https://github.com/cvg/depthsplat
[CVPR'25] DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth
https://github.com/cvg/depthsplat
feed-forward-gaussian-splatting monocular-depth multi-view-stereo view-synthesis
Last synced: 7 days ago
JSON representation
[CVPR'25] DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/cvg/depthsplat
- Owner: cvg
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-10-17T21:30:02.000Z (7 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-27T20:35:08.000Z (25 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-27T21:29:23.412Z (25 days ago)
- Topics: feed-forward-gaussian-splatting, monocular-depth, multi-view-stereo, view-synthesis
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://haofeixu.github.io/depthsplat/
- Size: 2.24 MB
- Stars: 777
- Watchers: 28
- Forks: 35
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth
Haofei Xu
·
Songyou Peng
·
Fangjinhua Wang
·
Hermann Blum
·
Daniel Barath
·
Andreas Geiger
·
Marc Pollefeys
CVPR 2025
Paper | Project Page | Models
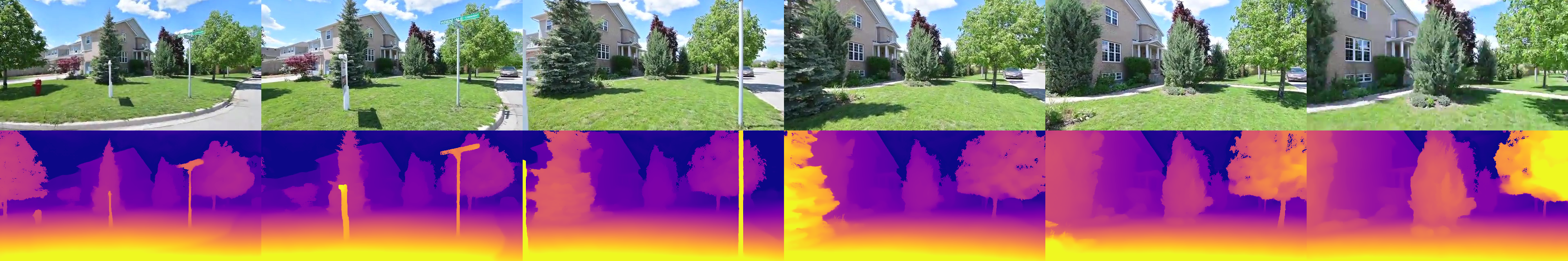
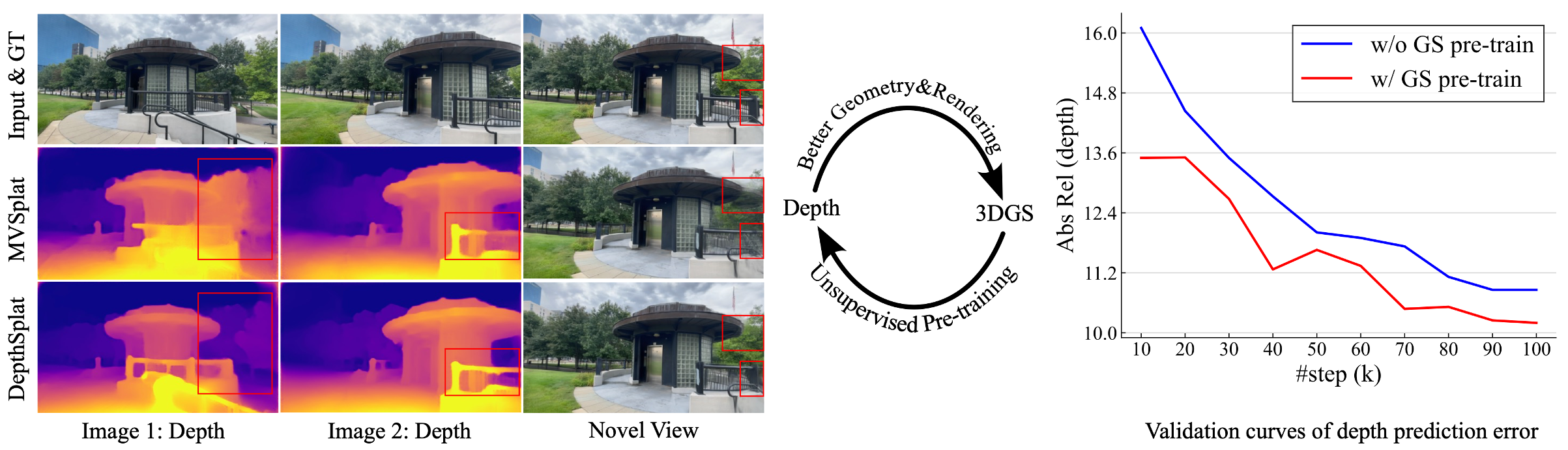
DepthSplat enables cross-task interactions between Gaussian splatting and depth estimation.
Left: Better depth leads to improved novel view synthesis with Gaussian splatting.
Right: Unsupervised depth pre-training with Gaussian splatting leads to reduced depth prediction error.
## Updates
- 2025-03-27: We simplified our model architecture while preparing the CVPR camera-ready version. The models have been re-trained, and the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.13862) has been updated accordingly. [The new models](MODEL_ZOO.md) are now simpler, faster, and perform as well as or better than the previous version.
## Installation
Our code is developed using PyTorch 2.4.0, CUDA 12.4, and Python 3.10.
We recommend setting up a virtual environment using either [conda](https://docs.anaconda.com/miniconda/) or [venv](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html) before installation:
```bash
# conda
conda create -y -n depthsplat python=3.10
conda activate depthsplat
# or venv
# python -m venv /path/to/venv/depthsplat
# source /path/to/venv/depthsplat/bin/activate
# installation
pip install torch==2.4.0 torchvision==0.19.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Model Zoo
Our pre-trained models are hosted on [Hugging Face 🤗](https://huggingface.co/haofeixu/depthsplat).
Model details can be found at [MODEL_ZOO.md](MODEL_ZOO.md).
## Camera Conventions
The camera intrinsic matrices are normalized, with the first row divided by the image width and the second row divided by the image height.
The camera extrinsic matrices follow the OpenCV convention for camera-to-world transformation (+X right, +Y down, +Z pointing into the screen).
## Datasets
For dataset preparation, please refer to [DATASETS.md](DATASETS.md).
## Gaussian Splatting
### Useful configs
- `dataset.test_chunk_interval=1`: Running on the full test set can be time-consuming due to the large number of scenes. You can run on a fraction of the test set for debugging or validation purposes. For example, setting `dataset.test_chunk_interval=10` will evaluate on 1/10 of the full test set.
- `output_dir=outputs/depthsplat`: Directory to save the results.
- `test.save_image=true`: Save the rendered images.
- `test.save_gt_image=true`: Save the ground truth (GT) images.
- `test.save_input_images=true`: Save the input images.
- `test.save_depth=true`: Save the predicted depths.
- `test.save_depth_concat_img=true`: Save the concatenated images and depths.
- `test.save_depth_npy=true`: Save the raw depth predictions in `.npy`.
- `test.save_gaussian=true`: Save the reconstructed Gaussians in `.ply` files, which can be viewed using online viewers like [SuperSplat](https://superspl.at/editor), [Antimatter15](https://antimatter15.com/splat/), etc.
### Rendering Video
DepthSplat enables feed-forward reconstruction from 12 input views (512x960 resolutions) in 0.6 seconds on a single A100 GPU.
#### RealEstate10K
6 input views at 512x960 resolutions: click to expand the script
- A preprocessed subset is provided to quickly run inference with our model, please refer to the details in [DATASETS.md](DATASETS.md).
```
# render video on re10k (need to have ffmpeg installed)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=1 \
dataset.roots=[datasets/re10k_720p] \
dataset.image_shape=[512,960] \
dataset.ori_image_shape=[720,1280] \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=4 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=8 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitb \
model.encoder.gaussian_adapter.gaussian_scale_max=0.1 \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-base-re10kdl3dv-448x768-randview2-6-f8ddd845.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=6 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/re10k_ctx_6v_video.json \
test.save_video=true \
test.compute_scores=false \
test.render_chunk_size=10 \
output_dir=outputs/depthsplat-re10k-512x960
```
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/3f228a3f-8d54-4a90-9db4-ff0874150883
2 input views at 256x256 resolutions:
```
# render video on re10k (need to have ffmpeg installed)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=re10k \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=100 \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=2 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitl \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-large-re10k-256x256-view2-e0f0f27a.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/evaluation_index_re10k_video.json \
test.save_video=true \
test.compute_scores=false
output_dir=outputs/depthsplat-re10k
```
#### DL3DV
12 input views at 512x960 resolutions:
- A preprocessed subset is provided to quickly run inference with our model, please refer to the details in [DATASETS.md](DATASETS.md).
- Tip: use `test.stablize_camera=true` to stablize the camera trajectory.
```
# render video on dl3dv (need to have ffmpeg installed)
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=1 \
dataset.roots=[datasets/dl3dv_960p] \
dataset.image_shape=[512,960] \
dataset.ori_image_shape=[540,960] \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=8 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=8 \
model.encoder.gaussian_adapter.gaussian_scale_max=0.1 \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-small-re10kdl3dv-448x768-randview4-10-c08188db.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=12 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/dl3dv_start_0_distance_100_ctx_12v_video.json \
test.save_video=true \
test.stablize_camera=true \
test.compute_scores=false \
test.render_chunk_size=10 \
output_dir=outputs/depthsplat-dl3dv-512x960
```
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/ea6d3b9c-af80-43e6-9a12-36c67e874366
### Evaluation
#### RealEstate10K
Evaluation scripts (small, base, and large models)
Please note that the numbers may differ slightly from those reported in the paper, as the models have been re-trained.
- To evalute the large model:
```
# Table 1 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=re10k \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=1 \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=2 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitl \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-large-re10k-256x256-view2-e0f0f27a.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation
```
- To evaluate the base model:
```
# Table 1 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=re10k \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=1 \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=2 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitb \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-base-re10k-256x256-view2-ca7b6795.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation
```
- To evaluate the small model:
```
# Table 1 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=re10k \
dataset.test_chunk_interval=1 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=4 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-small-re10k-256x256-view2-cfeab6b1.pth \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation
```
#### DL3DV
Evaluation scripts (6, 4, 2 input views, and zero-shot generalization)
- 6 input views:
```
# Table 7 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=6 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/dl3dv_start_0_distance_50_ctx_6v_video_0_50.json \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=4 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=8 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitb \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-base-dl3dv-256x448-randview2-6-02c7b19d.pth
```
- 4 input views:
```
# Table 7 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=4 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/dl3dv_start_0_distance_50_ctx_4v_video_0_50.json \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=4 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=8 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitb \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-base-dl3dv-256x448-randview2-6-02c7b19d.pth
```
- 2 input views:
```
# Table 7 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=2 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/dl3dv_start_0_distance_50_ctx_2v_video_0_50.json \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=4 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=8 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitb \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-base-dl3dv-256x448-randview2-6-02c7b19d.pth
```
- Zero-shot generalization from RealEstate10K to DL3DV:
```
# Table 8 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=dl3dv \
mode=test \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=2 \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/dl3dv_start_0_distance_10_ctx_2v_tgt_4v.json \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=2 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitl \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-large-re10k-256x256-view2-e0f0f27a.pth
```
#### ACID
Evaluation scripts (zero-shot generalization)
- Zero-shot generalization from RealEstate10K to ACID:
```
# Table 8 of depthsplat paper
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python -m src.main +experiment=re10k \
mode=test \
dataset.roots=[datasets/acid] \
dataset.view_sampler.index_path=assets/evaluation_index_acid.json \
dataset/view_sampler=evaluation \
dataset.view_sampler.num_context_views=2 \
model.encoder.num_scales=2 \
model.encoder.upsample_factor=2 \
model.encoder.lowest_feature_resolution=4 \
model.encoder.monodepth_vit_type=vitl \
checkpointing.pretrained_model=pretrained/depthsplat-gs-large-re10k-256x256-view2-e0f0f27a.pth
```
### Training
- Before training, you need to download the pre-trained [UniMatch](https://github.com/autonomousvision/unimatch) and [Depth Anything V2](https://github.com/DepthAnything/Depth-Anything-V2) weights, and set up your [wandb account](config/main.yaml) (in particular, by setting `wandb.entity=YOUR_ACCOUNT`) for logging.
```
wget https://s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/avg-projects/unimatch/pretrained/gmflow-scale1-things-e9887eda.pth -P pretrained
wget https://huggingface.co/depth-anything/Depth-Anything-V2-Small/resolve/main/depth_anything_v2_vits.pth -P pretrained
```
- By default, we train our models using four GH200 GPUs (96GB VRAM each). However, this is not a strict requirement—our model can be trained on different GPUs as well. For example, we have verified that configurations such as four RTX 4090 GPUs (24GB VRAM each) or a single A100 GPU (80GB VRAM) can achieve very similar results, with a PSNR difference of at most 0.1 dB. Just ensure that the total number of training samples, calculated as (number of GPUs × `data_loader.train.batch_size` × `trainer.max_steps`), remains the same. Check out the scripts [scripts/re10k_depthsplat_train.sh](scripts/re10k_depthsplat_train.sh) and [scripts/dl3dv_depthsplat_train.sh](scripts/dl3dv_depthsplat_train.sh) for details.
## Depth Prediction
We fine-tune our Gaussian Splatting pre-trained depth model using ground-truth depth supervision. The depth models are trained with a randomly selected number of input images (ranging from 2 to 8) and can be used for depth prediction from multi-view posed images. For more details, please refer to [scripts/inference_depth.sh](scripts/inference_depth.sh).
## Citation
```
@inproceedings{xu2024depthsplat,
title = {DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth},
author = {Xu, Haofei and Peng, Songyou and Wang, Fangjinhua and Blum, Hermann and Barath, Daniel and Geiger, Andreas and Pollefeys, Marc},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2025}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
This project is developed with several fantastic repos: [pixelSplat](https://github.com/dcharatan/pixelsplat), [MVSplat](https://github.com/donydchen/mvsplat), [MVSplat360](https://github.com/donydchen/mvsplat360), [UniMatch](https://github.com/autonomousvision/unimatch), [Depth Anything V2](https://github.com/DepthAnything/Depth-Anything-V2) and [DL3DV](https://github.com/DL3DV-10K/Dataset). We thank the original authors for their excellent work.