Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-coreos
Dockerfiles and scripts for running Couchbase Server under Docker and CoreOS
https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-coreos
Last synced: 1 day ago
JSON representation
Dockerfiles and scripts for running Couchbase Server under Docker and CoreOS
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-coreos
- Owner: couchbaselabs
- Created: 2014-12-03T16:35:52.000Z (about 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-03-22T14:46:54.000Z (almost 8 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-12T16:19:13.139Z (9 months ago)
- Size: 137 KB
- Stars: 43
- Watchers: 187
- Forks: 16
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://gitter.im/couchbase/discuss?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge)
# Couchbase Server under Docker + CoreOS.
Here are instructions on how to fire up a Couchbase Server cluster running under CoreOS on AWS CloudFormation. You will end up with the following system:

*Disclaimer*: this approach to running Couchbase Server and Sync Gateway is entirely **experimental** and you should do your own testing before running a production system.
## Launch CoreOS instances via AWS Cloud Formation
Click the "Launch Stack" button to launch your CoreOS instances via AWS Cloud Formation:
[ ](https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?region=us-east-1#cstack=sn%7ECouchbase-CoreOS%7Cturl%7Ehttp://tleyden-misc.s3.amazonaws.com/couchbase-coreos/sync_gateway.template)
](https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?region=us-east-1#cstack=sn%7ECouchbase-CoreOS%7Cturl%7Ehttp://tleyden-misc.s3.amazonaws.com/couchbase-coreos/sync_gateway.template)
*NOTE: this is hardcoded to use the us-east-1 region, so if you need a different region, you should edit the URL accordingly*
Use the following parameters in the form:
* **ClusterSize**: 3 nodes (default)
* **Discovery URL**: as it says, you need to grab a new token from https://discovery.etcd.io/new and paste it in the box.
* **KeyPair**: use whatever you normally use to start EC2 instances. For this discussion, let's assumed you used `aws`, which corresponds to a file you have on your laptop called `aws.cer`
### Wait until instances are up

### ssh into a CoreOS instance
Go to the AWS console under EC2 instances and find the public ip of one of your newly launched CoreOS instances.

Choose any one of them (it doesn't matter which), and ssh into it as the **core** user with the cert provided in the previous step:
```
$ ssh -i aws.cer -A [email protected]
```
## Sanity check
Let's make sure the CoreOS cluster is healthy first:
```
$ fleetctl list-machines
```
This should return a list of machines in the cluster, like this:
```
MACHINE IP METADATA
03b08680... 10.33.185.16 -
209a8a2e... 10.164.175.9 -
25dd84b7... 10.13.180.194 -
```
## Launch cluster
```
$ sudo docker run --net=host tleyden5iwx/couchbase-cluster-go:0.8.6 couchbase-fleet launch-cbs \
--version latest \
--num-nodes 3 \
--userpass "user:passw0rd" \
--docker-tag 0.8.6
```
Where:
* --version= Couchbase Server version -- see [Docker Tags](https://registry.hub.docker.com/u/couchbase/server/tags) for a list of versions that can be used.
* --num-nodes= number of couchbase nodes to start
* --userpass the username and password as a single string, delimited by a colon (:)
* --etcd-servers= Comma separated list of etcd servers, or omit to connect to etcd running on localhost
* --docker-tag= if present, use this docker tag the couchbase-cluster-go version in spawned containers, otherwise, default to "latest"
Replace `user:passw0rd` with a sensible username and password. It **must** be colon separated, with no spaces. The password itself must be at least 6 characters.
After you kick it off, you can expect it to take approximately **10-20 minutes** to download the Docker images and bootstrap the cluster. Once it's finished, you should see the following log entry:
```
Cluster is up!
```
If you never got that far, you can check your output against this [expected output](https://gist.github.com/tleyden/6b903e40cf87b5dd4ed8). Please file an [issue](https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-coreos/issues) here.
## Verify
To check the status of your cluster, run:
```
$ fleetctl list-units
```
You should see three units, all as active.
```
UNIT MACHINE ACTIVE SUB
[email protected] 3c819355.../10.239.170.243 active running
[email protected] 782b35d4.../10.168.87.23 active running
[email protected] 7cd5f94c.../10.234.188.145 active running
```
# Login to Admin Web UI
* Find the public ip of any of your CoreOS instances via the AWS console
* In a browser, go to `http://:8091`
* Login with the username/password you provided above
You should see:
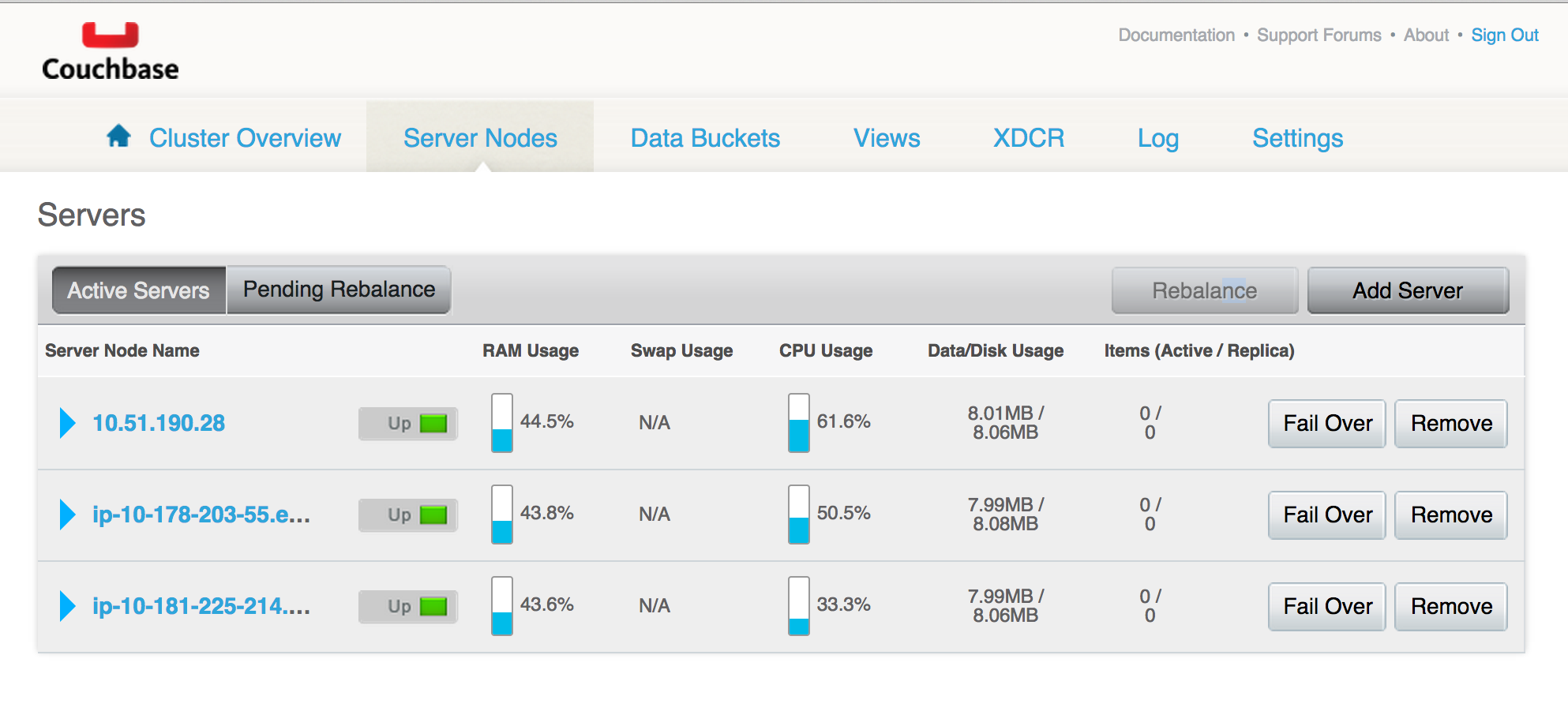
Congratulations! You now have a 3 node Couchbase Server cluster running under CoreOS / Docker.
# Sync Gateway
The steps below will walk you through adding Sync Gateway into the cluster.

### Kick off Sync Gateway cluster
```
$ sudo docker run --net=host tleyden5iwx/couchbase-cluster-go:0.8.6 sync-gw-cluster launch-sgw \
--num-nodes=1 \
--config-url=http://git.io/b9PK \
--create-bucket todos \
--create-bucket-size 512 \
--create-bucket-replicas 1 \
--docker-tag 0.8.6
```
Where:
* --num-nodes= number of sync gw nodes to start
* --config-url= the url where the sync gw config json is stored
* --sync-gw-commit= the branch or commit of sync gw to use, defaults to "image", which is the master branch at the time the docker image was built.
* --create-bucket= create a bucket on couchbase server with the given name
* --create-bucket-size= if creating a bucket, use this size in MB
* --create-bucket-replicas= if creating a bucket, use this replica count (defaults to 1)
* --etcd-servers= Comma separated list of etcd servers, or omit to connect to etcd running on localhost
* --docker-tag= if present, use this docker tag for spawned containers, otherwise, default to "latest"
### View cluster
After the above script finishes, run `fleetctl list-units` to list the services in your cluster, and you should see:
```
UNIT MACHINE ACTIVE SUB
[email protected] 2ad1cfaf.../10.95.196.213 active running
[email protected] a688ca8e.../10.216.199.207 active running
[email protected] fb241f71.../10.153.232.237 active running
[email protected] 2ad1cfaf.../10.95.196.213 active running
```
They should all be in the `active` state. If any are in the `activating` state -- which is normal because it might take some time to download the docker image -- then you should wait until they are all active before continuing.
## Verify internal
**Find internal ip**
```
$ fleetctl list-units
sync_gw_node.1.service 209a8a2e.../10.164.175.9 active running
```
**Curl**
On the CoreOS instance you are already ssh'd into, Use the ip found above and run a curl request against the server root:
```
$ curl 10.164.175.9:4984
{"couchdb":"Welcome","vendor":{"name":"Couchbase Sync Gateway","version":1},"version":"Couchbase Sync Gateway/master(6356065)"}
```
## Verify external
**Find external ip**
Using the internal ip found above, go to the EC2 Instances section of the AWS console, and hunt around until you find the instance with that internal ip, and then get the public ip for that instance, eg: `ec2-54-211-206-18.compute-1.amazonaws.com`
**Curl**
From your laptop, use the ip found above and run a curl request against the server root:
```
$ curl ec2-54-211-206-18.compute-1.amazonaws.com:4984
{"couchdb":"Welcome","vendor":{"name":"Couchbase Sync Gateway","version":1},"version":"Couchbase Sync Gateway/master(6356065)"}
```
Congratulations! You now have a Couchbase Server + Sync Gateway cluster running.
## Kicking off more Sync Gateway nodes.
To launch two more Sync Gateway nodes, run the following command:
```
$ sudo docker run --net=host tleyden5iwx/couchbase-cluster-go:0.8.6 sync-gw-cluster launch-sgw \
--num-nodes=2 \
--config-url=http://git.io/b9PK \
--docker-tag 0.8.6
```
## Shutting down the cluster.
Warning: if you try to shutdown the individual ec2 instances, **you must use the CloudFormation console**. If you try to shutdown the instances via the EC2 control panel, AWS will restart them, because that is what the CloudFormation is telling it to do.
Here is the web UI where you need to shutdown the cluster:

## Extended instructions
* [Disabling CoreOS restarts](https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-coreos/wiki/Disabling-CoreOS-auto-restart)
* [Running Sync Gateway behind an Nginx proxy](https://github.com/tleyden/couchbase-cluster-go#running-sync-gateway-behind-an-nginx-proxy)
* [How reboots are handled](https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-server-docker/issues/3#issuecomment-75984021)
* [Couchbase-Cluster-Go README](https://github.com/tleyden/couchbase-cluster-go/blob/master/README.md)
## References
* [Couchbase Server on Dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/u/couchbase/server)
* [Sync Gateway on Dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/u/couchbase/sync-gateway)
* [couchbase-cluster-go github repo](https://github.com/tleyden/couchbase-cluster-go)
* [How I built couchbase 2.2 for docker](https://gist.github.com/dustin/6605182) by [@dlsspy](https://twitter.com/dlsspy)
* https://registry.hub.docker.com/u/ncolomer/couchbase/
* https://github.com/lifegadget/docker-couchbase