https://github.com/core-go/kafka
https://github.com/core-go/kafka
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/core-go/kafka
- Owner: core-go
- Created: 2020-06-24T09:25:25.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-28T07:43:01.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-10T04:14:56.803Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Go
- Size: 44.9 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# kafka
Apache Kafka is an open-source stream processing platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation, designed for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. It is capable of handling high-throughput, low-latency data streams, making it ideal for use cases that require processing of large volumes of data in real-time.
### Libraries for Kafka
- GO: [kafka](https://github.com/core-go/kafka), to wrap and simplify [segmentio/kafka-go](https://github.com/segmentio/kafka-go), [IBM/sarama](https://github.com/IBM/sarama) and [confluent-kafka-go](https://github.com/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go). Example is at [go-kafka-sample](https://github.com/project-samples/go-kafka-sample).
- nodejs: [kafka-plus](https://www.npmjs.com/package/kafka-plus), to wrap and simplify [kafkajs](https://www.npmjs.com/package/kafkajs). Example is at [kafka-sample](https://github.com/typescript-tutorial/kafka-sample).
#### A common flow to consume a message from a message queue
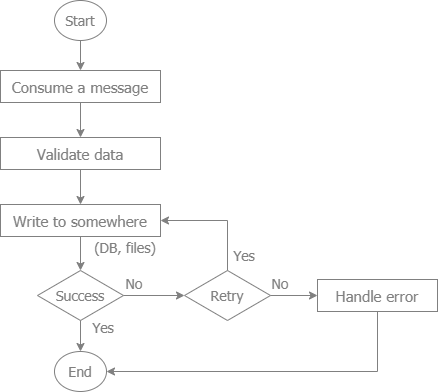
- The libraries to implement this flow are:
- [mq](https://github.com/core-go/mq) for GOLANG. Example is at [go-kafka-sample](https://github.com/project-samples/go-kafka-sample)
- [mq-one](https://www.npmjs.com/package/mq-one) for nodejs. Example is at [kafka-sample](https://github.com/typescript-tutorial/kafka-sample)
### Key Features of Kafka
#### High Throughput
- Capable of handling millions of messages per second with low latency.
#### Scalability
- Scales horizontally by adding more brokers to the cluster.
#### Durability
- Ensures data is stored reliably with configurable retention policies.
#### Fault Tolerance
- Provides replication of data across multiple brokers, ensuring resilience and fault tolerance.
#### High Availability
- Ensures continuous availability and reliability through distributed architecture.
#### Stream Processing
- Includes Kafka Streams API for building stream processing applications.
#### Multi-Subscriber Support
- Allows multiple consumers to read messages independently, supporting various use cases like real-time analytics and log aggregation.
### How Kafka Works
Kafka operates using the following core concepts:
#### Producer
- An application that sends records (messages) to Kafka topics.
#### Consumer
- An application that reads records from Kafka topics.
#### Topic
- A category or feed name to which records are sent by producers. Topics are partitioned and replicated across brokers.
#### Partition
- A division of a topic that allows for parallel processing. Each partition is an ordered, immutable sequence of records.
#### Broker
- A Kafka server that stores data and serves clients. Kafka clusters are composed of multiple brokers.
#### Cluster
- A collection of Kafka brokers working together to provide scalability and fault tolerance.
#### Zookeeper
- A coordination service used by Kafka to manage brokers, maintain configurations, and track topic partitions.
#### Offset
- A unique identifier assigned to each record within a partition, used by consumers to keep track of their position in the partition.
### Kafka vs. Traditional Message Queues
#### Data Storage
- Kafka: Stores data for a configurable amount of time, allowing consumers to reprocess or analyze historical data.
- Traditional Message Queues (e.g., RabbitMQ): Typically remove messages once they are consumed, focusing on point-to-point communication.
#### Scalability
- Kafka: Designed for horizontal scalability, handling large-scale data streams with ease.
- Traditional Message Queues: May require more complex configurations for scaling, often using clustering or sharding techniques.
#### Message Processing
- Kafka: Suited for real-time stream processing and analytics, allowing multiple consumers to read the same data independently.
- Traditional Message Queues: Focus on ensuring message delivery to one or more consumers, often used for task distribution.
#### Performance
- Kafka: Optimized for high throughput and low latency, making it ideal for big data applications.
- Traditional Message Queues: Generally optimized for reliable message delivery and simpler use cases.
### Advantages of Kafka
#### High Throughput and Low Latency
- Capable of handling large volumes of data with minimal delay, suitable for real-time applications.
#### Scalability
- Easily scales horizontally by adding more brokers and partitions, supporting the growth of data-intensive applications.
#### Durability and Fault Tolerance
- Ensures data reliability through replication and configurable retention policies, making it robust against failures.
#### Flexible Data Consumption
- Allows multiple consumers to independently read and process data, enabling various analytics and processing use cases.
#### Integration with Big Data Ecosystems
- Integrates seamlessly with other big data tools like Hadoop, Spark, and Flink, providing a comprehensive data processing pipeline.
### Disadvantages of Kafka
#### Complexity
- Requires careful configuration and management, including the use of Zookeeper, which adds to the complexity.
#### Resource Intensive
- High throughput and durability features can demand significant computational and storage resources.
#### Not Ideal for Small Messages or Low-Volume Use Cases
- Best suited for high-throughput scenarios; may be overkill for applications with low message volumes or small message sizes.
### Use Cases of Kafka
#### Real-Time Analytics
- Processing and analyzing streaming data in real-time, such as monitoring user activities on a website.
#### Log Aggregation
- Collecting and centralizing logs from various services for monitoring and analysis.
#### Event Sourcing
- Storing events as a sequence of state changes, enabling complex event-driven architectures.
#### Metrics Collection
- Collecting and processing metrics from distributed systems for monitoring and alerting.
#### Data Integration
- Integrating data from various sources into data lakes or warehouses for further analysis.
### Example Scenario: Real-Time User Activity Tracking
In a real-time user activity tracking system, Kafka can be used to collect and process user interactions from a website or application.
#### Producers
- Web applications and mobile apps send user interaction data (e.g., clicks, page views) to Kafka topics.
#### Topics
- Different topics are created for different types of interactions (e.g., "page_views", "clicks").
#### Consumers
- Analytics services consume data from these topics to generate real-time dashboards and reports.
- Storage services consume data to store historical user interaction data in data lakes or warehouses.
#### Stream Processing
- Kafka Streams or other stream processing tools like Apache Flink process the data in real-time to detect patterns, anomalies, or trigger actions (e.g., personalized recommendations).
### Conclusion
Apache Kafka is a powerful and scalable stream processing platform designed to handle high-throughput, low-latency data streams. Its robust architecture and extensive feature set make it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from real-time analytics to log aggregation and event-driven architectures. While it introduces some complexity and resource demands, its benefits in terms of scalability, durability, and flexibility make it a valuable tool for modern data-intensive applications. Understanding Kafka's core concepts and capabilities can help organizations build efficient and reliable data pipelines and streaming applications.
## Installation
Please make sure to initialize a Go module before installing core-go/kafka:
```shell
go get -u github.com/core-go/kafka
```
Import:
```go
import "github.com/core-go/kafka"
```