https://github.com/curran/setuphadoop
Shell scripts and instructions for setting up Hadoop on a cluster.
https://github.com/curran/setuphadoop
Last synced: 18 days ago
JSON representation
Shell scripts and instructions for setting up Hadoop on a cluster.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/curran/setuphadoop
- Owner: curran
- License: mit
- Created: 2015-03-01T00:04:37.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2015-03-11T17:19:50.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-07T03:43:12.313Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Shell
- Size: 153 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# setupHadoop
Shell scripts and instructions for setting up Hadoop on a cluster. Intended for use with fresh instances of Ubuntu Server 14.04.1 LTS on Amazon EC2. The instructions below show how to set up a 2 node cluster.
## Creating Instances
First, create two virtual machines using the Amazon Web Interface.
* Click through Services -> EC2 -> Instances -> Launch Instance.
* Select "Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type".
* Click "Review and Launch", then click "Launch".
* On the dialog "Select an existing key pair...", select "Create a new pair"
* Enter a name for the key pair (I used "cloudTest")
* Click "Download Key Pair", which will download "cloudTest.pem"
* Click "Launch Instance"
* Click "View Instances" to get back to the instances page.
* Repeat this process a second time, this time using the existing key pair "cloudTest", to create a second instance.
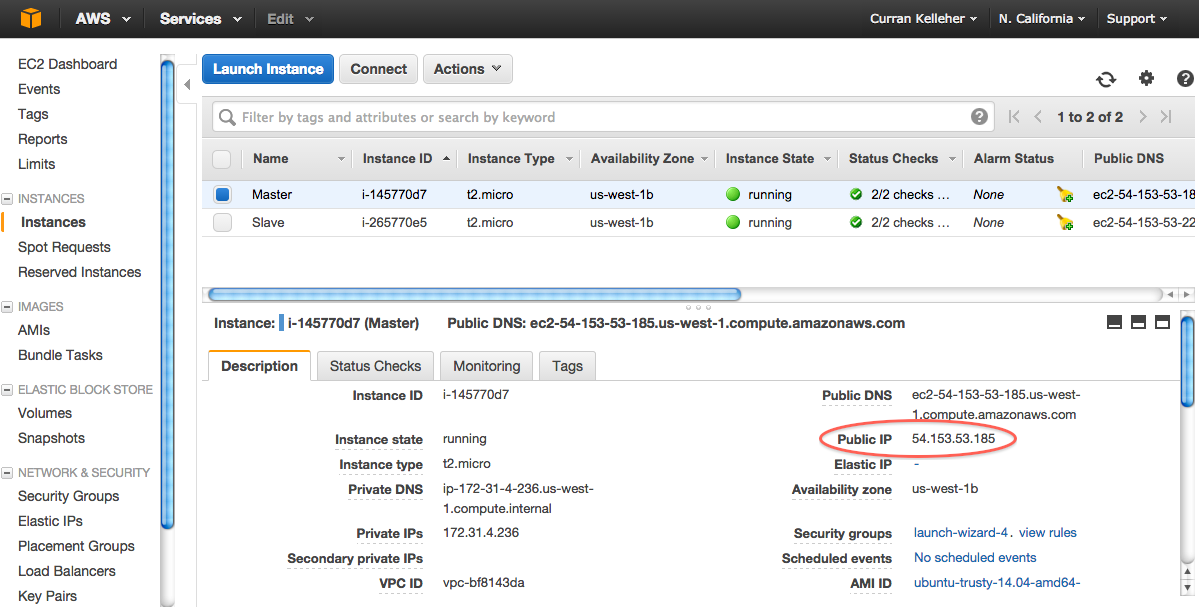
Once you have created two instances, you can name them by clicking on the empty "Name" field. For example, you can name them "Master" and "Slave", to help keep track of which is which. After doing this, you should see a listing like this:
## Connecting to an Instance
In a terminal, go to the directory where "cloudTest.pem" is.
`cd ~/Downloads`
Make sure the key file is not visible to others via ssh.
`chmod 400 cloudTest.pem`
If you don't do this, then you'll see this error later:
```
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
@ WARNING: UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE! @
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
```
Find the public IP of your instance in the AWS Web Interface.
Connect to the instance via SSH using the following command.
`ssh -i cloudTest.pem ubuntu@`
For example,
`ssh -i cloudTest.pem ubuntu@54.67.81.195`
Type "yes" at the prompt `Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes`
Once logged in, you can check what your Ubuntu version is by running
`lsb_release -a`
## Set Up Hadoop
Copy and paste this entire script into your console after logging into an instance. This should be done for all machines in the cluster.
```
sudo apt-get update;\
sudo apt-get install -y git default-jdk;\
curl -O http://mirror.cogentco.com/pub/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-2.6.0/hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz;\
tar xfz hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz;\
sudo mv hadoop-2.6.0 /usr/local/hadoop;\
rm hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz;\
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa;\
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys;\
echo export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64 >> ~/.bashrc;\
echo export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop >> ~/.bashrc;\
echo export YARN_CONF_DIR=/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop >> ~/.bashrc;\
echo export PATH=\$PATH:/usr/local/hadoop/bin >> ~/.bashrc;\
echo export PATH=\$PATH:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin >> ~/.bashrc;\
source ~/.bashrc
```
For the master, copy these config files into Hadoop directory.
```
git clone https://github.com/curran/setupHadoop.git; \
cd setupHadoop; \
cp -r master/* $HADOOP_CONF_DIR
```
We will want to access the Web Interfaces for HDSF and Yarn, which are blocked by default with AWS. Allow all traffic into the master node by scrolling to the right in the AWS instance listing page, clicking the link in the "Security Groups" column -> "Inbound" tab -> "Edit" button -> "Add Rule" button -> change "Custom TCP Rule" to "All TCP" -> "Save" button
# Setting up a Cluster
The approach to setting up a cluster is to first set up many machines as independent single-node Hadoop clusters, then reconfigure them such that one is a master and the others are slaves. Then you need to "start the cluster" by starting HDFS and YARN from the _master node only_. The master node will connect to slave nodes via SSH and start the appropriate processes on each, namely DataNode for HDFS and ResourceManager for YARN.
Since the master node needs to communicate to slaves over SSH, we need to add the public key of the master machine to the list of allowed hosts in the slave machine(s). To do this:
* Log into the master node over SSH
* Execute `cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub`
* Copy the output to the clipboard
* Log into the slave node over SSH
* Edit the file `~/.ssh/authorized_keys`
* Paste the contents of the clipboard into a new line of the file
* Save and close the file
(There very well may be a nicer way of doing this, please send a pull request if there is!)
## Getting HDFS to Work
Choose a single machine to be the master node for HDFS, which will run the NameNode daemon. All other machines will be slaves, and will run the DataNode daemon.
To set up a slave machine, do the following:
Edit the file `/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml`. Change the `fs.defaultFS` value to use the IP of the master node (found using `ifconfig` ran on the master node). This IP is also listed in the Amazon Web Interface, called "Private IP".
The file should look something like this:
```
fs.default.name
hdfs://52.11.95.33:9000
```
The following commands are defined in `/usr/local/hadoop/bin` and `/usr/local/hadoop/sbin`. They are available as commands to execute because these paths were added to `$PATH` by `setupHadoop.sh`.
Format the file system.
`hdfs namenode -format` WARNING - if you want to set up a cluster, make sure all configurations are set before executing this. If this is executed with config for a single machine, then it seems to break the state of the system and you cannot get the full cluster working without starting from scratch.
`start-dfs.sh` Start HDFS. This will launch the NameNode and DataNode Hadoop daemons on the master AND slaves (via SSH).
`stop-dfs.sh` Stop HDFS on master and slaves.
You can always check to see which daemons are running on a given node by executing `jps`. The output will look something like this:
```
$ jps
11296 NameNode
11453 DataNode
11768 Jps
```
Now you should see the following page on port `50070` of your master node:
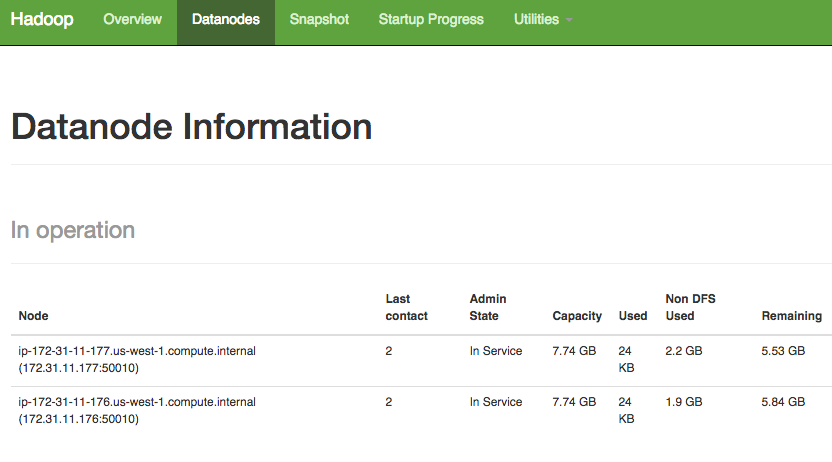
A working HDFS cluster with 2 DataNodes. (on port `50070`)
# Getting YARN to work
To get YARN working, edit the file `/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml` to set the IP of the Resource Manager (on both master and slave machines). In my case this is the same as the HDFS name node.
```
yarn.resourcemanager.hostname
52.11.95.33
```
Now run
`start-yarn.sh` to start,
`stop-yarn.sh` to stop.
After starting YARN, you should see the following page on port `8088` of your master node:
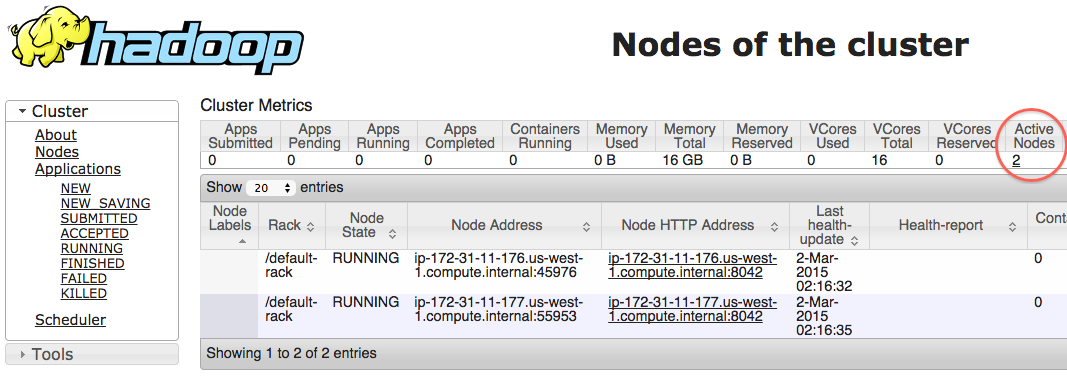
A working YARN cluster with 2 NodeManagers. (on port `8088`)
### Reformatting HDFS
If your HDFS somehow gets corrupted, you can reformat everything like this:
```
stop-yarn.sh
stop-dfs.sh
rm -r -f /tmp/hadoop-ubuntu/* # do this on all machines
hdfs namenode -format # do this on master
start-dfs.sh
start-yarn.sh
```
### Notes
When trying to run a Spark shell in YARN with the following command
`./bin/spark-shell --master yarn-client`
The YARN application initializes (I can see it in the YARN Web UI), but I get the following error after about 10 seconds:
```
15/03/04 00:32:35 WARN remote.ReliableDeliverySupervisor: Association with remote system [akka.tcp://sparkYarnAM@ip-172-31-4-232.us-west-1.compute.internal:57241] has failed, address is now gated for [5000] ms. Reason is: [Disassociated].
```
This seems to be [related to RAM capacity](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/28671171/spark-shell-cannot-connect-to-yarn). I am using AWS Micro instances that have only 1GB of RAM. Using the following command will show you memory usage every second on a given machine:
`watch -n 1 free -m`
The free memory was falling to around 60MB when the YARN connection gets "dissociated".
To get the Spark Shell to work on YARN on my Mac laptop, I experienced the same error as described in the blog post [YARN Job Problem: Application application_** failed 1 times due to AM Container for XX exited with exitCode: 127](https://cloudcelebrity.wordpress.com/2014/01/31/yarn-job-problem-application-application_-failed-1-times-due-to-am-container-for-xx-exited-with-exitcode-127/) and applied his solution:
`sudo ln -s /usr/bin/java /bin/java`
What finally worked in the Spark Shell in YARN-client mode:
```
val data = sc.textFile("hdfs://localhost:9000/data/adult/data.csv")
data.first()
```
Note the port 9000 in the hdfs URL. If no port is specified, the system assumes post 8020 (as listed in the [default HDFS ports](https://ambari.apache.org/1.2.3/installing-hadoop-using-ambari/content/reference_chap2_1.html)), which is not the default used by HDFS. The default is 9000.
Draws from
* https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-hadoop-on-ubuntu-13-10
* http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/ClusterSetup.html
* http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/SingleCluster.html
* http://www.alexjf.net/blog/distributed-systems/hadoop-yarn-installation-definitive-guide/
* https://help.ubuntu.com/community/CheckingYourUbuntuVersion
* http://www.michael-noll.com/tutorials/running-hadoop-on-ubuntu-linux-multi-node-cluster/
* https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3rb111Z9TVI
By Curran Kelleher March 2015