https://github.com/databricks/lilac
Curate better data for LLMs
https://github.com/databricks/lilac
artificial-intelligence data-analysis dataset-analysis unstructured-data
Last synced: about 1 year ago
JSON representation
Curate better data for LLMs
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/databricks/lilac
- Owner: databricks
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2023-03-23T21:19:10.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-03-19T12:41:30.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-07T04:47:19.399Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: artificial-intelligence, data-analysis, dataset-analysis, unstructured-data
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://lilacml.com
- Size: 37 MB
- Stars: 1,016
- Watchers: 13
- Forks: 97
- Open Issues: 88
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Lilac
Better data, better AI
Lilac is a tool for exploration, curation and quality control of datasets for training, fine-tuning
and monitoring LLMs.
Lilac is used by companies like [Cohere](https://cohere.com/) and
[Databricks](https://www.databricks.com/) to visualize, quantify and improve the quality of
pre-training and fine-tuning data.
Lilac runs **on-device** using open-source LLMs with a UI and Python API.
## 🆒 New
- [Lilac Garden](https://www.lilacml.com/#garden) is our hosted platform for blazing fast
dataset-level computations. [Sign up](https://forms.gle/Gz9cpeKJccNar5Lq8) to join the pilot.
- Cluster & title millions of documents with the power of LLMs.
[Explore and search](https://lilacai-lilac.hf.space/datasets#lilac/OpenOrca&query=%7B%7D&viewPivot=true&pivot=%7B%22outerPath%22%3A%5B%22question__cluster%22%2C%22category_title%22%5D%2C%22innerPath%22%3A%5B%22question__cluster%22%2C%22cluster_title%22%5D%7D)
over 36,000 clusters of 4.3M documents in OpenOrca
## Why use Lilac?
- Explore your data interactively with LLM-powered search, filter, clustering and annotation.
- Curate AI data, applying best practices like removing duplicates, PII and obscure content to
reduce dataset size and lower training cost and time.
- Inspect and collaborate with your team on a single, centralized dataset to improve data quality.
- Understand how data changes over time.
Lilac can offload expensive computations to [Lilac Garden](https://www.lilacml.com/#garden), our
hosted platform for blazing fast dataset-level computations.

> See our [3min walkthrough video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RrcvVC3VYzQ)
## 🔥 Getting started
### 💻 Install
```sh
pip install lilac[all]
```
If you prefer no local installation, you can duplicate our
[Spaces demo](https://lilacai-lilac.hf.space/) by following documentation
[here](https://docs.lilacml.com/deployment/huggingface_spaces.html).
For more detailed instructions, see our
[installation guide](https://docs.lilacml.com/getting_started/installation.html).
### 🌐 Start a webserver
Start a Lilac webserver with our `lilac` CLI:
```sh
lilac start ~/my_project
```
Or start the Lilac webserver from Python:
```py
import lilac as ll
ll.start_server(project_dir='~/my_project')
```
This will open start a webserver at http://localhost:5432/ where you can now load datasets and
explore them.
### Lilac Garden
Lilac Garden is our hosted platform for running dataset-level computations. We utilize powerful GPUs
to accelerate expensive signals like Clustering, Embedding, and PII.
[Sign up](https://forms.gle/Gz9cpeKJccNar5Lq8) to join the pilot.
- Cluster and title **a million** data points in **20 mins**
- Embed your dataset at **half a billion** tokens per min
- Run your own signal
### 📊 Load data
Datasets can be loaded directly from HuggingFace, Parquet, CSV, JSON,
[LangSmith from LangChain](https://www.langchain.com/langsmith), SQLite,
[LLamaHub](https://llamahub.ai/), Pandas, Parquet, and more. More documentation
[here](https://docs.lilacml.com/datasets/dataset_load.html).
```python
import lilac as ll
ll.set_project_dir('~/my_project')
dataset = ll.from_huggingface('imdb')
```
If you prefer, you can load datasets directly from the UI without writing any Python:
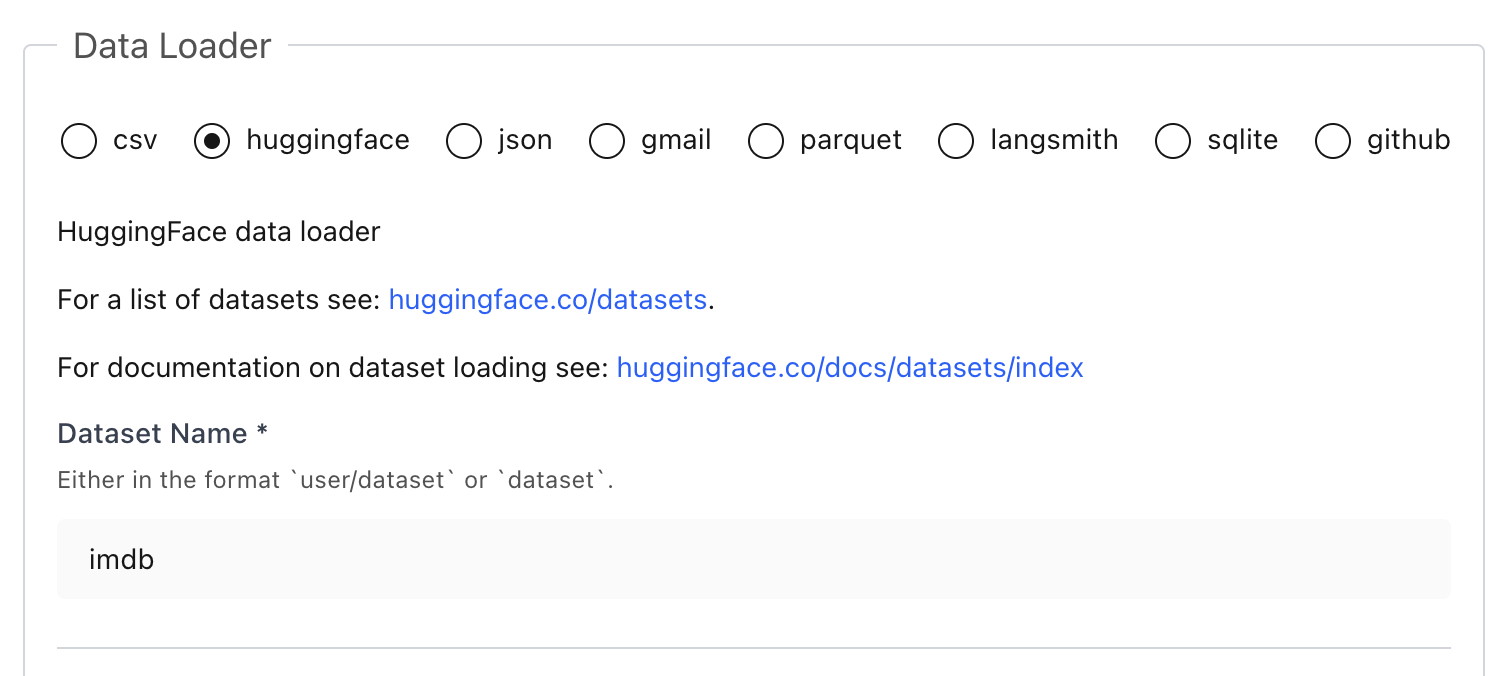
### 🔎 Explore
> [!NOTE]
> 🔗 Explore [OpenOrca](https://lilacai-lilac.hf.space/datasets#lilac/OpenOrca) and
> [its clusters](https://lilacai-lilac.hf.space/datasets#lilac/OpenOrca&query=%7B%7D&viewPivot=true&pivot=%7B%22outerPath%22%3A%5B%22question__cluster%22%2C%22category_title%22%5D%2C%22innerPath%22%3A%5B%22question__cluster%22%2C%22cluster_title%22%5D%7D)
> before installing!
Once we've loaded a dataset, we can explore it from the UI and get a sense for what's in the data.
More documentation [here](https://docs.lilacml.com/datasets/dataset_explore.html).

### ✨ Clustering
Cluster any text column to get automated dataset insights:
```python
dataset = ll.get_dataset('local', 'imdb')
dataset.cluster('text') # add `use_garden=True` to offload to Lilac Garden
```
> [!TIP]
> Clustering on device can be slow or impractical, especially on machines without a powerful GPU or
> large memory. Offloading the compute to [Lilac Garden](https://www.lilacml.com/#garden), our
hosted data processing platform, can speedup clustering by more than 100x.

### ⚡ Annotate with Signals (PII, Text Statistics, Language Detection, Neardup, etc)
Annotating data with signals will produce another column in your data.
```python
dataset = ll.get_dataset('local', 'imdb')
dataset.compute_signal(ll.LangDetectionSignal(), 'text') # Detect language of each doc.
# [PII] Find emails, phone numbers, ip addresses, and secrets.
dataset.compute_signal(ll.PIISignal(), 'text')
# [Text Statistics] Compute readability scores, number of chars, TTR, non-ascii chars, etc.
dataset.compute_signal(ll.PIISignal(), 'text')
# [Near Duplicates] Computes clusters based on minhash LSH.
dataset.compute_signal(ll.NearDuplicateSignal(), 'text')
# Print the resulting manifest, with the new field added.
print(dataset.manifest())
```
We can also compute signals from the UI:

### 🔎 Search
Semantic and conceptual search requires computing an embedding first:
```python
dataset.compute_embedding('gte-small', path='text')
```
#### Semantic search
In the UI, we can search by semantic similarity or by classic keyword search to find chunks of
documents similar to a query:

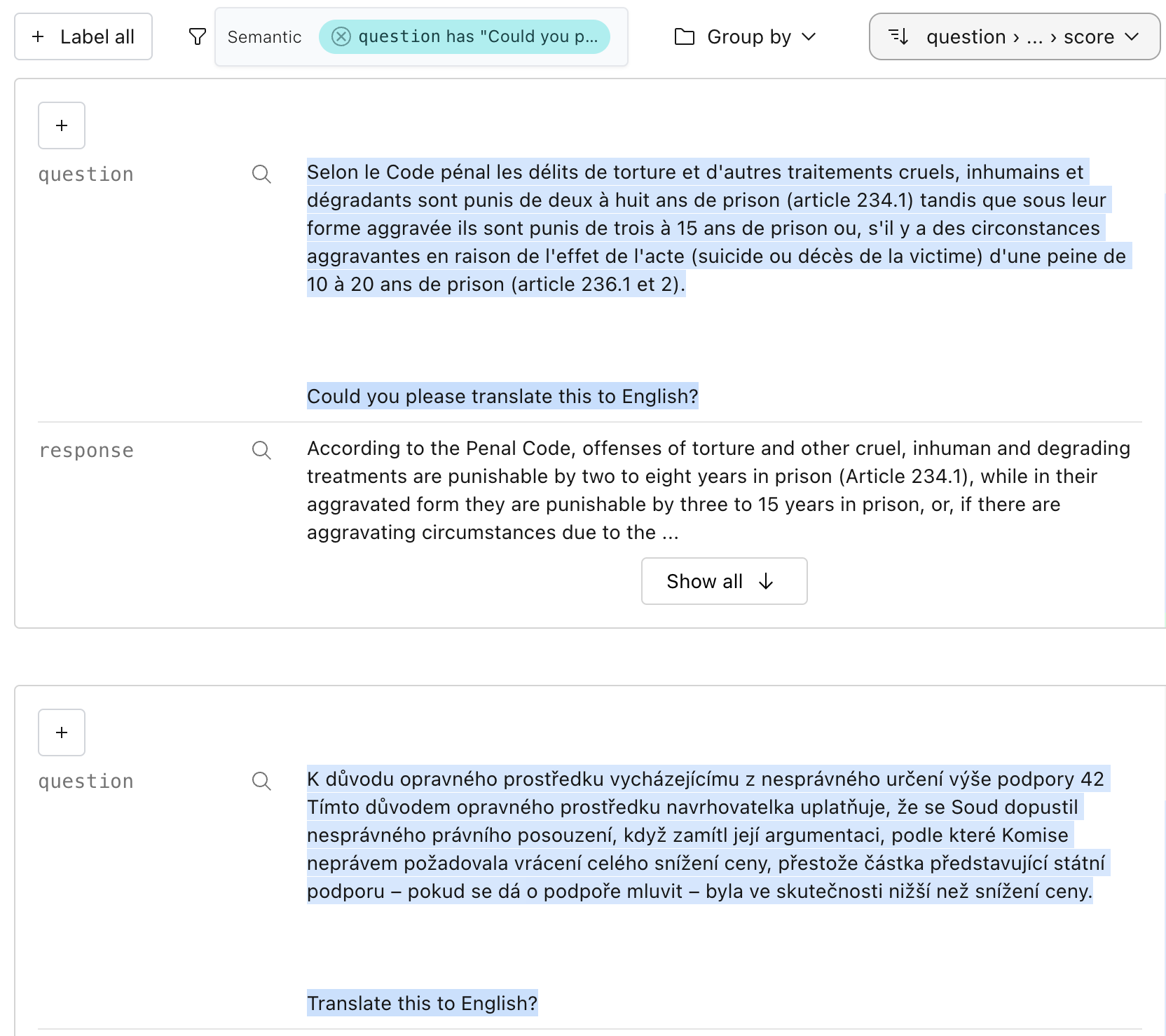
We can run the same search in Python:
```python
rows = dataset.select_rows(
columns=['text', 'label'],
searches=[
ll.SemanticSearch(
path='text',
embedding='gte-small')
],
limit=1)
print(list(rows))
```
#### Conceptual search
Conceptual search is a much more controllable and powerful version of semantic search, where
"concepts" can be taught to Lilac by providing positive and negative examples of that concept.
Lilac provides a set of built-in concepts, but you can create your own for very specif
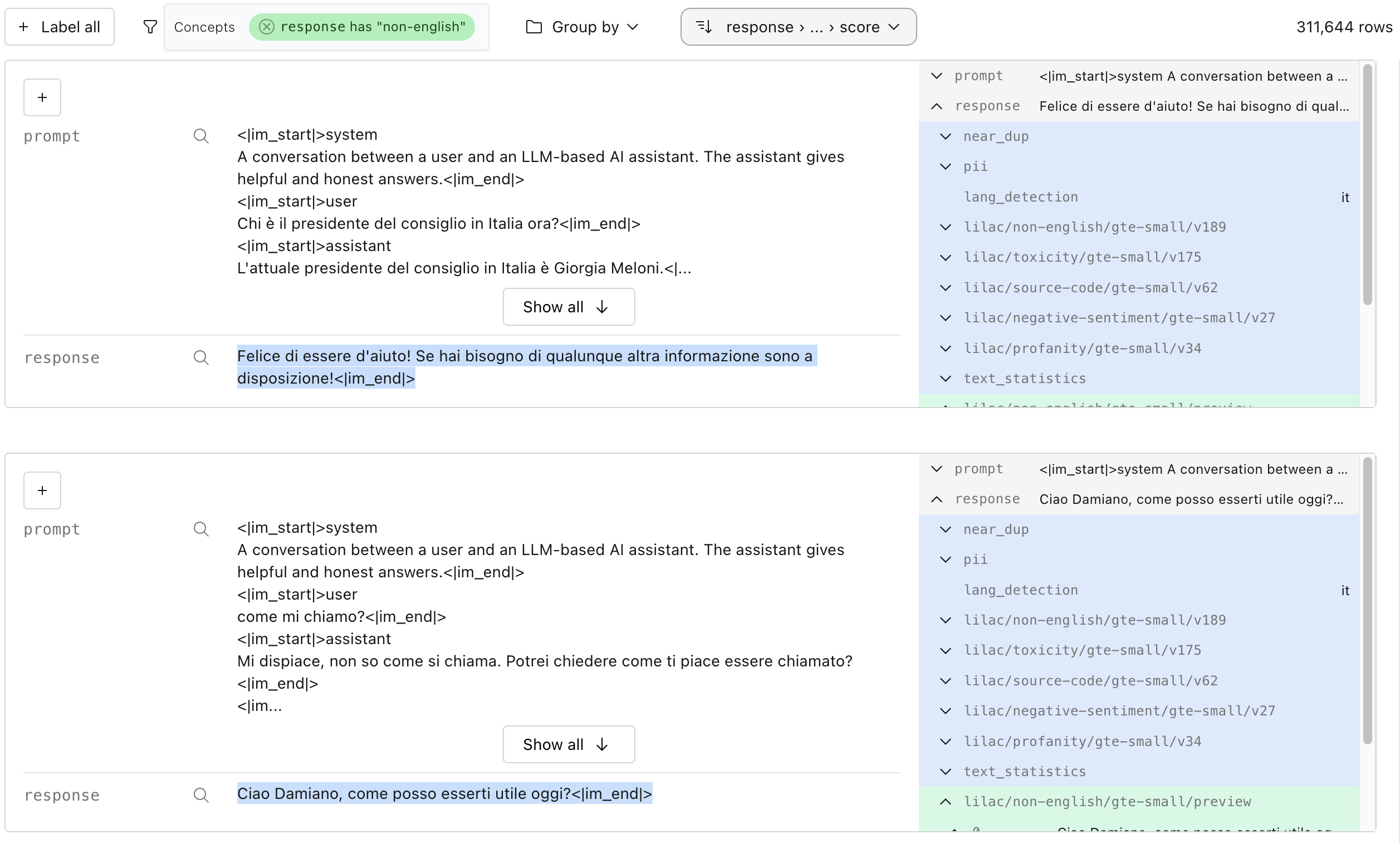
We can create a concept in Python with a few examples, and search by it:
```python
concept_db = ll.DiskConceptDB()
db.create(namespace='local', name='spam')
# Add examples of spam and not-spam.
db.edit('local', 'spam', ll.concepts.ConceptUpdate(
insert=[
ll.concepts.ExampleIn(label=False, text='This is normal text.'),
ll.concepts.ExampleIn(label=True, text='asdgasdgkasd;lkgajsdl'),
ll.concepts.ExampleIn(label=True, text='11757578jfdjja')
]
))
# Search by the spam concept.
rows = dataset.select_rows(
columns=['text', 'label'],
searches=[
ll.ConceptSearch(
path='text',
concept_namespace='lilac',
concept_name='spam',
embedding='gte-small')
],
limit=1)
print(list(rows))
```
### 🏷️ Labeling
Lilac allows you to label individual points, or slices of data:

We can also label all data given a filter. In this case, adding the label "short" to all text with a
small amount of characters. This field was produced by the automatic `text_statistics` signal.

We can do the same in Python:
```python
dataset.add_labels(
'short',
filters=[
(('text', 'text_statistics', 'num_characters'), 'less', 1000)
]
)
```
Labels can be exported for downstream tasks. Detailed documentation
[here](https://docs.lilacml.com/datasets/dataset_labels.html).
## 💬 Contact
For bugs and feature requests, please
[file an issue on GitHub](https://github.com/lilacai/lilac/issues).
For general questions, please [visit our Discord](https://discord.com/invite/jNzw9mC8pp).



