https://github.com/codelion/optillm
Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs
https://github.com/codelion/optillm
agent agentic-ai agentic-framework agentic-workflow agents api-gateway chain-of-thought genai large-language-models llm llm-inference llmapi mixture-of-experts moa monte-carlo-tree-search openai openai-api optimization prompt-engineering proxy-server
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/codelion/optillm
- Owner: codelion
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-08-22T19:46:07.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-06-02T08:59:15.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-02T20:07:06.154Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: agent, agentic-ai, agentic-framework, agentic-workflow, agents, api-gateway, chain-of-thought, genai, large-language-models, llm, llm-inference, llmapi, mixture-of-experts, moa, monte-carlo-tree-search, openai, openai-api, optimization, prompt-engineering, proxy-server
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.88 MB
- Stars: 2,469
- Watchers: 22
- Forks: 185
- Open Issues: 11
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- StarryDivineSky - codelion/optillm - Consistency 自我一致性,实施先进的自洽方法;Z3 Solver Z3 解算器,利用 Z3 定理证明器进行逻辑推理;R* Algorithm R*算法,实现 R* 算法来解决问题;LEAP,从几个示例中学习特定于任务的原则;Round Trip Optimization 往返优化,通过往返流程优化响应;Best of N Sampling 最佳 N 采样,生成多个响应并选择最佳的一个;Mixture of Agents 混合多个代理,结合多种批评的回应;Monte Carlo Tree Search 蒙特卡罗树搜索,使用 MCTS 在聊天响应中进行决策;prover-verifier game approach 证明者-验证者游戏(Prover-Verifier Games),在推理时应用证明者-验证者博弈方法;CoT Decoding CoT 解码,实现思路链解码以在没有明确提示的情况下引发推理;Entropy Decoding 熵解码,根据代币生成过程中的不确定性实现自适应采样。 (A01_文本生成_文本对话 / 大语言对话模型及数据)
- awesome-LLM-resources - optillm - of-the-art techniques that can improve the accuracy and performance of LLMs. (推理 Inference)
- awesome-ChatGPT-repositories - optillm - Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs (Prompts)
- awesome - codelion/optillm - Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs (Python)
README
# optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy which implements several state-of-the-art techniques that can improve the accuracy and performance of LLMs. The current focus is on implementing techniques that improve reasoning over coding, logical and mathematical queries.
It is possible to beat the frontier models using these techniques across diverse tasks by doing additional compute at inference time. A good example of how to combine such techniques together is the [CePO approach](optillm/cepo) from Cerebras.
[](https://huggingface.co/spaces/codelion/optillm)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1SpuUb8d9xAoTh32M-9wJsB50AOH54EaH?usp=sharing)
[](https://github.com/codelion/optillm/discussions)
## Installation
### Using pip
```bash
pip install optillm
optillm
2024-10-22 07:45:05,612 - INFO - Loaded plugin: privacy
2024-10-22 07:45:06,293 - INFO - Loaded plugin: memory
2024-10-22 07:45:06,293 - INFO - Starting server with approach: auto
```
### Using docker
```bash
docker pull ghcr.io/codelion/optillm:latest
docker run -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/codelion/optillm:latest
2024-10-22 07:45:05,612 - INFO - Loaded plugin: privacy
2024-10-22 07:45:06,293 - INFO - Loaded plugin: memory
2024-10-22 07:45:06,293 - INFO - Starting server with approach: auto
```
To use optillm without local inference and only as a proxy you can add the `-proxy` suffix.
```bash
docker pull ghcr.io/codelion/optillm:latest-proxy
```
### Install from source
Clone the repository with `git` and use `pip install` to setup the dependencies.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/codelion/optillm.git
cd optillm
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
We support all major LLM providers and models for inference. You need to set the correct environment variable and the proxy will pick the corresponding client.
| Provider | Required Environment Variables | Additional Notes |
|----------|-------------------------------|------------------|
| OptiLLM | `OPTILLM_API_KEY` | Uses the inbuilt local server for inference, supports logprobs and decoding techniques like `cot_decoding` & `entropy_decoding` |
| OpenAI | `OPENAI_API_KEY` | You can use this with any OpenAI compatible endpoint (e.g. OpenRouter) by setting the `base_url` |
| Cerebras | `CEREBRAS_API_KEY` | You can use this for fast inference with supported models, see [docs for details](https://inference-docs.cerebras.ai/introduction) |
| Azure OpenAI | `AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY`
`AZURE_API_VERSION`
`AZURE_API_BASE` | - |
| Azure OpenAI (Managed Identity) | `AZURE_API_VERSION`
`AZURE_API_BASE` | Login required using `az login`, see [docs for details](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/openai/how-to/managed-identity) |
| LiteLLM | depends on the model | See [docs for details](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers) |
You can then run the optillm proxy as follows.
```bash
python optillm.py
2024-09-06 07:57:14,191 - INFO - Starting server with approach: auto
2024-09-06 07:57:14,191 - INFO - Server configuration: {'approach': 'auto', 'mcts_simulations': 2, 'mcts_exploration': 0.2, 'mcts_depth': 1, 'best_of_n': 3, 'model': 'gpt-4o-mini', 'rstar_max_depth': 3, 'rstar_num_rollouts': 5, 'rstar_c': 1.4, 'base_url': ''}
* Serving Flask app 'optillm'
* Debug mode: off
2024-09-06 07:57:14,212 - INFO - WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8000
* Running on http://192.168.10.48:8000
2024-09-06 07:57:14,212 - INFO - Press CTRL+C to quit
```
## Usage
Once the proxy is running, you can use it as a drop in replacement for an OpenAI client by setting the `base_url` as `http://localhost:8000/v1`.
```python
import os
from openai import OpenAI
OPENAI_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
OPENAI_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8000/v1"
client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_KEY, base_url=OPENAI_BASE_URL)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="moa-gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a Python program to build an RL model to recite text from any position that the user provides, using only numpy."
}
],
temperature=0.2
)
print(response)
```
The code above applies to both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI, just remember to populate the `OPENAI_API_KEY` env variable with the proper key.
There are multiple ways to control the optimization techniques, they are applied in the follow order of preference:
- You can control the technique you use for optimization by prepending the slug to the model name `{slug}-model-name`. E.g. in the above code we are using `moa` or mixture of agents as the optimization approach. In the proxy logs you will see the following showing the `moa` is been used with the base model as `gpt-4o-mini`.
```bash
2024-09-06 08:35:32,597 - INFO - Using approach moa, with gpt-4o-mini
2024-09-06 08:35:35,358 - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2024-09-06 08:35:39,553 - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2024-09-06 08:35:44,795 - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2024-09-06 08:35:44,797 - INFO - 127.0.0.1 - - [06/Sep/2024 08:35:44] "POST /v1/chat/completions HTTP/1.1" 200 -
```
- Or, you can pass the slug in the `optillm_approach` field in the `extra_body`.
```bash
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{ "role": "user","content": "" }],
temperature=0.2,
extra_body={"optillm_approach": "bon|moa|mcts"}
)
```
- Or, you can just mention the approach in either your `system` or `user` prompt, within ` ` tags.
```bash
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{ "role": "user","content": "re2 How many r's are there in strawberry?" }],
temperature=0.2
)
```
> [!TIP]
> You can also combine different techniques either by using symbols `&` and `|`. When you use `&` the techniques are processed in the order from left to right in a pipeline
> with response from previous stage used as request to the next. While, with `|` we run all the requests in parallel and generate multiple responses that are returned as a list.
Please note that the convention described above works only when the optillm server has been started with inference approach set to `auto`. Otherwise, the `model` attribute in the client request must be set with the model name only.
We now suport all LLM providers (by wrapping around the [LiteLLM sdk](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/#litellm-python-sdk)). E.g. you can use the Gemini Flash model with `moa` by setting passing the api key in the environment variable `os.environ['GEMINI_API_KEY']` and then calling the model `moa-gemini/gemini-1.5-flash-002`. In the output you will then see that LiteLLM is being used to call the base model.
```bash
9:43:21 - LiteLLM:INFO: utils.py:2952 -
LiteLLM completion() model= gemini-1.5-flash-002; provider = gemini
2024-09-29 19:43:21,011 - INFO -
LiteLLM completion() model= gemini-1.5-flash-002; provider = gemini
2024-09-29 19:43:21,481 - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-1.5-flash-002:generateContent?key=[redacted] "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
19:43:21 - LiteLLM:INFO: utils.py:988 - Wrapper: Completed Call, calling success_handler
2024-09-29 19:43:21,483 - INFO - Wrapper: Completed Call, calling success_handler
19:43:21 - LiteLLM:INFO: utils.py:2952 -
LiteLLM completion() model= gemini-1.5-flash-002; provider = gemini
```
> [!TIP]
> optillm is a transparent proxy and will work with any LLM API or provider that has an OpenAI API compatible chat completions endpoint, and in turn, optillm also exposes
the same OpenAI API compatible chat completions endpoint. This should allow you to integrate it into any existing tools or frameworks easily. If the LLM you want to use
doesn't have an OpenAI API compatible endpoint (like Google or Anthropic) you can use [LiteLLM proxy server](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/proxy/quick_start) that supports most LLMs.
The following sequence diagram illustrates how the request and responses go through optillm.
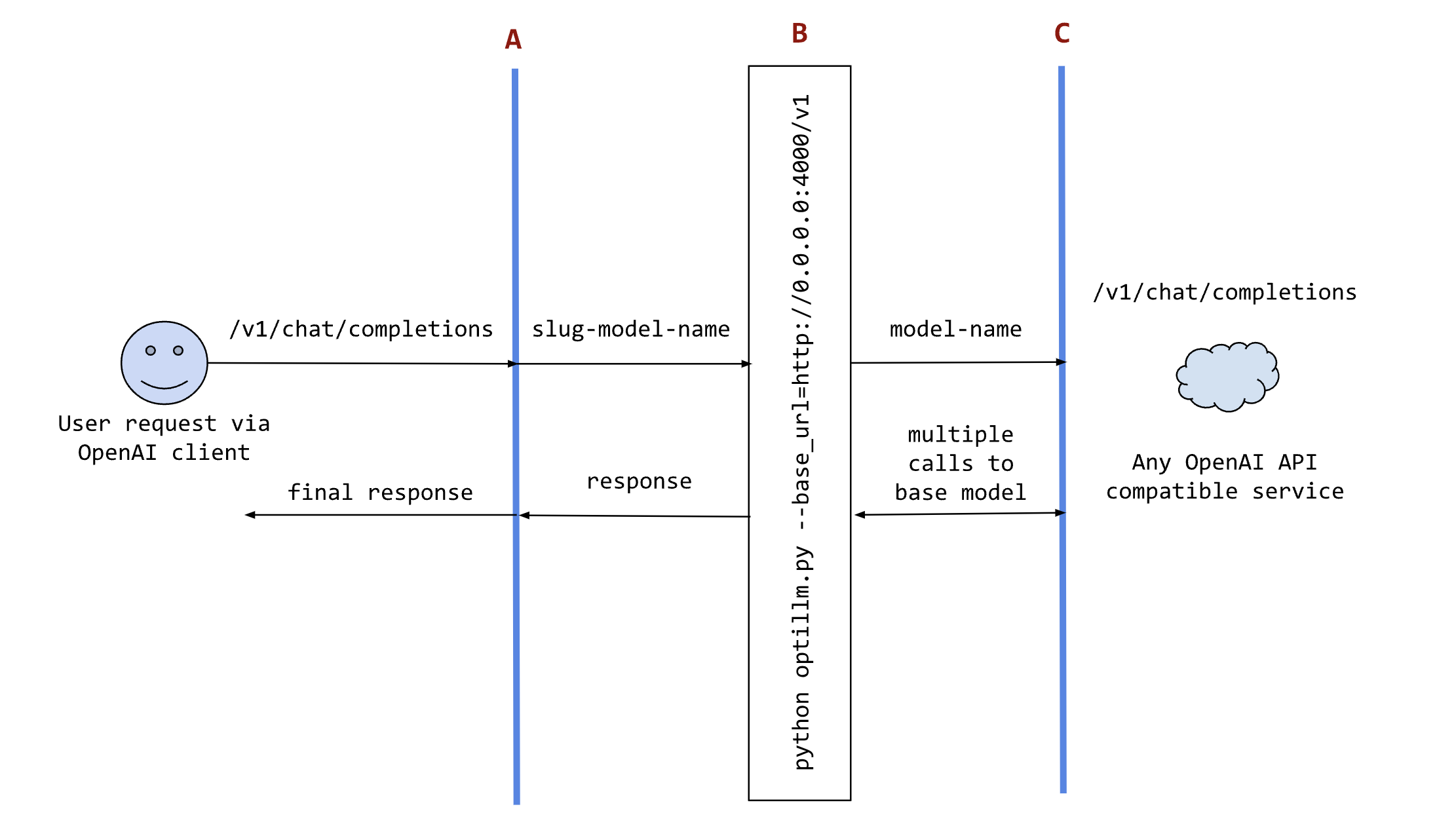
In the diagram:
- `A` is an existing tool (like [oobabooga](https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/)), framework (like [patchwork](https://github.com/patched-codes/patchwork))
or your own code where you want to use the results from optillm. You can use it directly using any OpenAI client sdk.
- `B` is the optillm service (running directly or in a docker container) that will send requests to the `base_url`.
- `C` is any service providing an OpenAI API compatible chat completions endpoint.
### Local inference server
We support loading any HuggingFace model or LoRA directly in optillm. To use the built-in inference server set the `OPTILLM_API_KEY` to any value (e.g. `export OPTILLM_API_KEY="optillm"`)
and then use the same in your OpenAI client. You can pass any HuggingFace model in model field. If it is a private model make sure you set the `HF_TOKEN` environment variable
with your HuggingFace key. We also support adding any number of LoRAs on top of the model by using the `+` separator.
E.g. The following code loads the base model `meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct` and then adds two LoRAs on top - `patched-codes/Llama-3.2-1B-FixVulns` and `patched-codes/Llama-3.2-1B-FastApply`.
You can specify which LoRA to use using the `active_adapter` param in `extra_args` field of OpenAI SDK client. By default we will load the last specified adapter.
```python
OPENAI_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8000/v1"
OPENAI_KEY = "optillm"
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct+patched-codes/Llama-3.2-1B-FastApply+patched-codes/Llama-3.2-1B-FixVulns",
messages=messages,
temperature=0.2,
logprobs = True,
top_logprobs = 3,
extra_body={"active_adapter": "patched-codes/Llama-3.2-1B-FastApply"},
)
```
You can also use the alternate decoding techniques like `cot_decoding` and `entropy_decoding` directly with the local inference server.
```python
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct",
messages=messages,
temperature=0.2,
extra_body={
"decoding": "cot_decoding", # or "entropy_decoding"
# CoT specific params
"k": 10,
"aggregate_paths": True,
# OR Entropy specific params
"top_k": 27,
"min_p": 0.03,
}
)
```
### Starting the optillm proxy with an external server (e.g. llama.cpp or ollama)
- Set the `OPENAI_API_KEY` env variable to a placeholder value
- e.g. `export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-no-key"`
- Run `./llama-server -c 4096 -m path_to_model` to start the server with the specified model and a context length of 4096 tokens
- Run `python3 optillm.py --base_url base_url` to start the proxy
- e.g. for llama.cpp, run `python3 optillm.py --base_url http://localhost:8080/v1`
> [!WARNING]
> The Anthropic API, llama.cpp-server, and ollama currently do not support sampling multiple responses from a model, which limits the available approaches to the following:
> `cot_reflection`, `leap`, `plansearch`, `rstar`, `rto`, `self_consistency`, `re2`, and `z3`. For models on HuggingFace, you can use the built-in local inference server as it supports multiple responses.
### MCP Plugin
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) plugin enables OptiLLM to connect with MCP servers, bringing external tools, resources, and prompts into the context of language models. This allows for powerful integrations with filesystem access, database queries, API connections, and more.
#### What is MCP?
The [Model Context Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/) (MCP) is an open protocol standard that allows LLMs to securely access tools and data sources through a standardized interface. MCP servers can provide:
- **Tools**: Callable functions that perform actions (like writing files, querying databases, etc.)
- **Resources**: Data sources for providing context (like file contents)
- **Prompts**: Reusable prompt templates for specific use cases
#### Configuration
##### Setting up MCP Config
1. Create a configuration file at `~/.optillm/mcp_config.json` with the following structure:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"/path/to/allowed/directory1",
"/path/to/allowed/directory2"
],
"env": {}
}
},
"log_level": "INFO"
}
```
Each server entry in `mcpServers` consists of:
- **Server name**: A unique identifier for the server (e.g., "filesystem")
- **command**: The executable to run the server
- **args**: Command-line arguments for the server
- **env**: Environment variables for the server process
- **description** (optional): Description of the server's functionality
#### Available MCP Servers
You can use any of the [official MCP servers](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/examples) or third-party servers. Some popular options include:
- **Filesystem**: `@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem` - File operations
- **Git**: `mcp-server-git` - Git repository operations
- **SQLite**: `@modelcontextprotocol/server-sqlite` - SQLite database access
- **Brave Search**: `@modelcontextprotocol/server-brave-search` - Web search capabilities
Example configuration for multiple servers:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", "/home/user/documents"],
"env": {}
},
"search": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-brave-search"],
"env": {
"BRAVE_API_KEY": "your-api-key-here"
}
}
},
"log_level": "INFO"
}
```
#### Using the MCP Plugin
Once configured, the MCP plugin will automatically:
1. Connect to all configured MCP servers
2. Discover available tools, resources, and prompts
3. Make these capabilities available to the language model
4. Handle tool calls and resource requests
The plugin enhances the system prompt with MCP capabilities so the model knows which tools are available. When the model decides to use a tool, the plugin:
1. Executes the tool with the provided arguments
2. Returns the results to the model
3. Allows the model to incorporate the results into its response
#### Example Queries
Here are some examples of queries that will engage MCP tools:
- "List all the Python files in my documents directory" (Filesystem)
- "What are the recent commits in my Git repository?" (Git)
- "Search for the latest information about renewable energy" (Search)
- "Query my database for all users who registered this month" (Database)
#### Troubleshooting
##### Logs
The MCP plugin logs detailed information to:
```
~/.optillm/logs/mcp_plugin.log
```
Check this log file for connection issues, tool execution errors, and other diagnostic information.
##### Common Issues
1. **Command not found**: Make sure the server executable is available in your PATH, or use an absolute path in the configuration.
2. **Connection failed**: Verify the server is properly configured and any required API keys are provided.
3. **Method not found**: Some servers don't implement all MCP capabilities (tools, resources, prompts). Verify which capabilities the server supports.
4. **Access denied**: For filesystem operations, ensure the paths specified in the configuration are accessible to the process.
## Implemented techniques
| Approach | Slug | Description |
| ------------------------------------ | ------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [Cerebras Planning and Optimization](optillm/cepo) | `cepo` | Combines Best of N, Chain-of-Thought, Self-Reflection, Self-Improvement, and various prompting techniques |
| CoT with Reflection | `cot_reflection` | Implements chain-of-thought reasoning with \, \ and \ sections |
| PlanSearch | `plansearch` | Implements a search algorithm over candidate plans for solving a problem in natural language |
| ReRead | `re2` | Implements rereading to improve reasoning by processing queries twice |
| Self-Consistency | `self_consistency` | Implements an advanced self-consistency method |
| Z3 Solver | `z3` | Utilizes the Z3 theorem prover for logical reasoning |
| R* Algorithm | `rstar` | Implements the R* algorithm for problem-solving |
| LEAP | `leap` | Learns task-specific principles from few shot examples |
| Round Trip Optimization | `rto` | Optimizes responses through a round-trip process |
| Best of N Sampling | `bon` | Generates multiple responses and selects the best one |
| Mixture of Agents | `moa` | Combines responses from multiple critiques |
| Monte Carlo Tree Search | `mcts` | Uses MCTS for decision-making in chat responses |
| PV Game | `pvg` | Applies a prover-verifier game approach at inference time |
| CoT Decoding | N/A for proxy | Implements chain-of-thought decoding to elicit reasoning without explicit prompting |
| Entropy Decoding | N/A for proxy | Implements adaptive sampling based on the uncertainty of tokens during generation |
| Thinkdeeper | N/A for proxy | Implements the `reasoning_effort` param from OpenAI for reasoning models like DeepSeek R1 |
| [AutoThink](optillm/autothink) | N/A for proxy | Combines query complexity classification with steering vectors to enhance reasoning |
## Implemented plugins
| Plugin | Slug | Description |
| ----------------------- | ------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [System Prompt Learning](optillm/plugins/spl) | `spl` | Implements what [Andrej Karpathy called the third paradigm](https://x.com/karpathy/status/1921368644069765486) for LLM learning, this enables the model to acquire program solving knowledge and strategies |
| [Deep Think](optillm/plugins/deepthink) | `deepthink` | Implements a Gemini-like Deep Think approach using inference time scaling for reasoning LLMs |
| [Long-Context Cerebras Planning and Optimization](optillm/plugins/longcepo) | `longcepo` | Combines planning and divide-and-conquer processing of long documents to enable infinite context |
| MCP Client | `mcp` | Implements the model context protocol (MCP) client, enabling you to use any LLM with any MCP Server |
| Router | `router` | Uses the [optillm-modernbert-large](https://huggingface.co/codelion/optillm-modernbert-large) model to route requests to different approaches based on the user prompt |
| Chain-of-Code | `coc` | Implements a chain of code approach that combines CoT with code execution and LLM based code simulation |
| Memory | `memory` | Implements a short term memory layer, enables you to use unbounded context length with any LLM |
| Privacy | `privacy` | Anonymize PII data in request and deanonymize it back to original value in response |
| Read URLs | `readurls` | Reads all URLs found in the request, fetches the content at the URL and adds it to the context |
| Execute Code | `executecode` | Enables use of code interpreter to execute python code in requests and LLM generated responses |
| JSON | `json` | Enables structured outputs using the outlines library, supports pydantic types and JSON schema |
## Available parameters
optillm supports various command-line arguments for configuration. When using Docker, these can also be set as environment variables prefixed with `OPTILLM_`.
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|--------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------|
| `--approach` | Inference approach to use | `"auto"` |
| `--simulations` | Number of MCTS simulations | 2 |
| `--exploration` | Exploration weight for MCTS | 0.2 |
| `--depth` | Simulation depth for MCTS | 1 |
| `--best-of-n` | Number of samples for best_of_n approach | 3 |
| `--model` | OpenAI model to use | `"gpt-4o-mini"` |
| `--base-url` | Base URL for OpenAI compatible endpoint | `""` |
| `--rstar-max-depth` | Maximum depth for rStar algorithm | 3 |
| `--rstar-num-rollouts` | Number of rollouts for rStar algorithm | 5 |
| `--rstar-c` | Exploration constant for rStar algorithm | 1.4 |
| `--n` | Number of final responses to be returned | 1 |
| `--return-full-response` | Return the full response including the CoT with tags | `False` |
| `--port` | Specify the port to run the proxy | 8000 |
| `--optillm-api-key` | Optional API key for client authentication to optillm | `""` |
| `--cepo_*` | See CePO Parameters section below for detailed config options | Various |
CePO Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|-----------|-------------|---------------|
| `--cepo_bestofn_n` | Number of responses to be generated in best of n stage | 3 |
| `--cepo_bestofn_temperature` | Temperature for verifier in best of n stage | 0.1 |
| `--cepo_bestofn_max_tokens` | Maximum number of tokens for verifier in best of n stage | 4096 |
| `--cepo_bestofn_rating_type` | Type of rating in best of n stage ("absolute" or "pairwise") | `"absolute"` |
| `--cepo_planning_n` | Number of plans generated in planning stage | 3 |
| `--cepo_planning_m` | Number of attempts to generate n plans in planning stage | 6 |
| `--cepo_planning_temperature_step1` | Temperature for generator in step 1 of planning stage | 0.55 |
| `--cepo_planning_temperature_step2` | Temperature for generator in step 2 of planning stage | 0.25 |
| `--cepo_planning_temperature_step3` | Temperature for generator in step 3 of planning stage | 0.1 |
| `--cepo_planning_temperature_step4` | Temperature for generator in step 4 of planning stage | 0 |
| `--cepo_planning_max_tokens_step1` | Maximum number of tokens in step 1 of planning stage | 4096 |
| `--cepo_planning_max_tokens_step2` | Maximum number of tokens in step 2 of planning stage | 4096 |
| `--cepo_planning_max_tokens_step3` | Maximum number of tokens in step 3 of planning stage | 4096 |
| `--cepo_planning_max_tokens_step4` | Maximum number of tokens in step 4 of planning stage | 4096 |
| `--cepo_print_output` | Whether to print the output of each stage | `False` |
| `--cepo_config_file` | Path to CePO configuration file | `None` |
| `--cepo_use_plan_diversity` | Use additional plan diversity step | `False` |
| `--cepo_rating_model` | Specify a model for rating step if different than for completion | `None` |
## Running with Docker
optillm can optionally be built and run using Docker and the provided [Dockerfile](https://github.com/codelion/optillm/blob/main/Dockerfile).
### Using Docker Compose
1. Make sure you have Docker and Docker Compose installed on your system.
2. Either update the environment variables in the docker-compose.yaml file or create a `.env` file in the project root directory and add any environment variables you want to set. For example, to set the OpenAI API key, add the following line to the `.env` file:
```bash
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key_here
```
3. Run the following command to start optillm:
```bash
docker compose up -d
```
This will build the Docker image if it doesn't exist and start the optillm service.
4. optillm will be available at `http://localhost:8000`.
When using Docker, you can set these parameters as environment variables. For example, to set the approach and model, you would use:
```bash
OPTILLM_APPROACH=mcts
OPTILLM_MODEL=gpt-4
```
To secure the optillm proxy with an API key, set the `OPTILLM_API_KEY` environment variable:
```bash
OPTILLM_API_KEY=your_secret_api_key
```
When the API key is set, clients must include it in their requests using the `Authorization` header:
```plain
Authorization: Bearer your_secret_api_key
```
## SOTA results on benchmarks with optillm
### AutoThink on GPQA-Diamond & MMLU-Pro (May 2025)
| **Model** | **GPQA-Diamond** | | **MMLU-Pro** | |
|----------------|-----------------------------|--------------------------|----------------------------|--------------------------|
| | Accuracy (%) | Avg. Tokens | Accuracy (%) | Avg. Tokens |
| DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B | 21.72 | 7868.26 | 25.58 | 2842.75 |
| with Fixed Budget | 28.47 | 3570.00 | 26.18 | 1815.67 |
| **with AutoThink** | **31.06** | **3520.52** | **26.38** | **1792.50** |
### LongCePO on LongBench v2 (Apr 2025)
| Model¹ | Context window | Short samples (up to 32K words) | Medium samples (32–128K words) |
|----------------------------------|----------------|------------------|----------------|
| Llama 3.3 70B Instruct | 128K | 36.7 (45.0) | 27.0 (33.0) |
| **LongCePO + Llama 3.3 70B Instruct** | **8K** | **36.8 ± 1.38** | **38.7 ± 2.574 (39.735)²** |
| Mistral-Large-Instruct-2411 | 128K | 41.7 (46.1) | 30.7 (34.9) |
| o1-mini-2024-09-12 | 128K | 48.6 (48.9) | 33.3 (32.9) |
| Claude-3.5-Sonnet-20241022 | 200K | 46.1 (53.9) | 38.6 (41.9) |
| Llama-4-Maverick-17B-128E-Instruct | 524K | 32.22 (50.56) | 28.84 (41.86) |
¹ Performance numbers reported by LongBench v2 authors, except for LongCePO and Llama-4-Maverick results.
² Numbers in parentheses for LongCePO indicate accuracy of majority voting from 5 runs.
### LongCePO on HELMET - InfiniteBench En.MC, 128K length (Apr 2025)
| Model | Accuracy (%) |
|---------|---------------|
| Llama 3.3 70B Instruct (full context) | 58.0 |
| **LongCePO + Llama 3.3 70B Instruct (8K context)** | **71.6 ± 1.855 (73.0)¹** |
| o1-mini-2024-09-12 (full context) | 58.0 |
| gpt-4o-2024-08-06 (full context) | 74.0 |
¹ Numbers in parentheses for LongCePO indicate accuracy of majority voting from 5 runs.
### CePO on math and code benchmarks (Mar 2025)
| Method | Math-L5 | MMLU-Pro (Math) | CRUX | LiveCodeBench (pass@1) | Simple QA |
| -----------------------------: | :-----: | :-------------: | :----: | :--------------------: | :-------: |
| Llama 3.3 70B | 51.0 | 78.6 | 72.6 | 27.1 | 20.9 |
| Llama 3.1 405B | 49.8 | 79.2 | 73.0 | 31.8 | 13.5 |
| CePO (using Llama 3.3 70B) | 69.6 | 84.8 | 80.1 | 31.9 | **22.6** |
| QwQ 32B | 61.4 | 90.8 | 82.5 | 44.3 | 7.8 |
| CePO (using QwQ 32B) | 88.1 | **92.0** | 86.3 | **51.5** | 8.2 |
| DeepSeek R1 Llama | 83.1 | 82.0 | 84.0 | 47.3 | 14.6 |
| CePO (using DeepSeek R1 Llama) |**90.2** | 84.0 |**89.4**| 47.2 | 15.5 |
### coc-claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 on AIME 2024 pass@1 (Nov 2024)
| Model | Score |
|-------|-----:|
| o1-mini | 56.67 |
| coc-claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 | 46.67 |
| coc-gemini/gemini-exp-1121 | 46.67 |
| o1-preview | 40.00 |
| gemini-exp-1114 | 36.67 |
| claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 | 20.00 |
| gemini-1.5-pro-002 | 20.00 |
| gemini-1.5-flash-002 | 16.67 |
### readurls&memory-gpt-4o-mini on Google FRAMES Benchmark (Oct 2024)
| Model | Accuracy |
| ----- | -------- |
| readurls&memory-gpt-4o-mini | 61.29 |
| gpt-4o-mini | 50.61 |
| readurls&memory-Gemma2-9b | 30.1 |
| Gemma2-9b | 5.1 |
| Gemma2-27b | 30.8 |
| Gemini Flash 1.5 | 66.5 |
| Gemini Pro 1.5 | 72.9 |
### plansearch-gpt-4o-mini on LiveCodeBench (Sep 2024)
| Model | pass@1 | pass@5 | pass@10 |
| ---------------------- | ------ | ------ | ------- |
| plansearch-gpt-4o-mini | 44.03 | 59.31 | 63.5 |
| gpt-4o-mini | 43.9 | 50.61 | 53.25 |
| claude-3.5-sonnet | 51.3 | | |
| gpt-4o-2024-05-13 | 45.2 | | |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 44.2 | | |
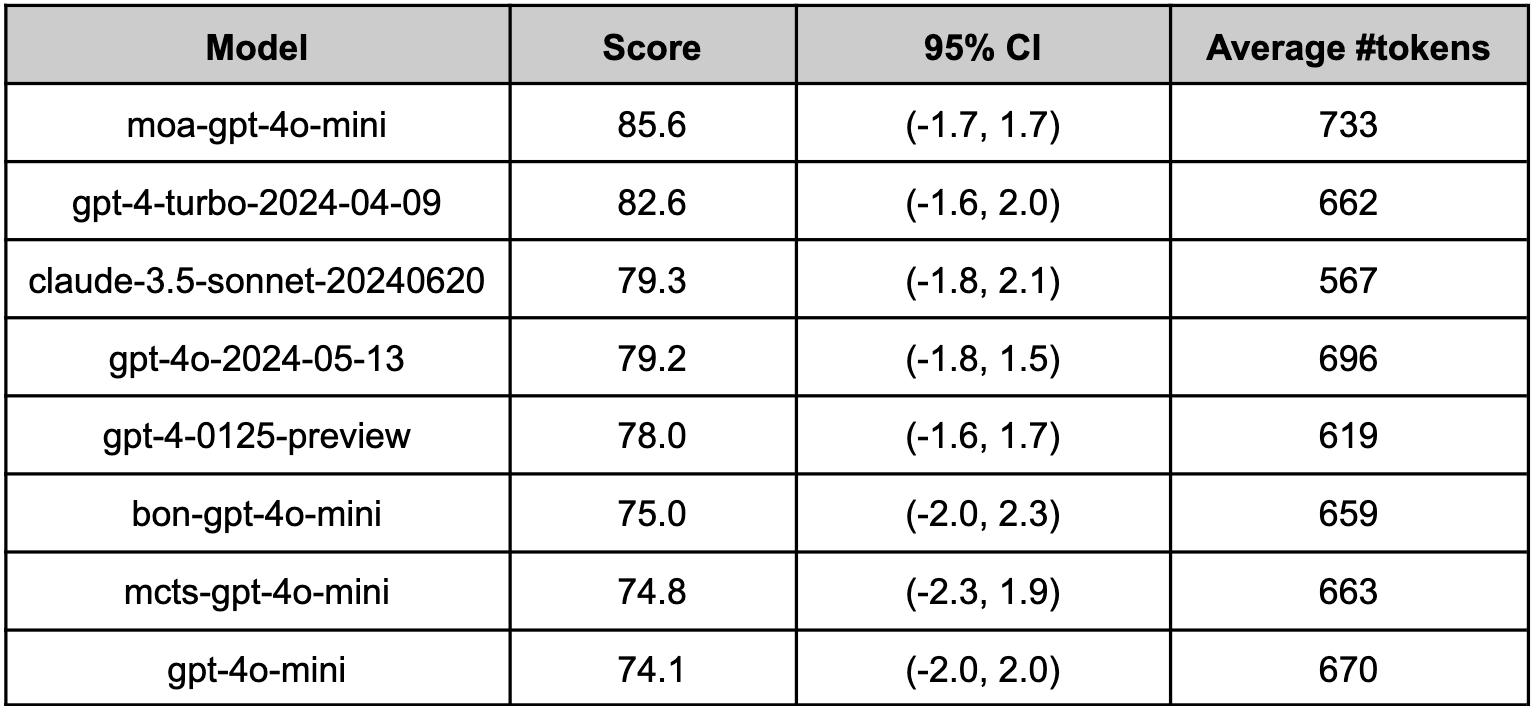
### moa-gpt-4o-mini on Arena-Hard-Auto (Aug 2024)
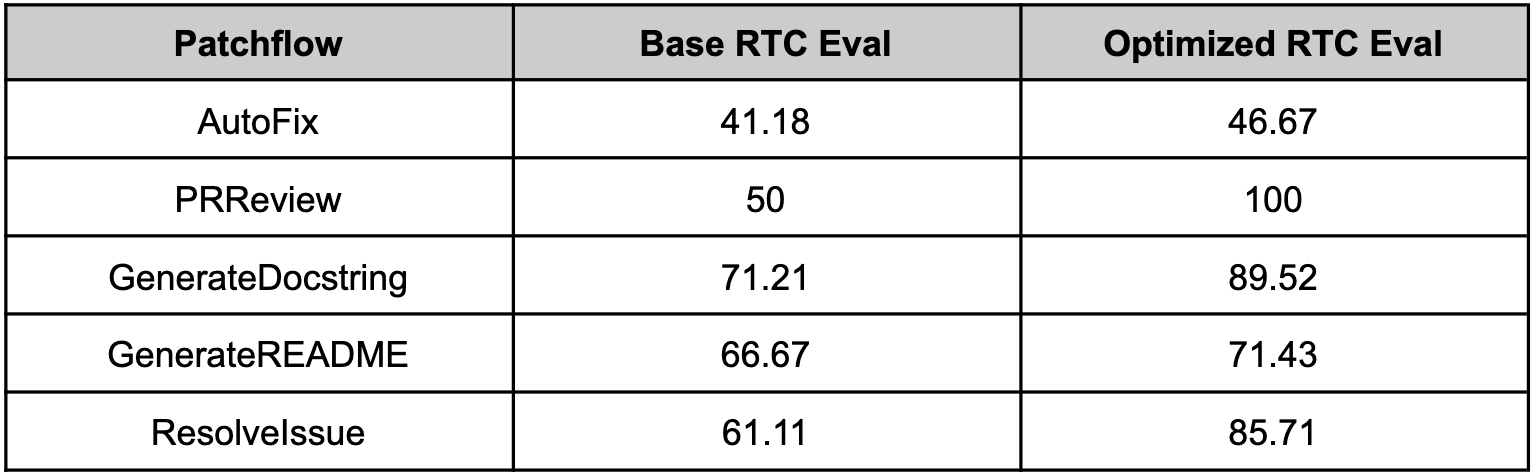
### optillm with Patchwork (July 2024)
Since optillm is a drop-in replacement for OpenAI API you can easily integrate it with existing tools and frameworks using the OpenAI client. We used optillm with [patchwork](https://github.com/patched-codes/patchwork) which is an open-source framework that automates development gruntwork like PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching using workflows
called patchflows. We saw huge performance gains across all the supported patchflows as shown below when using the mixture of agents approach (moa).
## References
- [AutoThink: efficient inference for reasoning LLMs](https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5253327) - [Implementation](optillm/autothink)
- [Self-Discover: Large Language Models Self-Compose Reasoning Structures
](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.03620) - [Implementation](optillm/plugings/deepthink)
- [CePO: Empowering Llama with Reasoning using Test-Time Compute](https://cerebras.ai/blog/cepo) - [Implementation](optillm/cepo)
- [LongCePO: Empowering LLMs to efficiently leverage infinite context](https://cerebras.ai/blog/longcepo) - [Implementation](optillm/plugins/longcepo)
- [Chain of Code: Reasoning with a Language Model-Augmented Code Emulator](https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.04474) - [Inspired the implementation of coc plugin](optillm/plugins/coc_plugin.py)
- [Entropy Based Sampling and Parallel CoT Decoding](https://github.com/xjdr-alt/entropix) - [Implementation](optillm/entropy_decoding.py)
- [Fact, Fetch, and Reason: A Unified Evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.12941) - [Evaluation script](scripts/eval_frames_benchmark.py)
- [Writing in the Margins: Better Inference Pattern for Long Context Retrieval](https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2408.14906) - [Inspired the implementation of the memory plugin](optillm/plugins/memory_plugin.py)
- [Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Without Prompting](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.10200) - [Implementation](optillm/cot_decoding.py)
- [Re-Reading Improves Reasoning in Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.06275) - [Implementation](optillm/reread.py)
- [In-Context Principle Learning from Mistakes](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.05403) - [Implementation](optillm/leap.py)
- [Planning In Natural Language Improves LLM Search For Code Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.03733) - [Implementation](optillm/plansearch.py)
- [Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thought Reasoning in Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.11171) - [Implementation](optillm/self_consistency.py)
- [Mutual Reasoning Makes Smaller LLMs Stronger Problem-Solvers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.06195) - [Implementation](optillm/rstar.py)
- [Mixture-of-Agents Enhances Large Language Model Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.04692) - [Inspired the implementation of moa](optillm/moa.py)
- [Prover-Verifier Games improve legibility of LLM outputs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.13692) - [Implementation](optillm/pvg.py)
- [Monte Carlo Tree Search Boosts Reasoning via Iterative Preference Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.00451) - [Inspired the implementation of mcts](optillm/mcts.py)
- [Unsupervised Evaluation of Code LLMs with Round-Trip Correctness](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.08699) - [Inspired the implementation of rto](optillm/rto.py)
- [Patched MOA: optimizing inference for diverse software development tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.18521) - [Implementation](optillm/moa.py)
- [Patched RTC: evaluating LLMs for diverse software development tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16557) - [Implementation](ptillm/rto.py)
## Citation
If you use this library in your research, please cite:
```bibtex
@software{optillm,
title = {Optillm: Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs},
author = {Asankhaya Sharma},
year = {2024},
publisher = {GitHub},
url = {https://github.com/codelion/optillm}
}
```