https://github.com/codait/flight-delay-notebooks
Analyzing flight delay and weather data using Elyra, IBM Data Asset Exchange, Kubeflow Pipelines and KFServing
https://github.com/codait/flight-delay-notebooks
codait data-science elyra jupyter jupyter-notebook jupyterlab kfserving kubeflow-pipelines machine-learning
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Analyzing flight delay and weather data using Elyra, IBM Data Asset Exchange, Kubeflow Pipelines and KFServing
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/codait/flight-delay-notebooks
- Owner: CODAIT
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-11-12T18:36:56.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-10-12T22:15:46.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-06T23:17:17.569Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: codait, data-science, elyra, jupyter, jupyter-notebook, jupyterlab, kfserving, kubeflow-pipelines, machine-learning
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.67 MB
- Stars: 15
- Watchers: 16
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Analyzing flight delay and weather data using Elyra, Kubeflow Pipelines and KFServing
This repository contains a set of Python scripts and Jupyter notebooks that analyze and predict flight delays. The datasets are hosted on the [IBM Developer Data Asset Exchange](https://ibm.biz/data-exchange).
We use [Elyra](https://github.com/elyra-ai/elyra) to create a pipeline that can be executed locally or using a [Kubeflow Pipelines](https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/pipelines/overview/pipelines-overview/) runtime. This pipeline:
* Loads the datasets
* Pre-processes the datasets
* Performs data merging and feature extraction
* Analyzes and visualizes the processed dataset
* Trains and evaluates machine learning models for predicting delayed flights, using features about flights as well as related weather features
* _Optionally_ deploys the trained model to Kubeflow Serving

### Configuring the local development environment
It's highly recommended to create a dedicated and consistent Python environment for running the notebooks in this repository:
1. Install [Anaconda](https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/)
or [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html)
1. Navigate to your local copy of this repository.
1. Create an Anaconda environment from the `yaml` file in the repository:
```console
$ conda env create -f flight-delays-env.yaml
```
1. Activate the new environment:
```console
$ conda activate flight-delays-env
```
1. If running JupyterLab and Elyra for the first time, build the extensions:
```console
$ jupyter lab build
```
1. Launch JupyterLab:
```console
$ jupyter lab
```
### Configuring a Kubeflow Pipeline runtime
[Elyra's Notebook pipeline visual editor](https://elyra.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting_started/overview.html#notebook-pipelines-visual-editor)
currently supports running these pipelines in a Kubeflow Pipeline runtime. If required, these are
[the steps to install a local deployment of KFP](https://elyra.readthedocs.io/en/latest/recipes/deploying-kubeflow-locally-for-dev.html).
After installing your Kubeflow Pipeline runtime, use the command below (with proper updates) to configure the new
KFP runtime with Elyra.
```bash
elyra-metadata install runtimes --replace=true \
--schema_name=kfp \
--name=kfp_runtime \
--display_name="Kubeflow Pipeline Runtime" \
--api_endpoint=http://[host]:[api port]/pipeline \
--cos_endpoint=http://[host]:[cos port] \
--cos_username=[cos username] \
--cos_password=[cos password] \
--cos_bucket=flights
```
**Note:** The cloud object storage endpoint above assumes a local minio object storage but other cloud-based object storage services could be configured and used in this scenario.
If using the default minio storage - following the local Kubeflow installation instructions above - the arguments should be `--cos_endpoint=http://minio-service:9000`, `--cos_username=minio`, `--cos_password=minio123`. The api endpoint for local Kubeflow Pipelines would then be `--api_endpoint=http://127.0.0.1:31380/pipeline`.
**Don't forget to setup port-forwarding for the KFP ML Pipelines API service and Minio service as per the above instructions.**
## Elyra Notebook pipelines
Elyra provides a visual editor for building Notebook-based AI pipelines, simplifying the conversion of
multiple notebooks into batch jobs or workflows. By leveraging cloud-based resources to run their
experiments faster, the data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI developers are then more productive,
allowing them to spend their time using their technical skills.
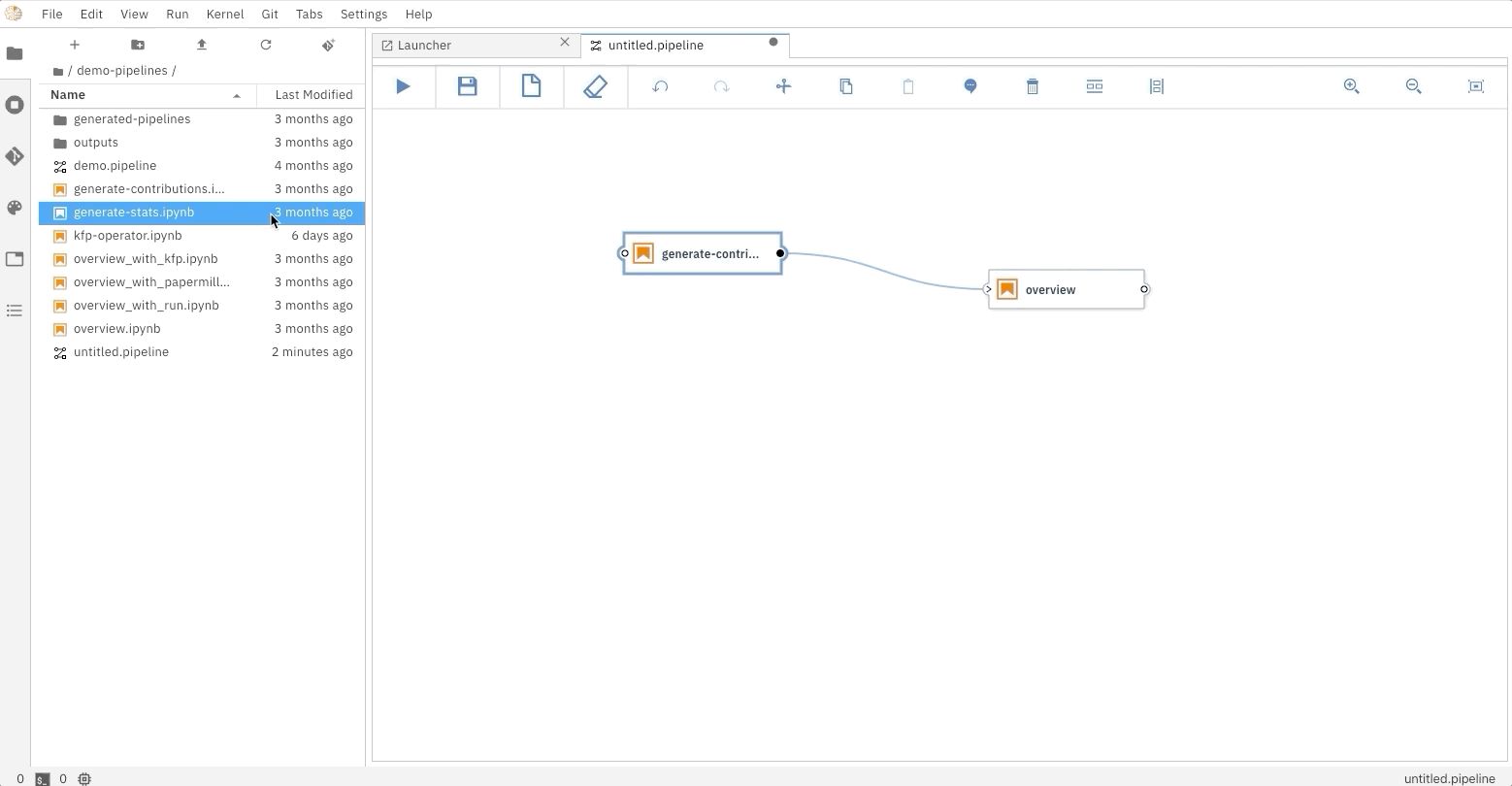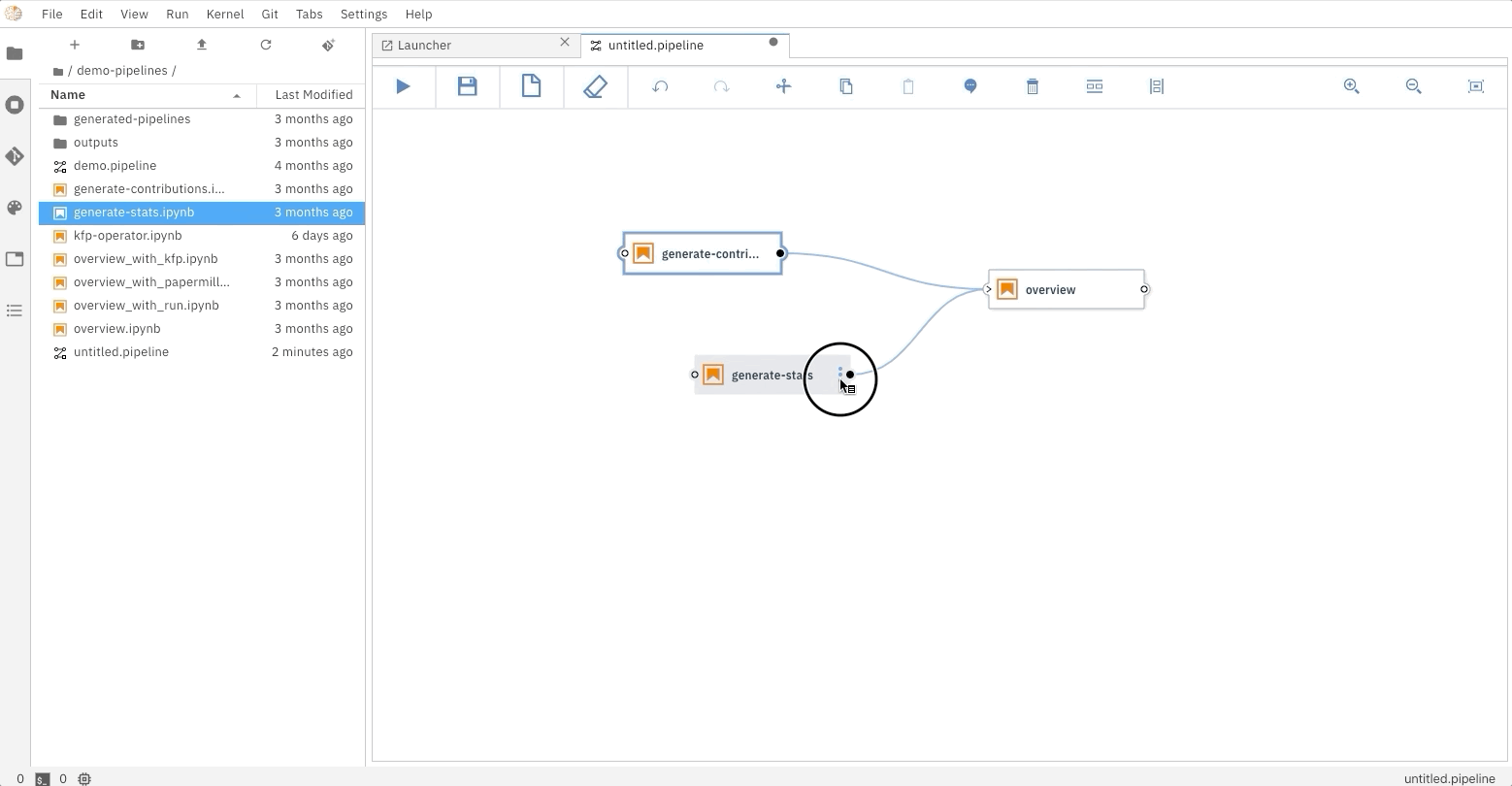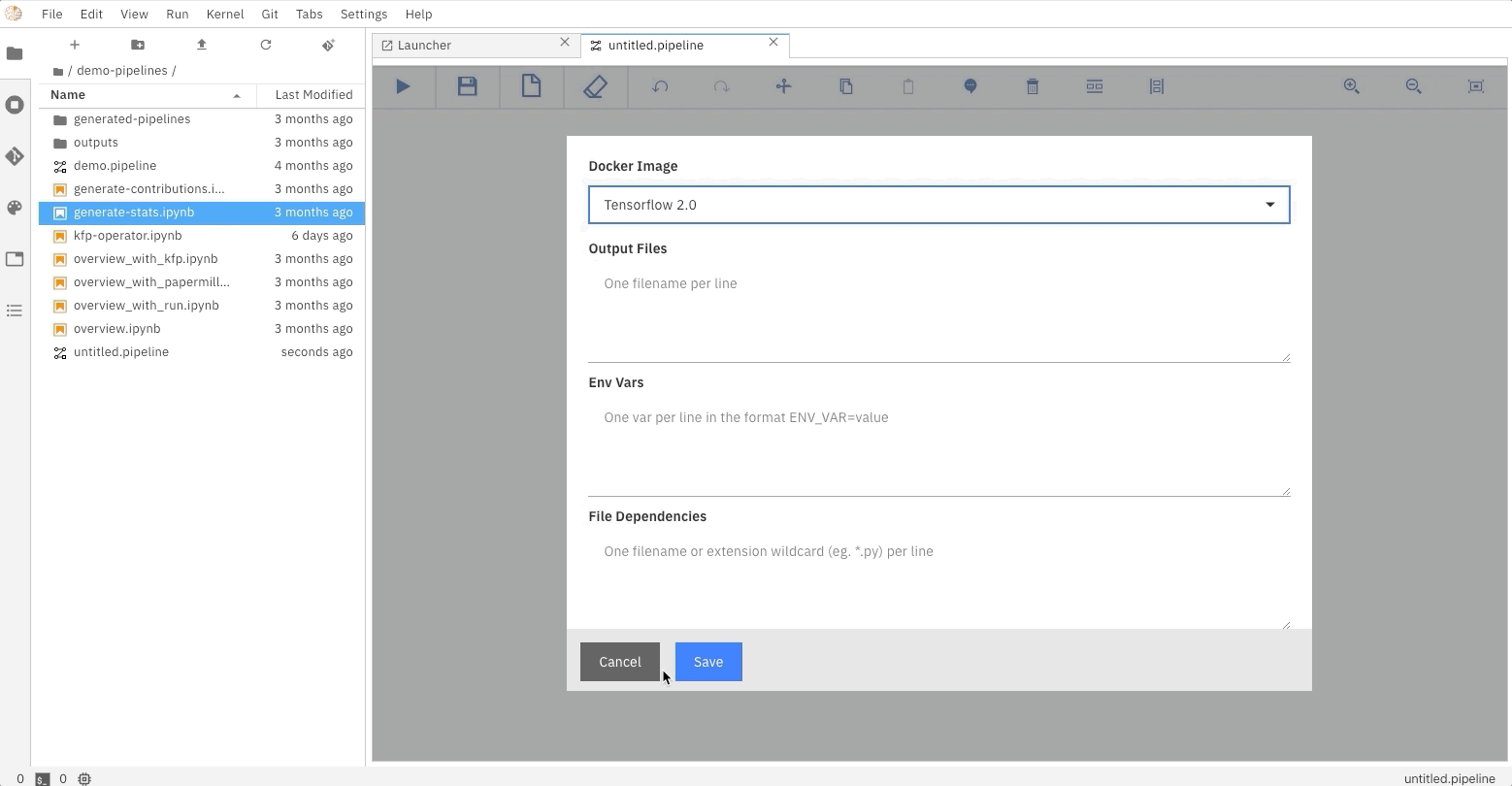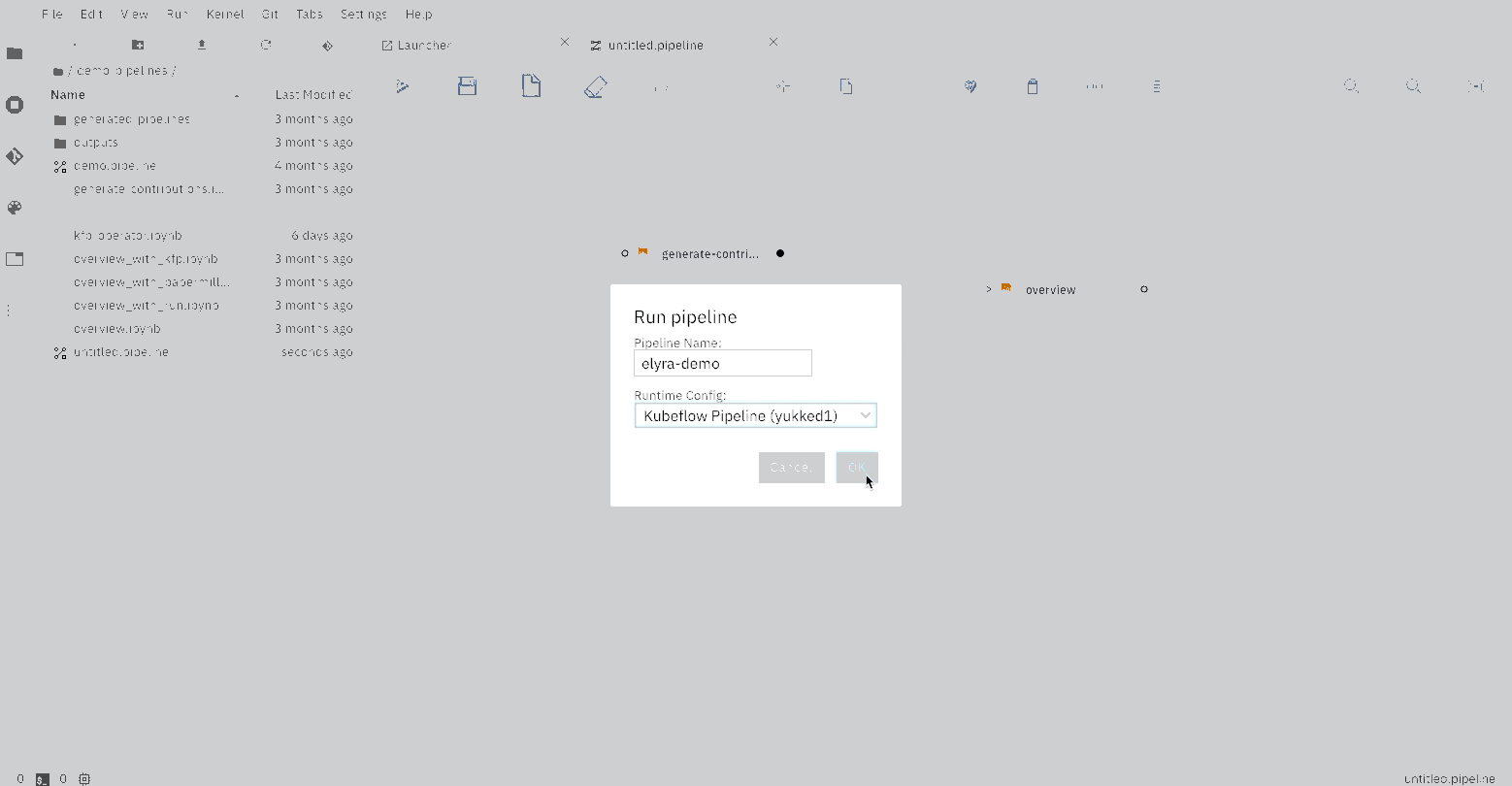
### Running the Elyra pipeline
The Elyra pipeline `flight_delays.pipeline`, which is located in the `pipelines` directory, can be run by clicking
on the `play` button as seen on the image above. The `submit` dialog will request two inputs from the user: a name
for the pipeline and a runtime to use while executing the pipeline.
The list of available runtimes comes from the registered Kubeflow Pipelines runtimes documented above and includes a `Run in-place locally` option for local execution.
#### Local execution
If running locally, the notebooks are executed and updated in-place. You can track the progress in the terminal screen where you ran `jupyter lab`. The downloaded and processed datasets will be available locally in `notebooks/data` in this case.
#### Kubeflow Pipelines execution
After submitting the pipeline to Kubeflow Pipelines, Elyra will show a dialog with a direct link to where the experiment is being executed on Kubeflow Piplines.
The user can access the pipelines, and respective experiment runs, via the `api_endpoint` of the Kubeflow Pipelines
runtime (e.g. `http://[host]:[port]/pipeline`)

The output from the executed experiments are then available in the associated `object storage`
and the executed notebooks are available as native `.ipynb` notebooks and also in `html` format
to facilitate the visualization and sharing of the results.

### Running the Elyra pipeline with model deployment to Kubeflow Serving
Please follow the [instructions](kfserving.md) for running the pipeline `flight_delays_with_deployment.pipeline`, which adds a node at the end of the pipeline for deploying the model to [KFServing](https://www.kubeflow.org/docs/components/serving/kfserving/).
### References
Find more project details on [Elyra's GitHub](https://github.com/elyra-ai/elyra) or watching the
[Elyra demo](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nj0yga6T4U8).