Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack
Elijah OpenStack integration
https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack
Last synced: 5 days ago
JSON representation
Elijah OpenStack integration
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack
- Owner: cmusatyalab
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2013-08-13T17:07:33.000Z (over 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-01-04T21:14:08.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-03T15:04:37.831Z (3 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://elijah.cs.cmu.edu/
- Size: 8.17 MB
- Stars: 27
- Watchers: 13
- Forks: 26
- Open Issues: 10
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# OpenStack++ - An OpenStack extension for Cloudlet support
A cloudlet is a new architectural element that arises from the convergence of
mobile computing and cloud computing. It represents the middle tier of a
3-tier hierarchy: mobile device - cloudlet - cloud. A cloudlet can be
viewed as a "data center in a box" whose goal is to "bring the cloud closer".
Copyright (C) 2012-2017 Carnegie Mellon University This is a developing project
and some features might not be stable yet. Please visit our website at [Elijah
page](http://elijah.cs.cmu.edu/).
## License
All source code, documentation, and related artifacts associated with the
cloudlet open source project are licensed under the [Apache License, Version
2.0](http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html).
## Tested Platform
We have tested OpenStack++ on __Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 64-bit__ using the __OpenStack Kilo release__.
## Installation (Using [Ansible](http://docs.ansible.com/))
### Step 1. Become root
```sh
$ sudo -i
```
### Step 2. Prepare the environment
Prepare Ubuntu 14.04 64-bit:
```sh
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get upgrade
```
### Step 3. Install [Ansible](http://docs.ansible.com/)
```sh
$ apt-get install software-properties-common
$ apt-add-repository -y ppa:ansible/ansible
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get install -y ansible git
```
### Step 4. Pull down the elijah-openstack repository
```sh
$ cd ~
$ git clone https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack
$ cd ~/elijah-openstack/ansible
```
### Step 5. Configure the [Ansible](http://docs.ansible.com/) scripts
#### Configure OpenStack variables
Ensure the variables defined in `roles/openstack-controller/vars/main.yml` and `roles/openstack-compute/vars/main.yml` are satisfactory.
> * Specifically you should ensure that the interfaces defined by `pub_iface` and `flat_iface` are valid. `pub_iface` is used by the physical machine to reach the internet. `flat_iface` is used by OpenStack in order to communicate with the virtual machines running on the host.
> * If you only have a single network interface, make sure that `flat_iface` is something unique as a virtual interface with that name will be created when the `one_nic` variable in openstack-kilo.yaml is `True`. **Please note that this virtual interface is not persistent and will be lost after reboot. To remedy this, you can run the entire Ansible playbook after rebooting which will recreate the dummy interface and restart the necessary nova services.**
> * By default, the script is setup to install all OpenStack components on a single node that has a single NIC card. If you have two network interface cards, set `one_nic` to `False` in `openstack-kilo.yaml`. If you are setting up a multi-node cluster where the compute node will reside on a separate host(s) from the controller, you must configure additional hosts in the `hosts/inventory`, change `openstack-kilo.yaml` to reflect which hosts should be compute nodes, and ensure that the `single_node` variable is set to `False`. You will also need to change the controller IP and hostname in the `var/main.yml` to reflect those of the controller.
#### Configure cloudlet variables
Installation of the cloudlet library from https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-provisioning requires a local user/password. Ensure that these are properly reflected in `roles/cloudlet/vars/main.yml`. You should also ensure that password login is enable in your ssh configuration in `/etc/ssh/sshd_config` (#PasswordAuthentication yes)
### Step 6. Launch ansible playbook to install OpenStack, the clouldet library, and the OpenStack++ extensions
```sh
$ cd ~/elijah-openstack/ansible
$ ansible-playbook -i ./hosts openstackpp.yaml
```
### Step 7. Create the initial private network
```sh
$ source ~/admin-openrc.sh
$ nova network-create --fixed-range-v4 --fixed-cidr --bridge --bridge-interface
```
**NOTE: The bridge name you specify here will be created by nova, so this can be any name. The bridge-interface however, must correspond to the name of the actual interface that was specified as the flat_iface in the Ansible variables.**
For example, to create a private 10.11.12.x network for VMs, with a bridge named br100, on the dummy flat interface called veth1:
```sh
$ nova network-create vmprivate --fixed-range-v4 10.11.12.0/24 --fixed-cidr 10.11.12.0/24 --bridge br100 --bridge-interface veth1
```
### Step 8. Create a pool of floating IP addresses
These can be assigned to VMs to allow public access to them.
```sh
$ nova floating-ip-bulk-create
```
### Step 9. Edit/create security group rules
In order to be able to access VM instances, you first need to edit the rules corresponding to the default security group or create a new security group and set of rules. From the 'Project' drop down menu at the left, select the 'Access & Security' panel. Under the 'Security Group' tab, you can then create a new security group or click the 'Manage Rules' button of the default security group. Once under the rules section, you can create rules for various types of traffic based on port/protocol and a CIDR range.
**NOTE: If you create a new security group, you must be sure to assign the VM that security group after launching it.**
## Cloudlet Gateway
You may optionally wish to install the Cloudlet Gateway which is a web server that launches cloudlet applications within VMs
and/or containers and sits behind an OpenVPN firewall to provide public access to VMs/containers running on OpenStack++. To install
the Cloudlet Gateway, please see the [README](https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack/tree/master/cloudlet-gateway)
## How to use
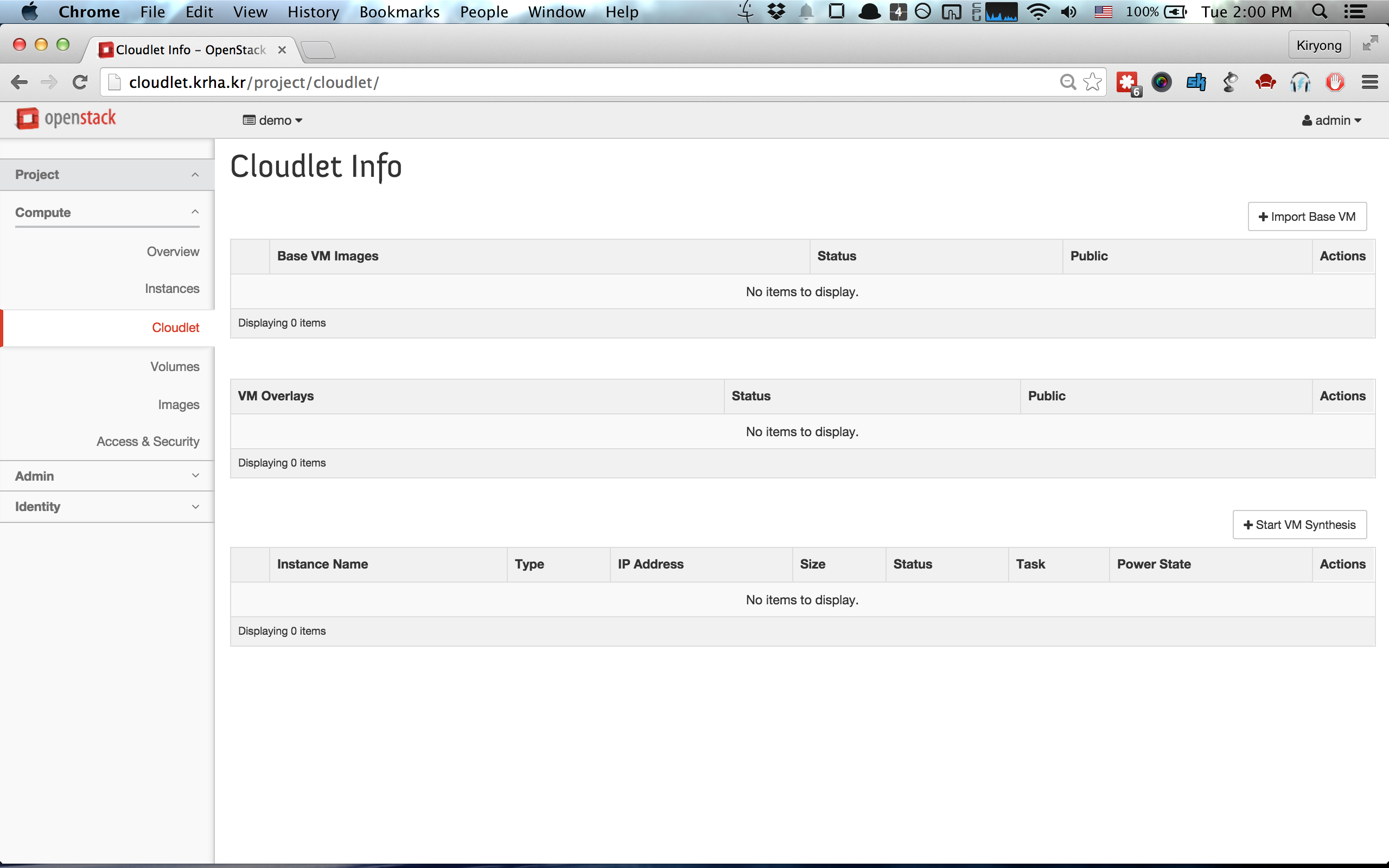
### 1. Check Installation
If the installation is successful, you will see a new panel on the project tab
as seen in the figure below. You can also check for the cloudlet extension by listing
the available OpenStack extensions using the standard [OpenStack
API](http://developer.openstack.org/api-ref-compute-v2.html#listExtensionsv2).
### 2. Import Base
Import a [Sample Base
VM](https://storage.cmusatyalab.org/cloudlet-vm/precise-hotplug-new.zip) using the
__[Import Base VM]__ button (This process may take a while). The zip file in the link above contains both disk
and memory snapshots of the vanilla Ubuntu distribution (VM's account:cloudlet, password: cloudlet). 
### 3. Resume VM
To resume a base VM, please use __[Resume Base VM]__ button atop the Base VM image
table. Initially, resuming Base VM can take a long time because the Base VM needs to be cached to
the compute node. 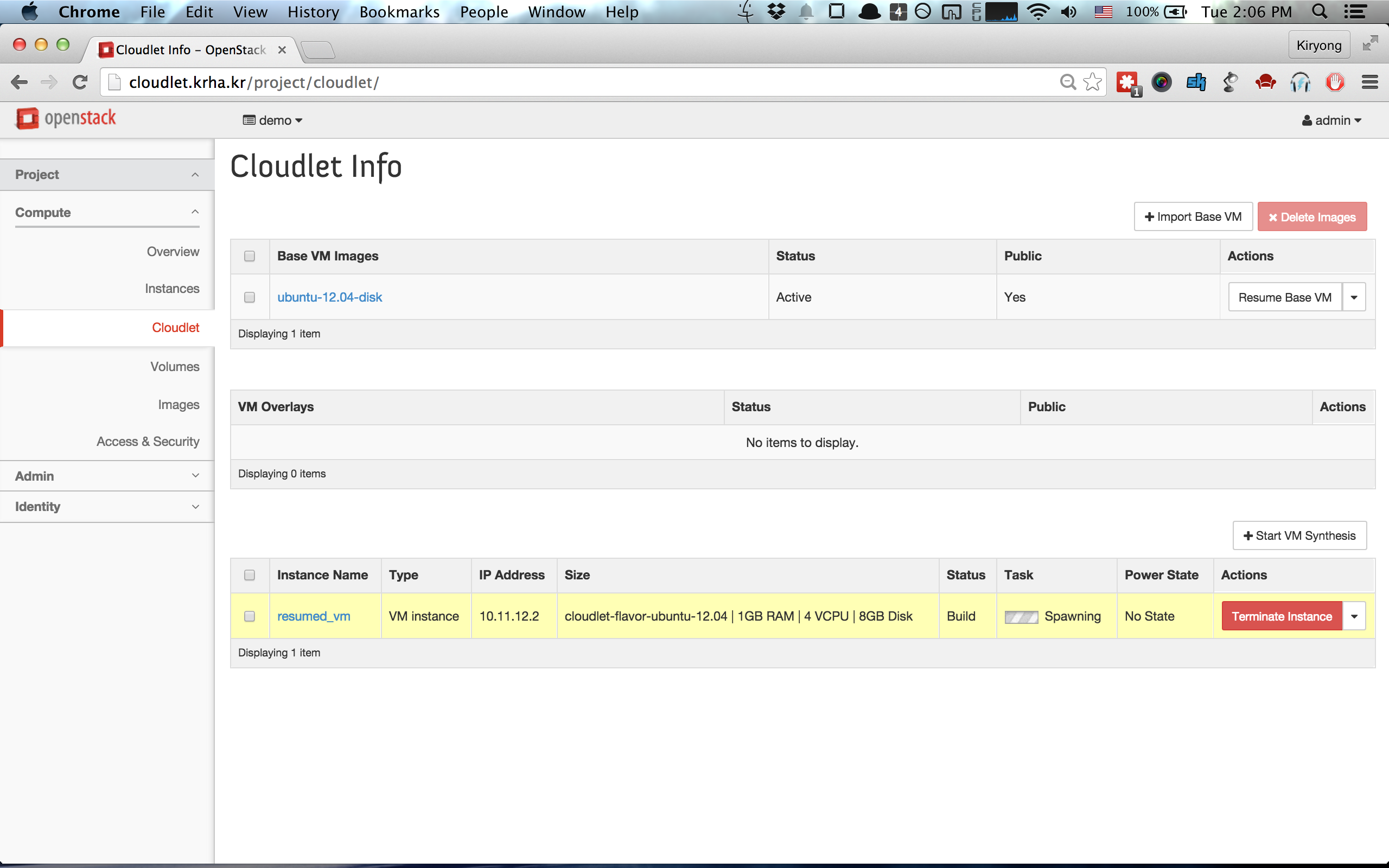
### 4. Create VM Overlay
Install application specific libraries and binaries on the resumed VM to customize the image.
Then use __[Create VM overlay]__ button when you ready to create a VM overlay from the base VM.
This will create a `VM overlay` which includes the compressed differences of the disk and memory snapshots with the base VM.

After the VM overlay is generated (this process may take a while), you
can download VM overlay using __[Download VM overlay]__ button.
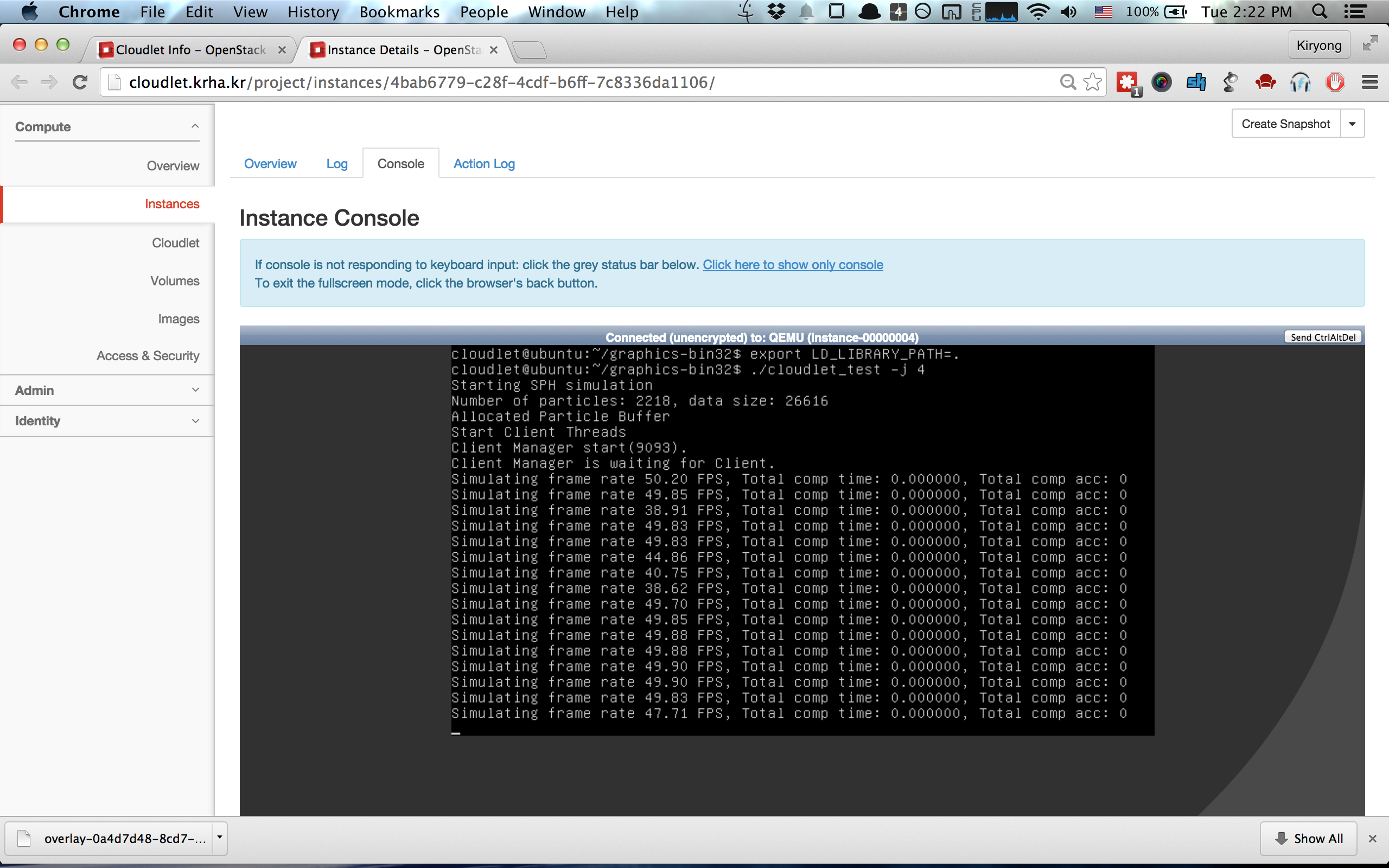
### 5. VM Synthesis
VM Synthesis is the instantiation of a VM instance by applying a VM overlay to an existing base VM image.
To perform VM synthesis, please use the __[Start VM Synthesis]__ button atop the Instance
table. You need to input a URL for your VM overlay. If you have created and
downloaded the VM overlay from the previous step, you can put that VM overlay on a separate Web
server and point at that URL for the VM overlay. Initially, VM synthesis can
be slow if the Base VM is not cached at the compute node. 
### 6. VM Handoff
To migrate a running VM instance to another OpenStack, please use __[VM Handoff]__
button atop the Action column of synthesized VM instance. This will ask for
credentials of the destination OpenStack as shown below. Although it
does not save any credential information, please use [a cloudlet command line
client](https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack/blob/master/client/cloudlet_client.py)
that accepts an auth-token instead of account/password if you don't want to transfer
account information. 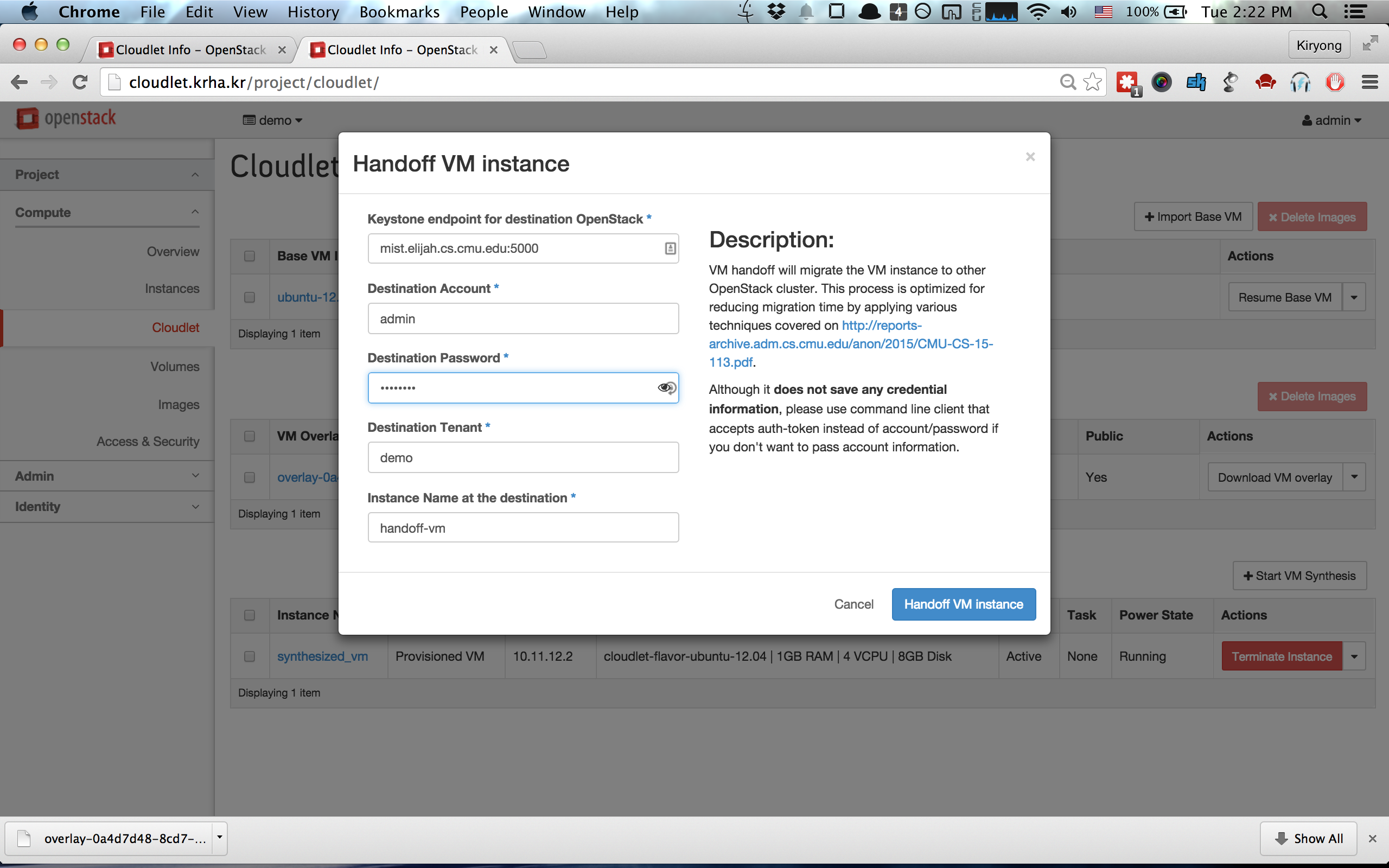
All the above steps can be done using the command line program at
[./client/cloudlet_client.py](https://github.com/cmusatyalab/elijah-openstack/blob/master/client/cloudlet_client.py)
## Troubleshooting
If you have any problems after installing OpenStack++ cloudlet extension, please follow
below steps to narrow the problem.
### Resumed VMs have incorrect IP address
When you resume a base VM you did not create (for example, the Ubuntu Precise image found here [Sample Base VM](https://storage.cmusatyalab.org/cloudlet-vm/precise-hotplug-new.zip) ) the network configuration may have been entirely different when the image was created. This can cause difficulty connecting to the VM. Soft rebooting the instance from the 'Project->Instances' panel should result in the proper IP addressed being assigned from the pool that was created when the `nova create-network` command was issued.