/downloads) of Python. Windows users may also take advantage of pre-compiled binaries for all dependencies, which can be found at [Christoph Gohlke's page](http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/).
## Optional dependencies
*bayesloop* supports multiprocessing for computationally expensive analyses, based on the [pathos](https://github.com/uqfoundation/pathos) module. The latest version can be obtained directly from GitHub using pip (requires git):
```
pip install git+https://github.com/uqfoundation/pathos
```
**Note**: Windows users need to install a C compiler *before* installing pathos. One possible solution for 64bit systems is to install [Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 SP1 Redistributable Package (x64)](http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/confirmation.aspx?id=2092) and [Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler for Python 2.7](http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=44266).
## License
[The MIT License (MIT)](https://github.com/christophmark/bayesloop/blob/master/LICENSE)
If you have any further questions, suggestions or comments, do not hesitate to contact me: bayesloop@gmail.com