https://github.com/danielmartensson/adaptive-control
Adaptive control methods developed by Karl Johan Åström and Björn Wittenmark from the 70-80's for industrial use
https://github.com/danielmartensson/adaptive-control
adaptive-control kalmanfilter model-reference-adaptive-control mras scilab self-tuning simulation xcos
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Adaptive control methods developed by Karl Johan Åström and Björn Wittenmark from the 70-80's for industrial use
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/danielmartensson/adaptive-control
- Owner: DanielMartensson
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-07-08T16:12:14.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-23T09:25:33.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-06T15:25:54.592Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: adaptive-control, kalmanfilter, model-reference-adaptive-control, mras, scilab, self-tuning, simulation, xcos
- Language: MATLAB
- Homepage:
- Size: 9.33 MB
- Stars: 101
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 32
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: Readme.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Introduction
This is a collection of adaptive control methods from the book "Adaptive Control" by Karl Johan Åström and Björn Wittenmark.
They are the masters of the classical methods for self tuning controllers. The book is made for an industrial audience and PhD students in
control theory. Those control methods is most used for hydraulic and electrical servo systems in space engineering and flight engineering and also in advanced control engineering problems for robotics at the industry.
The book has sevral interesting control methods:
* Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - For optimal systems
* Linear Quadratic Gaussian (LQG) - With kalman filtering
* Linear Quadratic Estimator (LQE) - Finding the kalman gain matrix
* Generalized Predictive Controller (GPC) - For future prediction
* Self Tuning Regulator (STR) - For deterministic systems
* Minimum Variance Controller (MVC) - For heavy stochastical systems
* Model Reference Adaptive Controller (MRAC) - For smooth reference tracking
* Extended Least Square (ELS) - For estimate stochastical models e.g ARMAX models
* Recursive Least Square (RLS) - For estimate transfer functions
The book does not contain this, but I have by my self read lots of papes about subspace identification and constrained control. At the bottom of this page, I will present:
* Adaptive Constrained MPC (ERAOKIDMPC) - Using Subspace identification methods
The collection is made by the open source software Scilab and Xcox 6.0.1 and the book "Adaptive Control"

# C code
If you want to try adaptive control with C-code. Have a look at this. It also work for embedded systems. MATLAB-files and C-code files as examples is available:
https://github.com/DanielMartensson/CControl
# Unscented Kalman Filter
I very good filter for you is the Unscented Kalman Filter for nonlinear and linear systems. Easy to use and easier than regular kalman filter.
https://github.com/DanielMartensson/Unscented-Kalman-Filter
# Square Root Uncented Kalman Filter for state estimation and parameter estimation
A very good algorithm located in here.
https://github.com/DanielMartensson/MataveID
# Identification library
If you want to identify models, then this library is for you - Mataveid.
https://github.com/DanielMartensson/mataveid
# Projects
This is a automatic brewery made of an MRAS adaptive controller. The project contains two controllers. The code is made in FLProg 8.1.0 for the school students at the Institution of Applied Hydraulics 2023.
The MRAS controller gives a very high accuracy, about +- 0.1 temperature error.
The project contains:
* 1 x Arduino UNO
* 6 x Digital inputs
* 3 x Digital outputs
* 1 x LCD 16x4 with I2C
* 2 x MAX31865 PT100 transmitters
* 3 x SSR DC/AC relay as output for the heating element
The FLProg 8.1.0 software

Inside of the eletronics

Outside of the box. No sensors are connected right now.

* Ärvärde = Measurement
* Börvärde = Setpoint/Reference
* Räknare = Counter for ON-time at the relays
* Värde på regulator = ON-time threshold for the regulator
* Integral summorna (4st med väldigt små värden) = Integral sums (4 pcs with very small values)

# Linear Quadratic Regulator
Diagram of the LQR system

Simulation of the LQR system. The green signal is the input signal and the black signal is the output signal. Between 0 to 50 seconds, the estimator learn the system behaviour.

Parameter estimation of the LQR system.

# Linear Quadratic Gaussian
Diagram of the LQG system. Here we can se that the system has a LQE - Linear Quadratic estimator and a Kalman Filter

Simulation of the LQG system. Green is our input signal, black is our noisy output signal and red is our filtered output signal by using a kalman filter.

# Generalized Predictive Control
Diagram of the GPC system

Simulation of the GPC system. The green line is our reference following line and the black line is the system output.

There is the input signal. Between 0 to 30 seconds, the GPC controller learns the system behaviour.

# Self Tuning Regulator - Minimum phase system
Diagram of the STR system with minimum phase. Here I use Recursive Least Square and STR learning the system between 0 to 15 seconds, then tune the STR controller.

# Self Tuning Regulator - Non-Minimum phase system
Diagram of the STR system with non-minimum phase. The difference between non-minimum phase and minimum phase is that non-minimum phase has zeros at the right half plane and minimum phase has zeros on the left half plane. On other words, non-minimum phase is much more difficult to handle.

# Minimum Variance Controller
Diagram of the MVC system. I'm using Extended Least Square to estimate a ARMAX model, it's a transfer function with disturbance.

Simulation of the MVC system. Here is green the input signal and black the output signal. Between 0 to 70 seconds, the MVC self learning the disturbance.

Here is the parameter estimation for the ARMAX model.

# Model Reference Adaptive Controller - MIT Rule
Diagram of MRAC system with uning of MIT rule

Simulation of MRAC system

# Model Reference Adaptive Controller - Lyapunov Rule
Diagram of MRAC system with uning of Lyapunov rule

Simulation of MRAC system. According to me - Lyapunov is much better than MIT rule.

# Extended Least Square
Diagram of ELS

Simulation of ELS. Here is the green signal our measured signal and the black signal is our estimated signal.

Parameter estimation

# Recursive Least Square
Diagram of RLS

Simulation of RLS

Parameter estimation of RLS

# Adaptive Constrained MPC
This simulation uses Eigensystem Realization Algorithm and Observer Kalmanfilter Identifcation to estimate a state space model by using the subspace identification technique. Minimal data is used. The code is available inside the Octave folder.
Second order system:
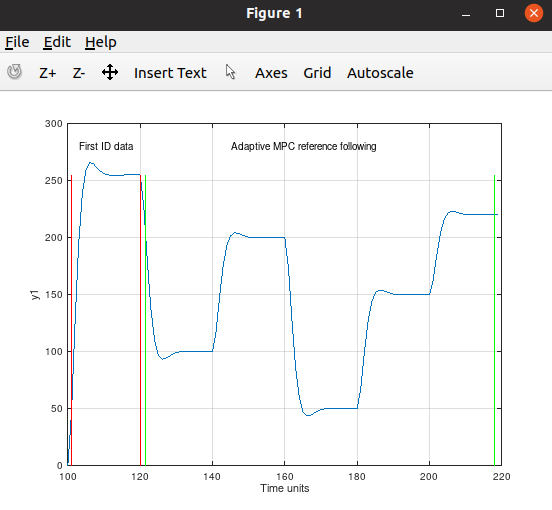
First order system (no change in the parameters for MPC):
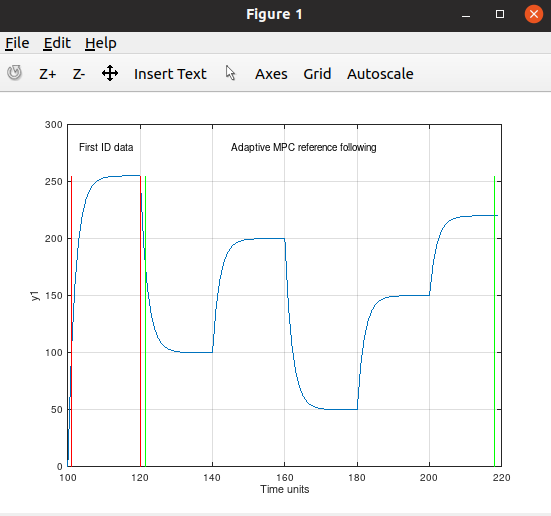
Second order with heavy time varying damping. It still tune in and follow the reference:
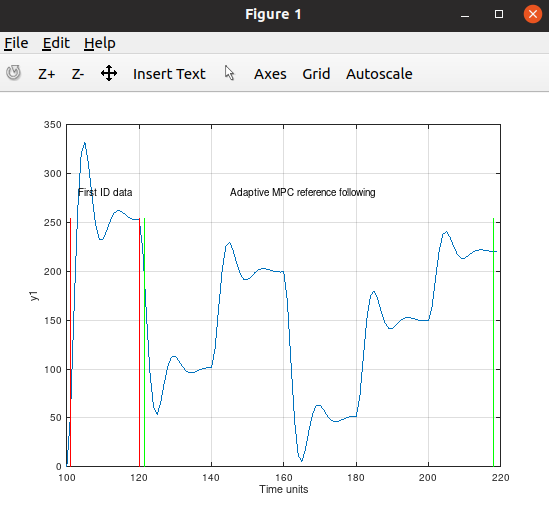
Second order with heavy time varying inertia.

The weakness of this MPC controller have is when it becomes radical changes for the static gain, like a mechanical spring changes its stiffness or a large watertank got extra or less isolation to prevent/increase e.g temperature leaks, or a capacitor changes its capacity. But if the mass of the spring changes, or the density of the water changes or the viscosity of the water changes or the electronic circuit changes its resistance or the coil got changes for the inductance, the adaptive MPC controller will handle it.