https://github.com/davide-sd/sympy-equation
Equations supporting mathematical operations for SymPy
https://github.com/davide-sd/sympy-equation
algebra algebraic-equations cas equation ipython-notebook jupyter-notebook symbolic-computation symbolic-expressions symbolic-manipulation symbolic-math sympy
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Equations supporting mathematical operations for SymPy
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/davide-sd/sympy-equation
- Owner: Davide-sd
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2025-05-14T16:33:02.000Z (5 months ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-05-18T07:07:41.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-30T01:47:18.279Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: algebra, algebraic-equations, cas, equation, ipython-notebook, jupyter-notebook, symbolic-computation, symbolic-expressions, symbolic-manipulation, symbolic-math, sympy
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://sympy-equation.readthedocs.io
- Size: 2.43 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: license-GPLV3.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# sympy_equation
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/sympy-equation)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/sympy_equation/badges/version.svg)
[](http://sympy-plot-backends.readthedocs.io/)
[](https://github.com/sponsors/Davide-sd)
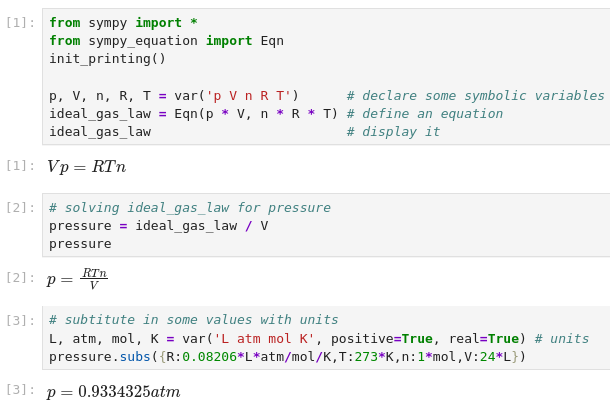
This package defines relations that all high school and college students would
recognize as mathematical equations, consisting of a left hand side (lhs) and
a right hand side (rhs) connected by the relation operator "=". This is
implemented by the ``Equation`` class, which also supports mathematical
operations applied to both sides simultaneously, just as students are taught
to do when attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement
``Equation/b`` yields a new equation ``Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b``.
The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange
equations and perform algebra in a stepwise fashion using as close to standard
mathematical notation as possible. In this way more people can successfully
perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling over missed details such
as a negative sign.
A simple example as it would appear in a [Jupyter](https://jupyter.org)
notebook is shown immediately below:
In IPython environments (IPython, Jupyter, Google Colab, etc...) there is
also a shorthand syntax for entering equations provided through the IPython
preparser. An equation can be specified as ``eq1 =@ a/b = c/d``.
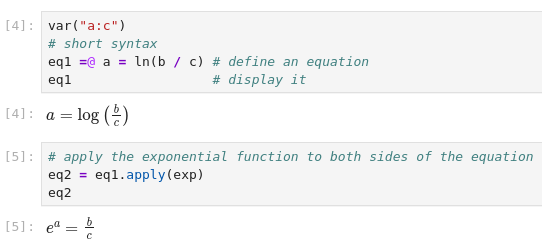
If no Python name is specified for the equation (no ``eq_name`` to the left of ``=@``), the equation will still be defined, but will not be easily accessible
for further computation. The ``=@`` symbol combination was chosen to avoid
conflicts with reserved python symbols while minimizing impacts on syntax
highlighting and autoformatting.
[More examples of the capabilities of Algebra with Sympy are
here](https://sympy-equation.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial.html).
## Development and Support
If you feel like a feature could be implemented, open an issue or create a PR. Implementing new features and fixing bugs requires time and energy too. If you found this module useful and would like to show your appreciation, please consider sponsoring this project with either one of these options:
[](https://www.buymeacoffee.com/davide_sd)
or
[](https://github.com/sponsors/Davide-sd)
## Installation
``sympy_equation`` can be installed with ``pip`` or ``conda``.
```
pip install sympy_equation
```
Or
```
conda install -c conda-forge sympy_equation
```
## Customizing the module
``equation_config`` is an object containing a few properties to customize
the behaviour of the module:
```py
from sympy_equation import equation_config
```
Arguably the most useful options are :
* ``equation_config.integers_as_exact`` (default is False).
When it's True and we are running in an IPython/Jupyter environment,
it preparses the content of a code line in order to convert integer numbers
to sympy's Integer. In doing so, we can write 2/3, which will be
converted to Integer(2)/Integer(3), which then SymPy converts
to Rational(2, 3). If False, no preparsing is done, and Python evaluates
2/3 to 0.6666667, which will then be converted by SymPy to a Float.
* ``equation_config.show_label`` (default is False). When it's True, a label
with the name of the equation in the python environment will be shown on
the screen.
Check out the documentation to read more about these and other options.
## Differences between sympy_equation and algebra_with_sympy
* ``sympy_equation`` is a fork of [algebra_with_sympy](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy), starting from the version 1.0.2.
* ``algebra_with_sympy`` installs a custom version of SymPy, which exposes
the ``Equation`` class. The basic idea is to better integrate the ``Equation``
class with other SymPy functionalities. The downside is that as new releases
of SymPy are available, the users of ``algebra_with_sympy`` must wait for a
new version of the package to be released as well.
Differently, ``sympy_equation`` is an external package that only depends on
SymPy: as new releases of SymPy are available, ``sympy_equation`` will work
with them right away. The downside is that it might not be as integrated with
SymPy's functionalities as one would like it to be.
* ``algebra_with_sympy`` exposes the ``algwsym_config`` object to customize
the behaviour of the module. Similarly, ``sympy_equation`` exposes the
``equation_config``. The available options are very similar, but their
default values are often different.
* ``algebra_with_sympy`` overwrites the default behaviour of SymPy's
``solve()`` and ``solveset()`` in order for them to return sets of solutions.
This can be annoying if you are used to the SymPy's way of doing things.
Differently, ``sympy_equation`` doesn't change the behaviour of these
functions, rather it extends it in order to deal with the ``Equation`` class.