https://github.com/condenast/fyi
Map & Explore your organization's System Architecture
https://github.com/condenast/fyi
architecture create-react-app dashboard pgsql probot vault
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Map & Explore your organization's System Architecture
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/condenast/fyi
- Owner: CondeNast
- License: apache-2.0
- Archived: true
- Created: 2017-11-20T20:51:33.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-08T13:43:25.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-19T14:32:22.824Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: architecture, create-react-app, dashboard, pgsql, probot, vault
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 4.97 MB
- Stars: 33
- Watchers: 11
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 64
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Archiving: Abandoned
# 💁 FYI
Map and Explore your organization's System Architecture
[](LICENSE) [](http://fyi.conde.io/link/56) [](http://fyi.conde.io/link/162)
_Proudly built by:_
## 🤔 Introduction
The FYI application was built by the Architecture Team at Condé Nast to stay on top of their growing technology portfolio of systems (sites, apps, apis) distributed across hundreds of repositories in multiple GitHub organizations.
This application has two parts:
- a Github App to discover code repositories and request FYIs from developers
- a Web App to view interactive architecture diagrams with system dependencies and metrics
### 🔨 Built Using
1. Probot (Github App Framework)
2. Create React App
3. Postgres SQL
4. Vault
5. Integrations with: Confluence, Slack, Datadog
## 👨🔧 Install
### 🔧 Step 1: Setting Up Services
The goal of this step is to setup the required services for the FYI application, and populate the files in the `config` directory.
__A note about configurations__
The configuration is split across 2 files: `default.js` and `secrets.json`.
`default.js` stores non-sensitive configuration settings and feature flags. Since we use `node-config`, these defaults can be overidden by the environment specific files: `staging.json` and `production.json`.
`secrets.json` stores sensitive account information like app keys and api tokens. The application first tries to use `node-vault` to connect to a Vault instance and get the secrets, incase it fails to do so, it uses the `secrets.json`. The instructions below guide you towards creating your own `secrets.json` to start the application. If you later want to move it to a secure and shareable location, consider setting up Vault and moving the secrets there.
Lets get started...
1. Create a secrets file
1. Run `cp config/secrets.json.example config/secrets.json`
2. Create a web proxy url
1. Go to `https://smee.io/new`
2. In `secrets.json`, copy this smee channel url as the value for `webhook-proxy-url`
3. Create a Github Org
1. If you do not have a GiHub organization, go to `https://github.com/organizations/new` to start a new one
2. In `default.js`, add your organization name to the `github.subscribedOrgs` list & `github.adminOrg`
4. Create & Install a Github App
1. Go to `https://github.com/settings/apps/new` and create a new Github App
2. Set `Application Name` as per your choice, can be something like `archbot-test-`
2. Set `Homepage URL` as per your choice, this will not be required for the application to work
2. Set `Webhook URL` to the webhook proxy url from above
3. Set `Webhook secret` as per your choice and then in `secrets.json` copy this as the value for `webhook-secret`
4. Update your Github App's permissions:
1. Read Only permission for: Repo Administration, Repo Metadata, Repo Webhooks, Commit Statuses, Org Members
2. Read and Write permission for: Checks, Repository Contents, Issues, Pull Requests,
5. Updates your Github Apps' event subscriptions:
1. Subscribe to events for: Repository, Issues, Issue Comments
6. For "Where can this GitHub App be installed?", choose "Any Account"
7. After the App is created, the ID will be listed in the About section. In `.env` file, copy this ID as the value for `APP_ID`
8. Generate a private key and download it. In order to use this key in our code, we will need to replace the carriage returns with `\n`. Run this command on your key file: `sed -E ':a;N;$!ba;s/\r{0,1}\n/\\n/g' .pem`. In `secrets.json` copy the output of the `sed` command as the value for `github-private-key`
9. Head over to `https://github.com/settings/apps//installations` and install this application to your organization
5. Create a FYI Admin GitHub repository
1. Go to `https://github.com/organizations//repositories/new` and create a new repository called `fyi-admin`
6. Create a Confluence Account, Space and Page
1. If you do not have a Confluence account, sign up for a free account here: https://www.atlassian.com/software/confluence/try
2. After account creation, you will be prompted to create a space (you can name it Arch)
3. After space creation, you will be prompted to create a page (you can name it FYIs). On this page, using "Insert More Content" dropdown, select "Other Macros" and add "Children Display".
4. In `default.js`, add your Confluence Site name (only the part before .attlassian.net) as `hostname`, your Confluence Space name as `spaceKey`, and your Confluence Page id as `fyiPageId`.
5. Now create a Confluence API token here: https://id.atlassian.com/manage/api-tokens
6. In `secrets.json`, add you Confluence account email as `confluence-username` and API token as `confluence-access-token`
7. Configure Slack channel (optional)
1. If you want to disable slack, update `default.js` for `slack.enabled` to be `false`
2. Install "Incoming Webhooks" for your Slack instance
3. Add a configuration for new incoming webhook for posting to your Slack channel
4. In `secrets.json`, copy the Slack webhook url as the value for `slack-webhook-url`
5. In `default.js`, set the channel name as value for `slack.channel`
8. Configure Datadog events (optional)
1. This integration is a WIP. For now, disable this integration, update `default.js` for `datadog.enabled` to be `false`
### 🏃 Step 2: Running With Docker (recommended)
0. Pre-requisites: Docker and Docker Compose
1. Build Docker Image: `docker build -t fyi-image .`
2. Run Application: `docker-compose up`
3. Open your browser and go to `http://localhost:3001`
### 🚶 Running Without Docker
0. Pre-requisites: Node v9+, Postgres SQL v10+
1. Create database called `easy-fyi-development`
1. `npm i`
2. `npm run install:client`
3. `npm start`
4. Open your browser and go to `http://localhost:3001`
## 🚀 Usage
### 🆕 Creating a new FYI
There are 2 ways to create a new FYI:
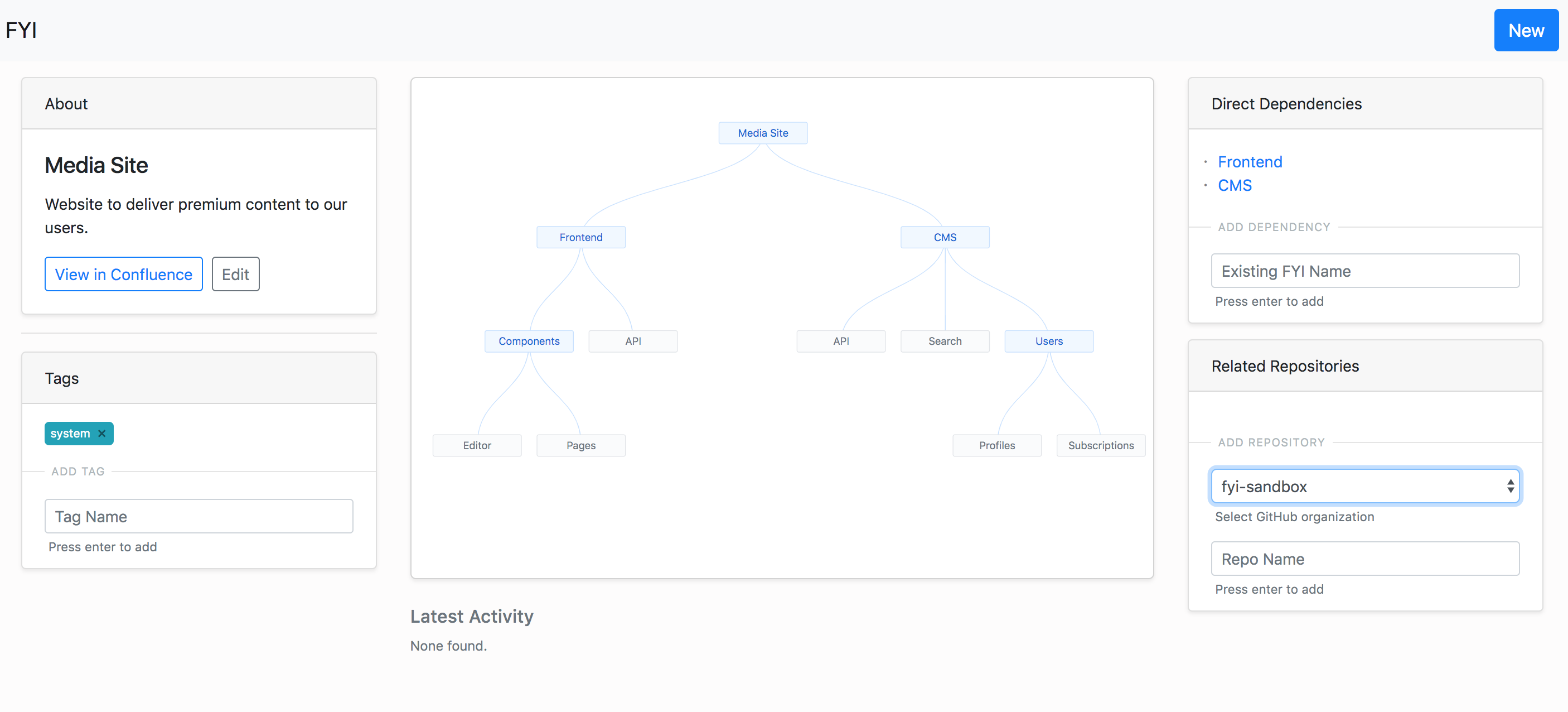
1. On the FYI homepage, click on the `New` button, add the FYI name and click `Submit`. This will create a FYI page for you to add dependencies, repositories and tags.
2. If a new repository is created or identified, then the `Request FYI` command by Admins will create a new FYI.
### 🔀 Adding a Dependency to FYI
A dependency for a FYI can only be from a set of other existing FYIs.
A new dependency can be added through that FYI's detail page in the toolbar.
### ℹ️ Adding a New Repository to FYI
When a new repository is created in the GitHub organization, the bot automatically detects it and sends a notification to the Admins who can choose to `Request a new FYI` or `Request to link to FYI` from the repository owner directly through Github issues.
### 🈁 Adding a Existing Repository to FYI
A request to add an existing repository can be submitted through the FYI's detail page in the toolbar. This triggers a notification to the Admins who can choose to pass the request to the repository owner or skip it.
### ⏹ Adding a Tag to FYI
A new tag can be added through the FYI's detail page in the toolbar.
## 🙏 Thanks
We would like to thank the [Probot team and community](https://probot.github.io/) for giving us a solid foundation of code and inspiration on top of which we could build this application.
## 👨🏭 Contributors
See the list of [contributors](https://github.com/CondeNast/fyi/contributors) who participated in writing this tool.
