Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/corels/rcppcorels
R Bindings to the Certifiably Optimal Rule Lists (Corels) Learner
https://github.com/corels/rcppcorels
Last synced: 18 days ago
JSON representation
R Bindings to the Certifiably Optimal Rule Lists (Corels) Learner
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/corels/rcppcorels
- Owner: corels
- Created: 2019-11-03T16:18:08.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-02-04T17:08:45.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-02T01:41:49.183Z (7 months ago)
- Language: C++
- Size: 396 KB
- Stars: 45
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: ChangeLog
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# corels: R interface to 'Certifiably Optimal RulE ListS' (Corels)
[](https://github.com/corels/rcppcorels/actions/workflows/ci.yaml)
[](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html)
[](https://cran.r-project.org/package=corels)
[](https://cran.r-project.org/package=corels)
[](https://www.r-pkg.org:443/pkg/corels)
## What is it?
CORELS is a custom discrete optimization technique for building rule lists
over a categorical feature space. The algorithm provides the optimal solution
with a certificate of optimality. By leveraging algorithmic bounds, efficient
data structures, and computational reuse, it achieves several orders of
magnitude speedup in time and a massive reduction of memory consumption. This
approach produces optimal rule lists on practical problems in seconds, and
offers a novel alternative to CART and other decision tree methods.
See the [C++ implementation](https://github.com/corels/corels), the
[live website](https://corels.eecs.harvard.edu/), the [Python
implementation](https://github.com/corels/pycorels), the [arXiv
paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.01701), the [JMLR
paper](https://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume18/17-716/17-716.pdf), the [senior
thesis](https://dash.harvard.edu/handle/1/38811502) or the [KDD 2017
paper](https://www.kdd.org/kdd2017/papers/view/learning-certifiably-optimal-rule-lists-for-categorical-data)
for more.
More about Corels can also be read in [this recent post at _The Morning Paper_](https://blog.acolyer.org/2019/10/30/corels/).
## Illustration
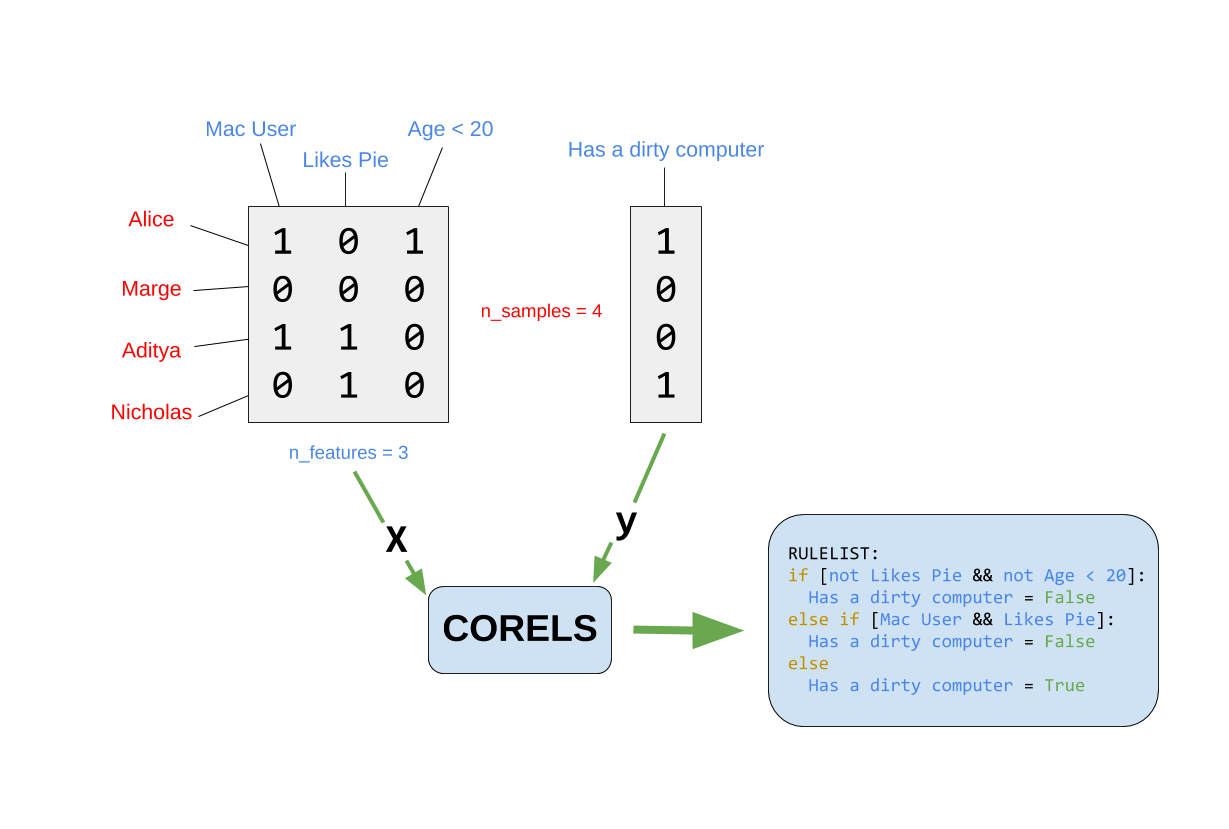
With thanks to the [Python
implementation](https://github.com/corels/pycorels) for the image.
## What is this package?
We use [Rcpp](https://github.com/RcppCore/Rcpp) to connect the [Corels C++
implementation](https://github.com/corels/corels) to R.
## Status
Installs and works fine, and passed `R CMD check`. Several extensions
possible, see below.
## Installation
As the package is not (yet?) on CRAN, do
```r
remotes::install_github("eddelbuettel/rcppcorels")
```
Note of the [GNU GMP library](https://gmplib.org/) is now optional;
`configure` will enable (via a `-DGMP` define and link instructions) if
found. GMP will improve performance, so you may want to do `sudo apt-get
install libgmp-dev`, or whatever equivalent command you need to install it on
your system.
## TODOs
Plenty such as adding Travis CI support, adding configure code to detect GNU
GMP presence, adding examples, factoring out (input) data reader code,
possibly visualizing decision trees, and more.
## Author
Dirk Eddelbuettel wrote the R package and integration.
Nicholas Larus-Stone and Elaine Angelino wrote the C++ implementation of
Corels.
Elaine Angelino, Nicholas Larus-Stone, Daniel Alabi, Margo Seltzer, and
Cynthia Rudin wrote the paper.
Corels uses the rulelib library by Yang _et al_ described in the [2016 arXiv paper
by Hongyu Yang, Cynthia Rudin, and Margo Seltzer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.08610) with
[this code repo](https://github.com/Hongyuy/sbrlmod) and in the [2015 arXiv
paper by Benjamin Letham, Cynthia Rudin, Tyler H. McCormick and David
Madigan](https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.01644) now published in _Annals of Statistics_.
## License
This package is released under the GPL-3, as is Corels.
The rulelib library is released under the MIT license.