https://github.com/core-go/nats
https://github.com/core-go/nats
Last synced: 6 days ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/core-go/nats
- Owner: core-go
- Created: 2020-06-29T11:03:27.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-21T14:29:09.000Z (12 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-10T04:15:01.592Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Go
- Size: 17.6 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# NATS
NATS is an open-source, lightweight, and high-performance messaging system designed for cloud-native applications, IoT messaging, and microservices architectures. It supports multiple messaging patterns, including publish/subscribe, request/reply, and queuing. Key features include:
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and use with minimal configuration.
- Performance: Low latency and high throughput.
- Scalability: Capable of handling millions of messages per second.
- Fault Tolerance: Supports clustering for high availability.
### Libraries for NATS
- GO: [NATS](https://github.com/core-go/nats), to wrap and simplify [nats.go](https://github.com/nats-io/nats.go). Example is at [go-nats-sample](https://github.com/project-samples/go-nats-sample)
- nodejs: [nats-plus](https://www.npmjs.com/package/nats-plus), to wrap and simplify [nats](https://www.npmjs.com/package/nats). Example is at [nats-sample](https://github.com/typescript-tutorial/nats-sample)
#### A common flow to consume a message from a message queue
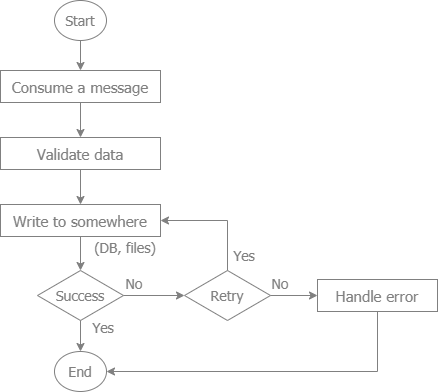
- The libraries to implement this flow are:
- [mq](https://github.com/core-go/mq) for GOLANG. Example is at [go-nats-sample](https://github.com/project-samples/go-nats-sample)
- [mq-one](https://www.npmjs.com/package/mq-one) for nodejs. Example is at [nats-sample](https://github.com/typescript-tutorial/nats-sample)
### Use Cases of NATS
#### Microservices Communication:
- Scenario: Facilitating communication between microservices in a distributed system.
- Benefit: Provides low-latency, reliable messaging, ensuring efficient inter-service communication.

#### Financial Services:
- Scenario: Enabling real-time transactions and data updates.
- Benefit: Provides reliable and fast message delivery critical for financial applications.
#### Real-Time Data Streaming:
- Scenario: Streaming data in real-time from various sources to data processing systems.
- Benefit: Low latency ensures real-time data processing and analytics.

#### Event-Driven Architectures:
- Scenario: Building applications based on event-driven paradigms.
- Benefit: Decouples services, allowing for scalable and maintainable architectures.
#### IoT Messaging:
- Scenario: Handling communication between numerous IoT devices.
- Benefit: Supports lightweight, scalable messaging suitable for IoT environments.
#### Edge Computing:
- Scenario: Managing communication between edge devices and cloud services.
- Benefit: Efficiently handles data transfer and command execution with minimal latency.
### Comparison of NATS, Kafka, and RabbitMQ
#### NATS:
- Type: Lightweight, high-performance messaging system.
- Use Cases: Microservices communication, IoT messaging, real-time data streaming.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-most-once (standard), at-least-once with JetStream.
- Persistence: Optional (JetStream for persistence).
- Latency: Very low, optimized for speed.
- Scalability: Highly scalable with clustering.
#### Apache Kafka:
- Type: Distributed event streaming platform.
- Use Cases: High-throughput messaging, event sourcing, log aggregation.
- Delivery Guarantees: Configurable (at-least-once, exactly-once).
- Persistence: Durable storage with configurable retention.
- Latency: Higher due to disk persistence.
- Scalability: Highly scalable with partitioned topics.
#### RabbitMQ:
- Type: Message broker.
- Use Cases: Decoupling applications, job queuing, asynchronous communication.
- Delivery Guarantees: At-least-once, exactly-once (with transactions).
- Persistence: Persistent storage of messages.
- Latency: Moderate, designed for reliability.
- Scalability: Scalable with clustering and federation.
### Key Differences:
- Latency and Performance: NATS offers the lowest latency, Kafka provides high throughput with persistence, RabbitMQ balances reliability and performance.
- Persistence: Kafka and RabbitMQ offer strong persistence guarantees, while NATS focuses on speed with optional persistence.
- Scalability: All three are scalable, but Kafka excels in handling high-throughput event streams, NATS in low-latency scenarios, and RabbitMQ in reliable message delivery.
### Use Case Suitability:
- NATS: Best for real-time, low-latency communication in microservices and IoT.
- Kafka: Ideal for high-throughput event streaming and log aggregation.
- RabbitMQ: Suitable for reliable message queuing and asynchronous task processing.
## Installation
Please make sure to initialize a Go module before installing core-go/nats:
```shell
go get -u github.com/core-go/nats
```
Import:
```go
import "github.com/core-go/nats"
```