https://github.com/devgru/ffp
FFP algorithm implementation
https://github.com/devgru/ffp
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
FFP algorithm implementation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/devgru/ffp
- Owner: devgru
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-07-11T07:33:47.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-08-15T09:46:32.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-28T19:22:52.388Z (7 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 120 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Farthest feasible point algorithm implementation
Algorithm is used to filter timeseries points to speed up rendering by defining maximum error on ordinate axis
and skipping all points that fit in resulting corridor.
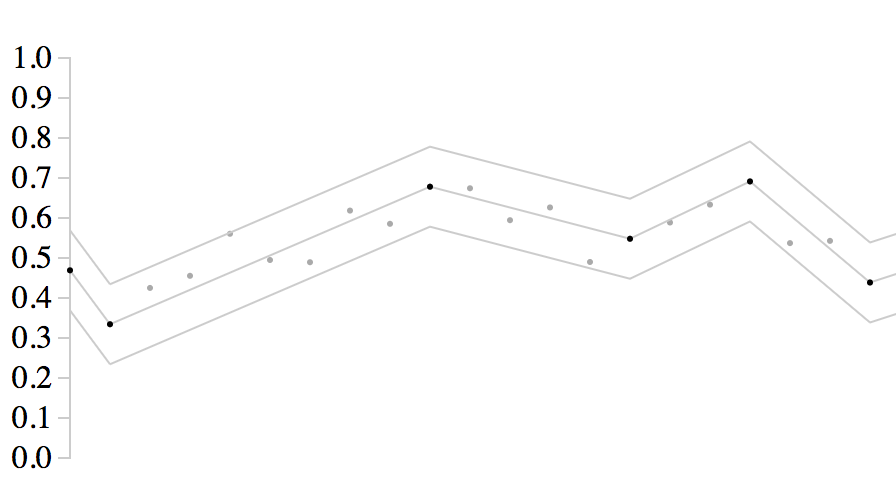
FFP algorithm is described in [this](http://masc.cs.gmu.edu/wiki/uploads/GuilinLiu/ffp.pdf) paper, authored by Guilin Xinyu and Zhe Cheng.
The library is distributed as ES module.
Check [spec/ffp.spec.js](spec/ffp.spec.js) to see usage example.
Built in collaboration with [Erohina Elena](https://github.com/erohinaelena), original version of FFP implementation can be found [here](http://bl.ocks.org/erohinaelena/882e7cadc2fd687cf2b3).
## Installation
```sh
$ yarn add ffp
# or
$ npm install --save ffp
```
## Usage
FFP is instantiated and used like this:
```js
import FFP from "ffp";
const ffp = FFP()
.maxDeltaY(0.5) // define maximum delta
.x(({ x }) => x) // define x accessor
.y(({ y }) => y) // define y accessor
.result(({ value }) => value); // consume filtered points
const array = [
{ x: 0, y: 3 },
{ x: 1, y: 4 },
{ x: 2, y: 5 },
// ...
{ x: 5, y: 0 },
];
ffp(array);
```
FFP library exports a function.
## FFP()
Creates FFP utility.
## ffp(array)
FFP utility is a function, invoke it on array of elements to filter them out.
## ffp.maxDeltaY([*delta*])
If _delta_ is specified, sets the maximum _delta_ to the specified number. If _delta_ is not specified, returns the current maximum _delta_ value, which defaults to 1.
Maximum _delta_ determines maximum variation between resulting trend and point position on ordinate axis.
## ffp.epsilon([*epsilon*])
If _epsilon_ is specified, sets the _epsilon_ to the specified number. If _epsilon_ is not specified, returns the current _epsilon_ value, which defaults to 1/2³².
_epsilon_ determines the maximum margin of error.
## ffp.x([*xAccessor*])
If _xAccessor_ is specified, sets the _x_ accessor to the specified function. If _xAccessor_ is not specified, returns the current _x_ accessor, which defaults to `(value, index) => index`.
_x_ accessor is invoked for each point.
## ffp.y([*yAccessor*])
If _yAccessor_ is specified, sets the _y_ accessor to the specified function. If _yAccessor_ is not specified, returns the current _y_ accessor, which defaults to `(value) => value`.
_x_ accessor is invoked for each point.
## ffp.result([*resultMapper*])
If _resultMapper_ is specified, sets the _result_ mapper to the specified function. If _resultMapper_ is not specified, returns the current _result_ mapper, which defaults to `({ value }) => value`.
_result_ mapper is invoked for each point. By default, `ffp(array)` returns an array of objects with `value` and `index` keys. Define custom _result_ mapper to modify this behavior.
## Development
- Run tests: `yarn test`;
## License
MIT © [Dmitriy Semyushkin](https://devg.ru)