https://github.com/datakitchen/dataops-observability
DataOps Observability is part of DataKitchen's Open Source Data Observability. DataOps Observability monitors every data journey from data source to customer value, from any team development environment into production, across every tool, team, environment, and customer so that problems are detected, localized, and understood immediately.
https://github.com/datakitchen/dataops-observability
data data-engineering data-observability data-science dataops pipleine-monitoring
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
DataOps Observability is part of DataKitchen's Open Source Data Observability. DataOps Observability monitors every data journey from data source to customer value, from any team development environment into production, across every tool, team, environment, and customer so that problems are detected, localized, and understood immediately.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/datakitchen/dataops-observability
- Owner: DataKitchen
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-04-17T11:23:27.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-20T22:48:15.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-24T05:23:27.841Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: data, data-engineering, data-observability, data-science, dataops, pipleine-monitoring
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://datakitchen.io
- Size: 3.79 MB
- Stars: 42
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# DataOps Observability
  [](https://hub.docker.com/r/datakitchen/dataops-observability) [](https://docs.datakitchen.io/articles/#!dataops-observability-help/dataops-observability-help)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/datakitchen/dataops-observability-be)
[](https://data-observability-slack.datakitchen.io/join)
*
DataOps Observability is part of DataKitchen's Open Source Data Observability. DataOps Observability monitors every data journey from data source to customer value, from any team development environment into production, across every tool, team, environment, and customer so that problems are detected, localized, and understood immediately.
*
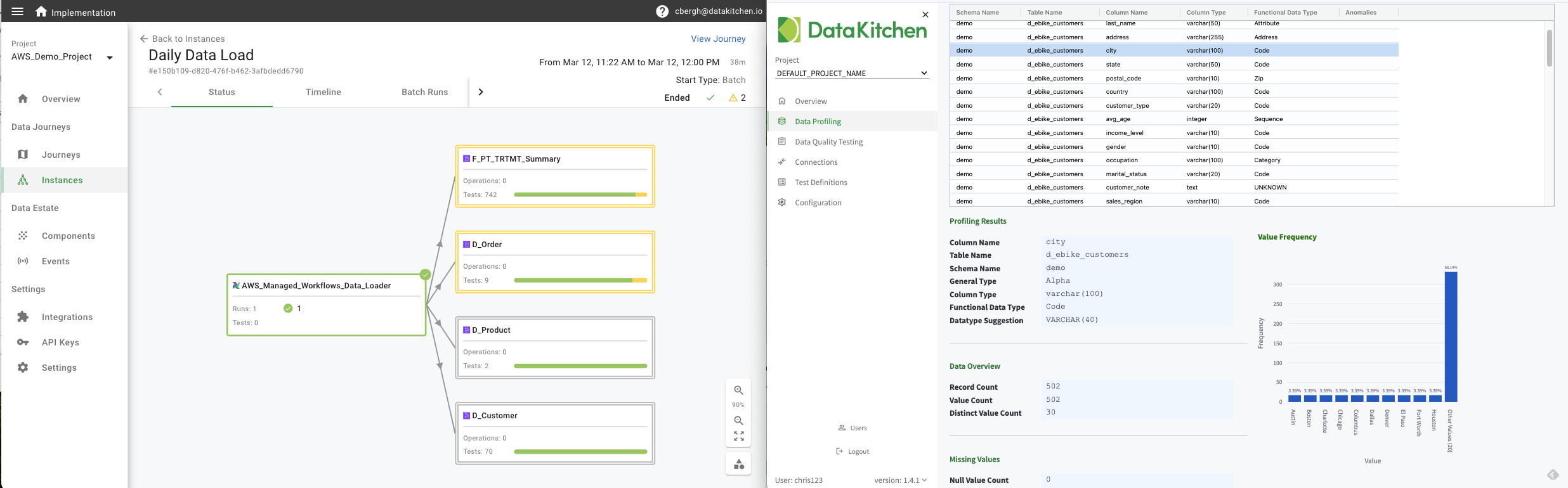
## Developer Setup
**This repository requires `Python 3.10` at minimum -- prefer the latest `3.10.X`.**
A local Kubernetes cluster requires
* [docker](https://www.docker.com/)
* [helm](https://helm.sh/)
* [minikube](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/)
### Installation
Prefer using a virtual Python environment when installing. Tools such as
[virtualenv](https://virtualenv.pypa.io) can be used to set up the environment
using a specific Python version. [pyenv](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv) can be
used to install the desired Python version if your choice of OS does not provide
it for you.
Example install
```bash
python -m virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python3.10 venv
source venv/bin/activate
# Install platform and developer extra packages
pip install --editable '.[dev]'
```
### Testing
`pytest` is used to run test.
```bash
cd /to/observability
pytest # runs both unit and integration tests
```
### Invoke Testing
While tests can be run with ``pytest `` there is an invoke handler to run tests using common patterns. The
tests are run in parallel by default (which can help determine if there are any unexpected dependencies between tests)
so that running the tests locally takes less time.
**NOTE:** *Requires* ``pytest-xdist`` *package to be installed. This is specified as a* **dev** *dependency when you
perform initial environment setup. If you set up your local environment before the invoke commands were added, you
may need to install this package.*
#### Commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---------|---------|
| `invoke test.all` | Run all tests |
| `invoke test.unit` | Run all tests marked as unittests |
| `invoke test.integration` | Run all tests marked as integration tests |
#### Arguments
All of the ``invoke text.`` commands have a few common arguments you may pass.
- ``--level= `` [str] (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL) Set logging output level. DEFAULT: DEBUG
- ``--maxfail=`` [int] Maximum number of tests allowed to fail before aborting test run. DEFAULT: 10
- ``--processes=`` [int] Number of test processes to run in parallel. DEFAULT: 5
Example:
```shell
$ invoke test.all --processes=2 --level="INFO" --maxfail=50
```
## Running the App
After installing the [required tools](#developer-setup), run `invoke deploy.local` for an initial local installation of
the Observability backend. It creates a minikube node in a docker instance (i.e. in a separate logical machine) running the
required infrastructure along with the Observability services. Destroy the installation with `invoke deploy.nuke`.
[More `invoke` info](#additional-tools).
### Useful commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---------|---------|
| `minikube ssh` | SSH into minikube machine |
| `minikube service list` | List all services and the endpoints to reach them |
| `minikube image build ` | Build docker image inside minikube machine |
| `minikube image load ` | Push docker image from host to minikube machine |
## Developer Experience
### Pre-commit + Linting
We enforce the use of certain linting tools. To not get caught by the build-system's checks, you should use
`pre-commit` to scan your commits before they go upstream.
The following hooks are enabled in pre-commit:
- `black`: The black formatter is enforced on the project. We use a basic configuration. Ideally this should solve any and all
formatting questions we might encounter.
- `isort`: the isort import-sorter is enforced on the project. We use it with the `black` profile.
To enable pre-commit from within your virtual environment, simply run:
```bash
pip install pre-commit
pre-commit install
```
### Additional tools
These tools should be used by the developer because the build-system will enforce that the code complies with them.
These tools are pinned in the `dev` extra-requirements of `pyproject.toml`, so you can acquire them with
```sh
# within environment
pip install .[dev]
```
We use the following additional tools:
- `pytest`: This tool is used to run the test e.g. `pytest .`
- `mypy`: This is a static and dynamic type-checking tool. This also checks for unreachable and non-returning code. See `pyproject.toml` for its settings. This
tool is not included in pre-commit because doing so would require installing this repo's package and additional stubs into the pre-commit environment, which
is inadvised by pre-commit, and poorly supported.
- `invoke` (shorthand `inv`): This is a `make` replacement.
- Run `invoke --list` to see available commands and e.g. `invoke deploy.restart --help` for additional info on command `restart`.
- [Shell tab completion](https://docs.pyinvoke.org/en/stable/invoke.html#shell-tab-completion)
### FAQ: mypy errors
#### I've encountered 'Unused "type: ignore" comment'
Good news, this means that `mypy` has found symbols for the thing which you are ignoring. That means its time to enable
type-checking on these code-paths.
To resolve this error, do two things:
1. Remove the ignore and fix any type errors.
2. run `mypy . --install-types` and add any newly installed `types-*` packages installed to our `dev` dependencies.
## Community
### Getting Started Guide
We recommend you start by going through the [Data Observability Overview Demo](https://docs.datakitchen.io/articles/open-source-data-observability/data-observability-overview).
### Support
For support requests, [join the Data Observability Slack](https://data-observability-slack.datakitchen.io/join) and ask post on #support channel.
### Connect
Talk and Learn with other data practitioners who are building with DataKitchen. Share knowledge, get help, and contribute to our open-source project.
Join our community here:
* 🌟 [Star us on GitHub](https://github.com/DataKitchen/data-observability-installer)
* 🐦 [Follow us on Twitter](https://twitter.com/i/flow/login?redirect_after_login=%2Fdatakitchen_io)
* 🕴️ [Follow us on LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/company/datakitchen)
* 📺 [Get Free DataOps Fundamentals Certification](https://info.datakitchen.io/training-certification-dataops-fundamentals)
* 📚 [Read our blog posts](https://datakitchen.io/blog/)
* 👋 [Join us on Slack](https://data-observability-slack.datakitchen.io/join)
* 🗃 [Sign The DataOps Manifesto](https://DataOpsManifesto.org)
* 🗃 [Sign The Data Journey Manifesto](https://DataJourneyManifesto.org)
### Contributing
For details on contributing or running the project for development, check out our contributing guide (coming soon!).
### License
DataKitchen DataOps Observability is Apache 2.0 licensed.