https://github.com/cst/cst
:herb: JavaScript Concrete Syntax Tree
https://github.com/cst/cst
ast babylon cst
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
:herb: JavaScript Concrete Syntax Tree
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cst/cst
- Owner: cst
- License: mit
- Created: 2015-06-11T17:44:47.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-12-06T19:46:59.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-01T22:47:58.654Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: ast, babylon, cst
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.03 MB
- Stars: 458
- Watchers: 25
- Forks: 21
- Open Issues: 39
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://travis-ci.org/cst/cst)
# JavaScript CST implementation
## CST
Check out code [samples](https://github.com/cst/cst/wiki/How-to-add-a-property-to-an-object) and rest of the wiki for more.
`CST` means Concrete Syntax Tree. Unlike an `AST` (Abstract Syntax Tree), a `CST` contains all the information
from the JavaScript source file: whitespace, punctuators, comments. This information is extremely useful for
code style checkers and other code linters. `CST` is also useful for cases when you need to apply modifications
to existing JavaScript files while preserving the initial file formatting.
This `CST` implementation is designed to be `100%` compatible with JS `AST` (https://github.com/estree/estree).
Main principles:
* CST contains all the information from a parsed file (including whitespace and comments).
* Compatible with AST (https://github.com/estree/estree).
* Requires tokens to modify CST structure.
* The tree is always valid (it protects itself against breaking changes).
* CST can be rendered to valid JS at any time.
Let's see an example:
```js
x = 0;
if (x) x++;
```
The CST for this example:
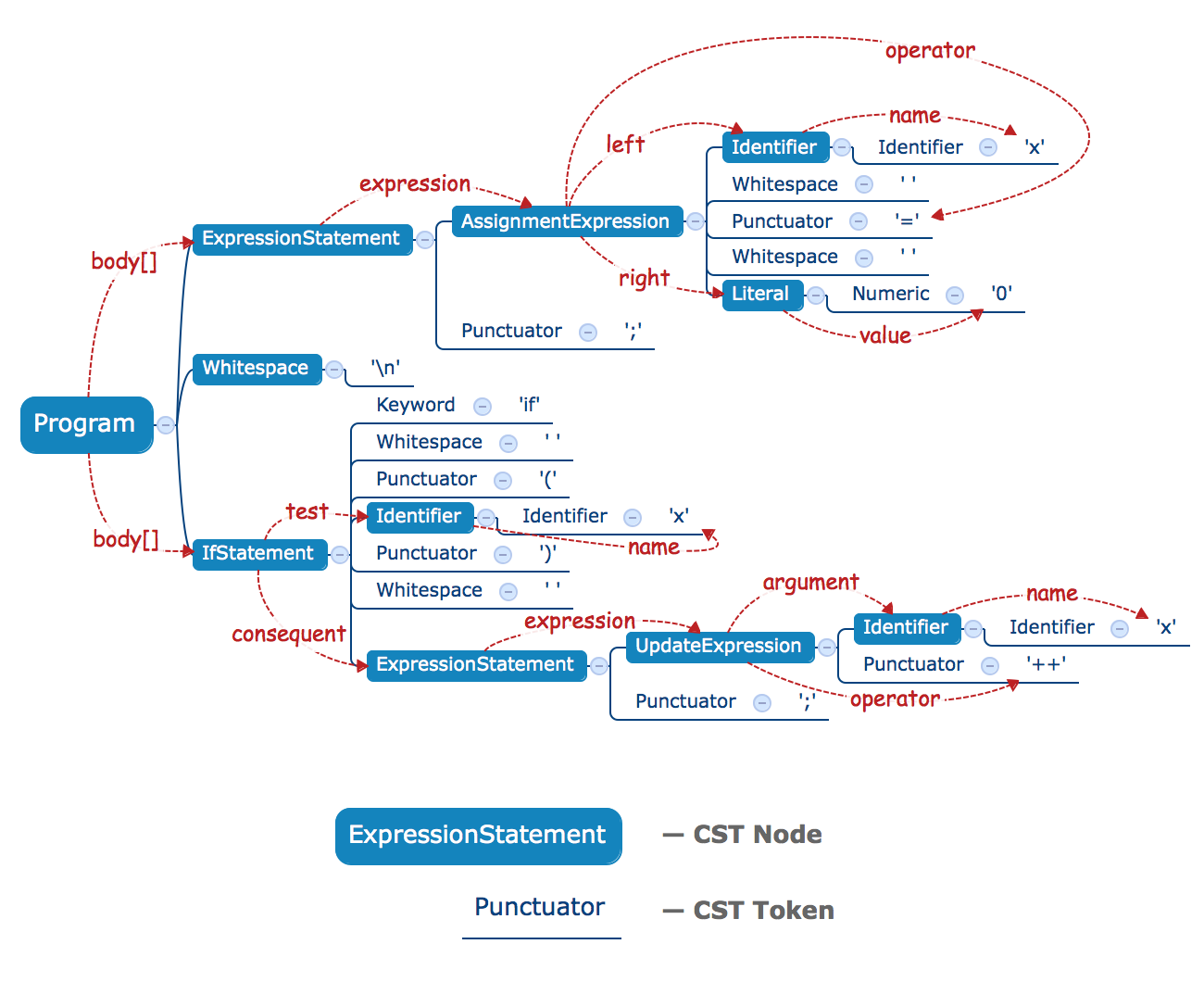
* Blue text — CST Tokens.
* White text in blue blocks — CST Nodes (their structure is equal to an AST).
* Blue lines — CST Structure.
* Red lined — AST Links.
## Classes
### Element
`Element` is the base class for `Node` and `Token`.
```js
declare class Element {
// traversal for children
childElements: Array;
firstChild: ?Element;
lastChild: ?Element;
// traversal for parent
parentElement: ?Element;
// traversing between siblings
nextSibling: ?Element;
previousSibling: ?Element;
// traversing to first/last tokens (not only direct tokens)
getFirstToken(): ?Token;
getLastToken(): ?Token;
// traversing to next/previous tokens (not only siblings)
getNextToken(): ?Token;
getPreviousToken(): ?Token;
// Code properties
type: string;
isToken: boolean;
isNode: boolean;
isExpression: boolean;
isStatement: boolean;
isWhitespace: boolean;
isFragment: boolean;
isModuleDeclaration: boolean;
isModuleSpecifier: boolean;
// Code methods
getSourceCode(): string;
getSourceCodeLength(): number;
// Mutation methods
// appends child to the end of the `Element`
appendChild(newElement: Element): void;
// prepends child to the end of the `Element`
prependChild(newElement: Element): void;
// inserts child before `referenceChild`
insertChildBefore(newElement: Element, referenceChild: Element): void;
// replaces specified child interval (from `firstChildRef` to lastChildRef`) with specified child.
replaceChildren(newElement: Element, firstRefChild: Element, lastRefChild: Element): void;
// Location methods
getRange(): Range;
getLoc(): Location;
}
declare class Token extends Element {
// token value
value: string;
}
type Range = [
start: number;
end: number;
];
type Position = {
line: number,
column: number
};
type Location = {
start: Position,
end: Position
};
```
### Node
`Node` extends `Element`. The Nodes are the "AST part of a CST". If you drop everything but Nodes from a `CST`, you will
get a pure `AST` from the Node structure. So it is fair to say that Nodes provide the `AST` logic for a `CST`. Currently
only Nodes can contain children.
The Node property `isNode` always returns `true`.
### Token
`Token` extends `Element`. The purpose of a `CST` is to have tokens in the tree. By only manipulating tokens,
we can change code formatting without any effect on the behaviour.
The Token property `isToken` always returns `true`.