https://github.com/datastax/astrapy
AstraPy is a Pythonic interface for DataStax Astra DB and the Data API
https://github.com/datastax/astrapy
astradb datastax python stargate
Last synced: 4 days ago
JSON representation
AstraPy is a Pythonic interface for DataStax Astra DB and the Data API
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/datastax/astrapy
- Owner: datastax
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2021-04-28T13:15:54.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-10-02T10:17:33.000Z (6 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-10-02T11:39:46.346Z (6 days ago)
- Topics: astradb, datastax, python, stargate
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://github.com/datastax/astrapy
- Size: 4.99 MB
- Stars: 34
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 31
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGES
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE.md
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# AstraPy
A pythonic client for [DataStax Astra DB](https://astra.datastax.com).
_This README targets **AstraPy version 2.0+**. Click [here](https://github.com/datastax/astrapy/blob/4601c5fa749925d961de1f114ca27690d1a71b13/README.md) for v1 and [here](https://github.com/datastax/astrapy/blob/cd3f5ce8146093e10a095709c0f5c3f8e3f2c7da/README.md) for the v0 API (which you should not really be using by now)._
## Quickstart
Install with `pip install astrapy`.
Get the *API Endpoint* and the *Token* to your Astra DB instance at [astra.datastax.com](https://astra.datastax.com).
Try the following code after replacing the connection parameters:
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.constants import VectorMetric
from astrapy.ids import UUID
from astrapy.info import CollectionDefinition
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
# Connect and create the Database object
my_client = DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
# Create a vector collection
my_collection = my_database.create_collection(
"dreams_collection",
definition=(
CollectionDefinition.builder()
.set_vector_dimension(3)
.set_vector_metric(VectorMetric.COSINE)
.build()
)
)
# Populate the collection with some documents
my_collection.insert_many(
[
{
"_id": UUID("018e65c9-e33d-749b-9386-e848739582f0"),
"summary": "Riding the waves",
"tags": ["sport"],
"$vector": [0, 0.2, 1],
},
{
"summary": "Friendly aliens in town",
"tags": ["scifi"],
"$vector": [-0.3, 0, 0.8],
},
{
"summary": "Meeting Beethoven at the dentist",
"$vector": [0.2, 0.6, 0],
},
],
)
my_collection.update_one(
{"tags": "sport"},
{"$set": {"summary": "Surfers' paradise"}},
)
# Run a vector search
cursor = my_collection.find(
{},
sort={"$vector": [0, 0.2, 0.4]},
limit=2,
include_similarity=True,
)
for result in cursor:
print(f"{result['summary']}: {result['$similarity']}")
# This would print:
# Surfers' paradise: 0.98238194
# Friendly aliens in town: 0.91873914
# Resource cleanup
my_collection.drop()
```
Next steps:
- More info and usage patterns are given in the docstrings of classes and methods
- [Data API reference](https://docs.datastax.com/en/astra-db-serverless/api-reference/overview.html)
- [AstraPy reference](https://docs.datastax.com/en/astra-api-docs/_attachments/python-client/astrapy/index.html)
- Package on [PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/astrapy/)
### Server-side embeddings
AstraPy works with the "vectorize" feature of the Data API. This means that one can define server-side computation for vector embeddings and use text strings in place of a document vector, both in writing and in reading.
The transformation of said text into an embedding is handled by the Data API, using a provider and model you specify.
```python
my_collection = database.create_collection(
"my_vectorize_collection",
definition=(
CollectionDefinition.builder()
.set_vector_service(
provider="example_vendor",
model_name="embedding_model_name",
authentication={"providerKey": ""} # if needed
)
.build()
)
)
my_collection.insert_one({"$vectorize": "text to make into embedding"})
documents = my_collection.find(sort={"$vectorize": "vector search query text"})
```
See the [Data API reference](https://docs.datastax.com/en/astra-db-serverless/databases/embedding-generation.html)
for more on this topic.
### Hybrid search
AstraPy supports the "findAndRerank" Data API command,
which performs a hybrid search by combining results from a lexical search
and a vector-based search in a single operation.
```python
r_results = my_collection.find_and_rerank(
sort={"$hybrid": "query text"},
limit=10,
include_scores=True,
)
for r_result in r_results:
print(r_result.document, r_results.scores)
```
This command will execute if the collection was created with the required settings
(they are enabled by default).
See the Data API reference, and the docstring for the `find_and_rerank` method,
for more on this topic.
### Using Tables
The example above uses a _collection_, where schemaless "documents" can be stored and retrieved.
Here is an equivalent code that uses Tables, i.e. uniform, structured data where each _row_ has the
same _columns_, which are of a specific type:
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.constants import VectorMetric
from astrapy.data_types import DataAPIVector
from astrapy.info import (
CreateTableDefinition,
ColumnType,
TableVectorIndexDefinition,
TableVectorIndexOptions,
)
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
# Connect and create the Database object
my_client = DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
# Create a table and a vector index on it
table_definition = (
CreateTableDefinition.builder()
.add_column("dream_id", ColumnType.INT)
.add_column("summary", ColumnType.TEXT)
.add_set_column("tags", ColumnType.TEXT)
.add_vector_column("dream_vector", dimension=3)
.add_partition_by(["dream_id"])
.build()
)
index_options=TableVectorIndexOptions(
metric=VectorMetric.COSINE,
)
my_table = my_database.create_table("dreams_table", definition=table_definition, if_not_exists=True)
my_table.create_vector_index("dreams_table_vec_idx", column="dream_vector", options=index_options, if_not_exists=True)
# Populate the table with some rows
my_table.insert_many(
[
{
"dream_id": 103,
"summary": "Riding the waves",
"tags": ["sport"],
"dream_vector": DataAPIVector([0, 0.2, 1]),
},
{
"dream_id": 119,
"summary": "Friendly aliens in town",
"tags": ["scifi"],
"dream_vector": DataAPIVector([-0.3, 0, 0.8]),
},
{
"dream_id": 37,
"summary": "Meeting Beethoven at the dentist",
"dream_vector": DataAPIVector([0.2, 0.6, 0]),
},
],
)
my_table.update_one(
{"dream_id": 103},
{"$set": {"summary": "Surfers' paradise"}},
)
# Run a vector search
cursor = my_table.find(
{},
sort={"dream_vector": DataAPIVector([0, 0.2, 0.4])},
limit=2,
include_similarity=True,
)
for result in cursor:
print(f"{result['summary']}: {result['$similarity']}")
# This would print:
# Surfers' paradise: 0.98238194
# Friendly aliens in town: 0.91873914
# Resource cleanup
my_table.drop()
```
For more on Tables, consult the [Data API documentation about Tables](https://docs.datastax.com/en/astra-db-serverless/api-reference/tables.html). Note that most features of Collections, with due modifications, hold for Tables as well (e.g. "vectorize", i.e. server-side embeddings).
#### Maps as association lists
When working with Tables, `map` columns with key of a type other than text
must be expressed as association lists,
i.e. nested lists of lists: `[[key1, value1], [key2, value2], ...]`, in payloads.
By default, `Table` objects in AstraPy will use the association-list representation
only for maps wrapped by a `DataAPIMap`, and leave regular Python `dict` objects
unchanged in payloads: in practice the following row would be sent to the API as shown:
```python
from astrapy.data_types import DataAPIMap
row_to_insert = {
"map_1": {"k": "v"},
"map_2": DataAPIMap({"k1": "v1", "k2": "v2"}),
}
# Will be serialized as JSON like this:
# {
# "map_1": {"k": "v"},
# "map_2": [["k1", "v1"], ["k2", "v2"]]
# }
```
This behaviour is controlled by the API Option `serdes_options.encode_maps_as_lists_in_tables`,
which defaults to `MapEncodingMode.DATAAPIMAPS`. Other options are:
- `MapEncodingMode.ALWAYS` to convert also regular Python `dict` values into lists of pairs;
- `MapEncodingMode.NEVER` to never apply such conversion.
The following code demonstrates getting a `Table` object with the desired setting:
```python
from astrapy.api_options import APIOptions, SerdesOptions
from astrapy.constants import MapEncodingMode
my_options = APIOptions(serdes_options=SerdesOptions(
encode_maps_as_lists_in_tables=MapEncodingMode.ALWAYS # or even just "ALWAYS"
))
my_table = my_database.get_table("my_table", spawn_api_options=my_options)
```
See the section about API Options, and the docstring, for more details.
_Caution: if one plans to use regular Python `dict` objects to express user-defined types (UDTs),_
_setting this option to ALWAYS would interfere with the format expected by the API for UDTs._
_See the section on UDTs for more details._
#### User-defined types (UDTs)
The Data API allows creation of "user-defined types" (UDTs), composite data types
that can be subsequently used as table column types.
```python
from astrapy.info import (
ColumnType,
CreateTableDefinition,
CreateTypeDefinition,
TableScalarColumnTypeDescriptor,
)
player_udt_def = CreateTypeDefinition(
fields={
"name": TableScalarColumnTypeDescriptor(ColumnType.TEXT),
"age": TableScalarColumnTypeDescriptor(ColumnType.INT),
},
)
my_database.create_type("player_udt", definition=player_udt_def)
table_definition = (
CreateTableDefinition.builder()
.add_column("match_id", ColumnType.TEXT)
.add_userdefinedtype_column("player1", "player_udt")
.add_userdefinedtype_column("player2", "player_udt")
.add_partition_by(["match_id"])
.build()
)
udt_table = my_database.create_table("matches", definition=table_definition)
```
To write data to UDT columns, the default settings (in part. the `SerdesOptions` settings)
admit using plain Python dictionaries. When reading from a `Table`, by default the
UDT will be returned in the form of an `astrapy.data_types.DataAPIDictUDT`, a subclass
of `dict`.
The default write behaviour can be changed through the
`serdes_options.encode_maps_as_lists_in_tables` API Option,
described in the "Maps as association lists" section.
The default read behaviour can be changed by setting `serdes_options.custom_datatypes_in_reading`
to False, in which case UDT data will be returned as a regular `dict`.
The following code demonstrates the default read and write behaviour, using the `udt_table` just created:
```python
from astrapy.data_types import DataAPIDictUDT
# both are valid ways to express a 'player_udt':
udt_table.insert_one({
"match_id": "x001",
"player1": {"name": "Anita", "age": 49},
"player2": DataAPIDictUDT({"name": "Pedro", "age": 50}),
})
# Conversely, use of DataAPIMap for UDTs is an error under the default serdes settings.
```
_Note that if the map list-encoding is set to "ALWAYS", the above insertion
will fail because of `"player1"`: usage of `DataAPIDictUDT` is guaranteed to work
in all circumstances instead._
##### Using models for UDTs
In many cases, one wants to 'bind' a certain UDT to a model class. AstraPy provides
a way to "register" model classes both for the write and read paths, through the following
serdes API Options:
- `serdes_options.serializer_by_class`: a map from _classes_ (not class names; not class instances) to serializer functions. A serializer function accepts an instance of the model class and returns a corresponding `dict` representation;
- `serdes_options.deserializer_by_udt`: a map from _UDT names_ to deserializer functions. A deserializer function accepts a dict representation, along with the UDT definition, and returns an instance of the model class.
The following example demonstrates this procedure, including ser/deserializers.
Suppose you have a `dataclass` corresponding to `player_udt`:
```python
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Player:
name: str
age: int
```
The two required ser/des functions can be defined and configured for the API options in order to spawn a `Table` object able to use `Player`:
```python
from typing import Any
from astrapy.api_options import APIOptions, SerdesOptions
from astrapy.info import CreateTypeDefinition
def player_serializer(pl: Player) -> dict[str, Any]:
# the logic in this function will depend on the model class being used:
return pl.__dict__
def player_deserializer(
pl_dict: dict[str, Any],
udt_def: CreateTypeDefinition | None,
) -> Player:
# the logic in this function will depend on the model class being used:
return Player(**pl_dict)
my_options = APIOptions(serdes_options=SerdesOptions(
serializer_by_class={Player: player_serializer},
deserializer_by_udt={"player_udt": player_deserializer},
))
# This statement does not create the table on DB, that is assumed to exist already:
my_model_capable_table = database.get_table("matches", spawn_api_options=my_options)
```
At this point, writes and reads can seamlessly use the `Player` class:
```python
my_model_capable_table.insert_one({
"match_id": "x001",
"player1": Player(name="Anita", age=49),
"player2": Player(name="Pedro", age=50),
})
the_match = my_model_capable_table.find_one({"match_id": "x001"})
# the_match["player1"] and the_match["player2"] are Player objects:
print(the_match["player1"])
# prints: Player(name='Anita', age=49)
print(the_match["player2"])
# prints: Player(name='Pedro', age=50)
```
##### Summary for UDT usage and maps in Tables
Under the default serdes settings, the following rules apply and constitute the suggested approach:
- use DataAPIMap to write map columns;
- use DataAPIDictUDTs, or plain `dict`, to write UDTs;
- expect DataAPIMap when reading map columns;
- expect DataAPIDictUDTs when reading UDTs;
- to use model classes, associate them for reads and writes correspondingly.
The following tables summarize the interplay between `dict`, `DataAPIMap`, `DataAPIDictUDT` and the
serdes options for writes and reads in Tables:
_Items in insertions vs. `serdes_options.encode_maps_as_lists_in_tables`._
("D" = `dict` in payload, "L" = list of pairs in payload.)
| Item being written | NEVER | **DATAAPIMAPS** (default) | ALWAYS |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| DataAPIDictUDT | ok, D | ok, D | ok, D |
| dict (for UDT) | ok, D | ok, D | NO (L: rejected) |
| dict (for map, string keys) | ok, D | ok, D | ok, L |
| dict (for map, nonstring keys) | NO [1] | NO [1] | ok, L |
| `MyClass`, in `serializer_by_class` | ok, D [2] | ok, D [2] | ok, D [2] |
| `MyClass`, no registered serializer | NO [3] | NO [3] | NO [3] |
Notes:
1. The JSON serialization would silently convert the keys to string, leading to a type-mismatch API error upon insertion.
2. In this case the `dict` is the result of the serializer function, of course.
3. An error _"Object of type `` is not JSON serializable"_ is raised.
_Items in reads vs. `serdes_options.custom_datatypes_in_reading`._
("M" = `DataAPIMap` found in row, "U" = `DataAPIDictUDT` found in row, "D" = `dict` found in row.)
| Item being read | **True** (default) | False |
| --- | --- | --- |
| map (as object, string keys) | ok, M | ok, D |
| map (as list, string keys) | ok, M | ok, D |
| map (as list, nonstring keys) | ok, M | ok, D [4] |
| UDT, with entry in `deserializer_by_udt` | ok [5] | ok [5] |
| UDT, no registered deserializer | ok, U | ok, D |
Notes:
4. Caution: the returned regular Python `dict` will have nonstring keys.
5. The class of the result is whatever the deserializer returns.
### Usage with HCD and other non-Astra installations
The main difference when targeting e.g. a Hyper-Converged Database (HCD)
installation is how the client is
initialized. Here is a short example showing just how to get to a `Database`
(what comes next is unchaged compared to using Astra DB).
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.constants import Environment
from astrapy.authentication import UsernamePasswordTokenProvider
# Build a token
tp = UsernamePasswordTokenProvider("username", "password")
# Initialize the client and get a "Database" object
client = DataAPIClient(environment=Environment.HCD)
database = client.get_database("http://localhost:8181", token=tp)
```
For more on this case, please consult the [dedicated reference](https://docs.datastax.com/en/hyper-converged-database/1.0/connect/python-client.html).
## AstraPy's API
### Abstraction diagram
AstraPy's abstractions for working at the data and admin layers are structured
as depicted by this diagram:

Here's a small admin-oriented example:
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
# this must have "Database Administrator" permissions:
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
my_client = DataAPIClient(ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN)
my_astra_admin = my_client.get_admin()
database_list = list(my_astra_admin.list_databases())
db_info = database_list[0].info
print(db_info.name, db_info.id, db_info.region)
my_database_admin = my_astra_admin.get_database_admin(db_info.id)
my_database_admin.list_keyspaces()
my_database_admin.create_keyspace("my_dreamspace")
```
### Exceptions
The package comes with its own set of exceptions, arranged in this hierarchy:
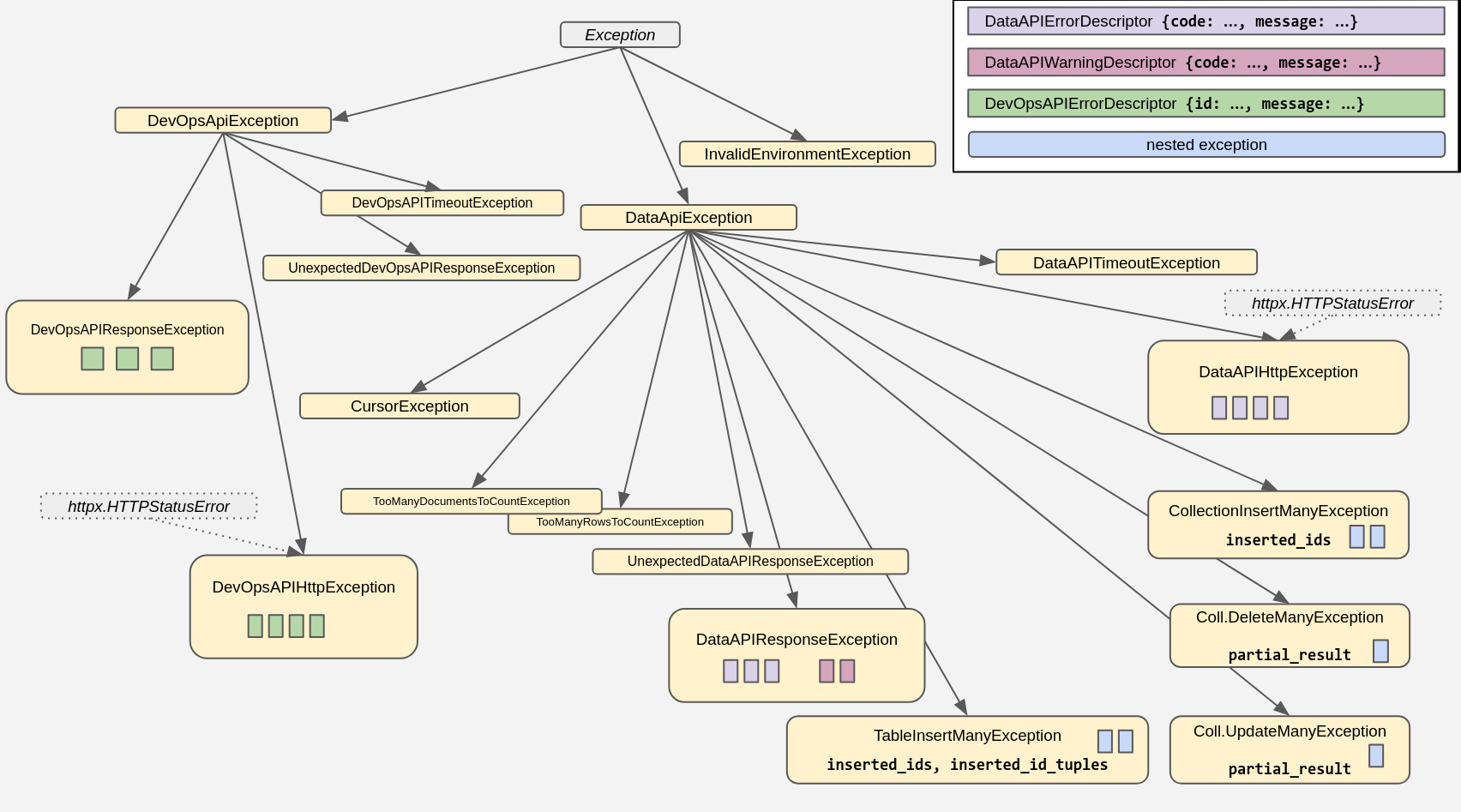
For more information, and code examples, check out the docstrings and consult
the API reference linked above.
### API Options
You can configure many aspects of the interaction with the API by providing
customized "API Options" objects when either spawning a client, copying objects,
or spawning "children classes" (such as a Table from a Database).
For the details, please check the docstring for `astrapy.api_options.APIOptions`
and the other classes in that module. Here is a small example script to show a
practical starting point:
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.api_options import (
APIOptions,
SerdesOptions,
)
# Disable custom datatypes in all reads:
no_cdt_options = APIOptions(
serdes_options=SerdesOptions(
custom_datatypes_in_reading=False,
)
)
my_client = DataAPIClient(api_options=no_cdt_options)
# These spawned objects inherit that setting:
my_database = my_client.get_database(
"https://...",
token="my-token-1",
)
my_table = my_database.get_table("my_table")
```
### Working with dates in Collections and Tables
Date and datetime objects, i.e. instances of the standard library
`datetime.datetime` and `datetime.date` classes, can be used
anywhere when sending documents and queries to the API.
By default, what you get back is an instance of `astrapy.data_types.DataAPITimestamp`
(which has a much wider range of expressable timestamps than Python's stdlib).
If you want to revert to using the standard library `datetime.datetime`, you can do so
by turn on the `APIOptions.SerdesOptions.custom_datatypes_in_reading` API Options setting for the
collection/table object (note that this setting affects the returned format for several other table data types).
If you choose to have timestamps returned as standard-library `datetime.datetime` objects,
both for collections and tables, you may supply a specific timezone for these
(the default is UTC). You do so by providing an appropriate `datetime.timezone` value
to the `APIOptions.SerdesOptions.datetime_tz` API Options setting for the
collection/table object. You can also specify `None` for a timezone, in which case
the resulting values will be timezone-unaware (or "naive") datetimes.
_Naive_ datetimes (i.e. those without a timezone information attached)
are inherently ambiguous when it comes to translating them into a unambiguous timestamp.
For this reason, if you want to work with naive datetimes, and in particular you want
AstraPy to accept them for writes, you need to explicitly
turn on the `APIOptions.SerdesOptions.accept_naive_datetimes` API Options setting for the
collection/table object, otherwise AstraPy will raise an error.
_Remember that what effectively gets_
_written to DB is always a (numeric) **timestamp**: for naive quantities, this timestamp value depends_
_on the implied timezone used in the conversion, potentially leading to unexpected results_
_e.g. if multiple applications are running with different locale settings._
The following diagram summarizes the behaviour of the write and read paths for datetime objects,
depending on the `SerdesOptions` settings:

Here an example code snippet showing how to switch to having reads return regular `datetime` objects
and have them set to one's desired timezone offset:
```python
from datetime import timezone,timedelta
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.api_options import APIOptions, SerdesOptions
my_timezone = timezone(timedelta(hours=4, minutes=30))
my_client = DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
spawn_api_options=APIOptions(
serdes_options=SerdesOptions(
custom_datatypes_in_reading=False,
datetime_tzinfo=my_timezone,
),
),
)
my_collection = my_database.get_collection("my_collection")
# This document will have datetimes set to the desired timezone
document = my_collection.find_one({"code": 123})
```
### Working with ObjectIds and UUIDs in Collections
Astrapy repackages the ObjectId from `bson` and the UUID class and utilities
from the `uuid` package and its `uuidv6` extension. You can also use them directly.
Even when setting a default ID type for a collection, you still retain the freedom
to use any ID type for any document:
```python
from astrapy import DataAPIClient
from astrapy.constants import DefaultIdType
from astrapy.ids import ObjectId, uuid8, UUID
import bson
ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN = "AstraCS:..."
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT = "https://01234567-....apps.astra.datastax.com"
my_client = DataAPIClient()
my_database = my_client.get_database(
ASTRA_DB_API_ENDPOINT,
token=ASTRA_DB_APPLICATION_TOKEN,
)
my_collection = my_database.create_collection(
"ecommerce",
definition=CollectionDefinition.builder().set_default_id(
DefaultIdType.UUIDV6
).build(),
)
my_collection.insert_one({"_id": ObjectId("65fd9b52d7fabba03349d013")})
my_collection.find({
"_id": UUID("018e65c9-e33d-749b-9386-e848739582f0"),
})
my_collection.update_one(
{"tag": "in_stock"},
{"$set": {"inventory_id": bson.objectid.ObjectId()}},
upsert=True,
)
my_collection.insert_one({"_id": uuid8()})
```
### Escaping field names
Field names containing special characters (`.` and `&`) must be correctly escaped
in certain Data API commands. It is a responsibility of the user to ensure escaping
is done when needed; however, AstraPy offers utilities to escape sequences of "path
segments" and -- should it ever be needed -- unescape path-strings back into
literal segments:
```python
from astrapy.utils.document_paths import escape_field_names, unescape_field_path
print(escape_field_names("f1", "f2", 12, "g.&3"))
# prints: f1.f2.12.g&.&&3
print(escape_field_names(["f1", "f2", 12, "g.&3"]))
# prints: f1.f2.12.g&.&&3
print(unescape_field_path("a&&&.b.c.d.12"))
# prints: ['a&.b', 'c', 'd', '12']
```
## For contributors
First install `uv` (e.g. `pipx install uv`), then set up a dev environment with `make venv`, or equivalently:
```
uv venv
uv sync --dev
```
Linter, style and typecheck should all pass for a PR:
```bash
make format
```
With `make format-fix` the style and imports are autofixed (by `ruff`)
Features must be thoroughly covered in tests (have a look at `tests/*` to infer
naming convention and module structure).
### Running tests
#### Typical testing
In most cases you want to run the "base" test suite (the one in the CI/CD automation) against either Astra DB or a local Data API + HCD.
Steps:
- Export variables as in one of the `tests/env_templates/*.base.template` examples.
- Export variables as in the `tests/env_templates/env.vectorize-minimal.template` example.
- Run: `uv venv --python ">=3.8<3.13" && uv run pytest tests/base`
#### All available tests/targets
Tests are grouped in:
- "base", covering general-purpose astrapy functionality. Divided in unit/integration;
- "vectorize", extensively running a base workload on all provider/integration choices;
- "admin", doing a whole sweep of admin operations. Very slow on Astra DB.
Astrapy's CI only runs "base". The others are to be checked manually when it's needed.
Tests can be run on three types of Data API _targets_ (with slight differences in what is applicable):
- **Astra**: an Astra DB target account (or two, as some tests are specific to dev environment)
- **Local**: a ready-to-use (user-supplied) local Data API on top of a DSE/HCD (e.g. using `tests/hcd_compose`).
- **DockerCompose**: HCD+Data API, started by the test itself on startup. This is used in the Github action `local` workflow. _Note that in this case the containers created will not be automatically destroyed._
Depending on the target chosen, different environment variables are needed: refer to
the `tests/env_templates/*.base.template` examples.
Note that the variables defined in the desired "base" template **must** be set to run test, even for unit tests.
Additionally, you will need to define the environment variables in `tests/env_templates/env.vectorize-minimal.template`,
which are needed by the minimal set of "vectorize" testing belonging to the "base" test group.
For Astra DB, you can include "shared secret" vectorize tests (i.e. KMS-based authentication).
To run those tests, you must scope an OpenAI API key
to the target Astra DB with secret name `"SHARED_SECRET_EMBEDDING_API_KEY_OPENAI"`
and comment the environment flag that suppresses them (see the base Astra env template).
For non-Astra, the reranking-related tests run only if one sets
`HEADER_RERANKING_API_KEY_NVIDIA="AstraCS:` (as shown in the Local/DockerCompose base env templates).
#### Docker vs. Podman
In case you use a different Docker-compatible container runtime (e.g. `podman`) and are running against the
"DockerCompose" target make sure to export the environment variable such as `DOCKER_COMMAND_NAME="podman"`
to maek the test startup logic work properly.
#### Keyspaces
You shoud never need to worry about keyspaces. Tests use two keyspaces, which are created if not found, with default names.
The env templates show how to override those names, if you want to.
#### Multiple Python versions
If may be useful to run e.g. unit tests with multiple Python versions. You can have `uv`
create more than one venv and specify the version, e.g. for each one:
```
uv venv --python 3.8 .venv-3.8
. .venv-3.8/bin/activate
uv sync --dev --active
```
Then, with the desired virtual env active, you will run e.g. `uv run --active pytest [...]`.
Most make targets will also support running in the named virtual env:
assuming you activated a certain virtual env, you can run e.g.: `make format VENV=true`.
**Warning: Python 3.13+ currently not supported to run integration tests! (but the package itself is all right).**
#### Adding/changing dependencies
After editing the `pyproject.toml`, make sure you run
```
uv lock
uv sync --dev
```
and then commit the new `uv.lock` to the repo as well.
#### Sample testing commands
Base:
```
# choose one:
uv run pytest tests/base
uv run pytest tests/base/unit
uv run pytest tests/base/integration
```
Admin:
```
# depending on the environment, different 'admin tests' will run:
uv run pytest tests/admin
```
Extended vectorize:
```
# very many env. variables required for this one:
uv run pytest tests/vectorize
# restrict to some combination(s) with e.g.:
EMBEDDING_MODEL_TAGS="openai/text-embedding-3-large/HEADER/0,voyageAI/voyage-finance-2/SHARED_SECRET/f" \
uv run pytest tests/vectorize/integration/test_vectorize_providers.py \
-k test_vectorize_usage_auth_type_header_sync
```
All the usual `pytest` ways of restricting the test selection hold
(e.g. `uv run pytest tests/idiomatic/unit` or `[...] -k `). Also e.g.:
```
# suppress log noise
uv run pytest [...] -o log_cli=0
# increase log level
uv run pytest [...] -o log_cli=1 --log-cli-level=10
```
### Special tests
The following are special provision to manage features under evolution or not
entirely deployed to all environments. Typically they require manually passing
certain environment variables, otherwise the associated tests are excluded from CI.
#### Cutting-edge features on `main`
Prepend tests with a `ASTRAPY_TEST_LATEST_MAIN=y` for features found on `main` that are not released anywhere.
_(Tip: run a code search first to see what is currently marked as such. Chances are nothing is.)_
## Appendices
### Appendix A: quick reference for key imports
_Note: check `tests/base/unit/test_imports.py` for more._
Client, data and admin abstractions
```python
from astrapy import (
AstraDBAdmin,
AstraDBDatabaseAdmin,
AsyncCollection,
AsyncDatabase,
AsyncTable,
Collection,
Database,
DataAPIClient,
DataAPIDatabaseAdmin,
Table,
)
```
Constants for data-related use:
```python
from astrapy.constants import (
DefaultIdType,
Environment,
MapEncodingMode,
ReturnDocument,
SortMode,
VectorMetric,
)
```
Cursor for find-like operations:
```python
from astrapy.cursors import (
AbstractCursor,
AsyncCollectionFindAndRerankCursor,
AsyncCollectionFindCursor,
AsyncTableFindCursor,
CollectionFindAndRerankCursor,
CollectionFindCursor,
CursorState,
RerankedResult,
TableFindCursor,
)
```
ObjectIds and UUIDs:
```python
from astrapy.ids import (
UUID,
ObjectId,
uuid1,
uuid3,
uuid4,
uuid5,
uuid6,
uuid7,
uuid8,
)
```
API Options:
```python
from astrapy.api_options import (
APIOptions,
DataAPIURLOptions,
DevOpsAPIURLOptions,
SerdesOptions,
TimeoutOptions,
)
```
Data types:
```python
from astrapy.data_types import (
DataAPIDate,
DataAPIDuration,
DataAPIMap,
DataAPISet,
DataAPITime,
DataAPITimestamp,
DataAPIDictUDT,
DataAPIVector,
)
```
Info/metadata classes:
```python
from astrapy.info import (
AlterTableAddColumns,
AlterTableAddVectorize,
AlterTableDropColumns,
AlterTableDropVectorize,
AlterTypeAddFields,
AlterTypeOperation,
AlterTypeRenameFields,
AstraDBAdminDatabaseInfo,
AstraDBDatabaseInfo,
CollectionDefaultIDOptions,
CollectionDefinition,
CollectionDescriptor,
CollectionInfo,
CollectionLexicalOptions,
CollectionRerankOptions,
CollectionVectorOptions,
ColumnType,
CreateTableDefinition,
CreateTypeDefinition,
EmbeddingProvider,
EmbeddingProviderAuthentication,
EmbeddingProviderModel,
EmbeddingProviderParameter,
EmbeddingProviderToken,
FindEmbeddingProvidersResult,
FindRerankingProvidersResult,
ListTableDefinition,
ListTableDescriptor,
ListTypeDescriptor,
RerankingProvider,
RerankingProviderAuthentication,
RerankingProviderModel,
RerankingProviderParameter,
RerankingProviderToken,
RerankServiceOptions,
TableAPIIndexSupportDescriptor,
TableAPISupportDescriptor,
TableBaseIndexDefinition,
TableIndexDefinition,
TableIndexDescriptor,
TableIndexOptions,
TableInfo,
TableKeyValuedColumnType,
TableKeyValuedColumnTypeDescriptor,
TablePrimaryKeyDescriptor,
TableScalarColumnTypeDescriptor,
TableTextIndexDefinition,
TableTextIndexOptions,
TableUnsupportedColumnTypeDescriptor,
TableUnsupportedIndexDefinition,
TableUDTColumnDescriptor,
TableValuedColumnType,
TableValuedColumnTypeDescriptor,
TableVectorColumnTypeDescriptor,
TableVectorIndexDefinition,
TableVectorIndexOptions,
VectorServiceOptions,
)
```
Authentication:
```python
from astrapy.authentication import (
StaticTokenProvider,
UsernamePasswordTokenProvider,
EmbeddingAPIKeyHeaderProvider,
AWSEmbeddingHeadersProvider,
)
```
Miscellaneous utilities:
```python
# Parsing API Endpoints for Astra DB:
from astrapy.admin import (
ParsedAPIEndpoint,
parse_api_endpoint,
)
# Escaping/unescaping document paths:
from astrapy.utils.document_paths import (
escape_field_names,
unescape_field_path,
)
# API Options defaults:
from astrapy.utils.api_options import defaultAPIOptions
```
### Appendix B: compatibility with pre-1.0.0 library
If your code still uses the pre-1.0.0 astrapy (i.e. `from astrapy.db import AstraDB, AstraDBCollection` and so on)
you are strongly advised to migrate to the current API. All of the astrapy pre-1.0 API (later dubbed "core")
works throughout *astrapy v1*, albeit with a deprecation warning on astrapy v. 1.5.
Version 2 drops "core" support entirely. In order to use astrapy version 2.0+, you need to migrate your application.
Check the links at the beginning of this README for the updated documentation and API reference.
Check out previous versions of this README for more on "core": [1.5.2](https://github.com/datastax/astrapy/blob/4601c5fa749925d961de1f114ca27690d1a71b13/README.md) and [pre-1.0](https://github.com/datastax/astrapy/blob/cd3f5ce8146093e10a095709c0f5c3f8e3f2c7da/README.md).