https://github.com/dimatura/binvox-rw-py
Python module to read and write .binvox files.
https://github.com/dimatura/binvox-rw-py
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Python module to read and write .binvox files.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/dimatura/binvox-rw-py
- Owner: dimatura
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2012-05-23T13:37:17.000Z (about 13 years ago)
- Default Branch: public
- Last Pushed: 2019-11-17T04:40:02.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-09T23:15:41.277Z (3 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 74.2 KB
- Stars: 240
- Watchers: 9
- Forks: 100
- Open Issues: 14
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: COPYING
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# binvox-rw-py
Small Python module to read and write `.binvox` files. The voxel data is
represented as dense 3-dimensional Numpy arrays in Python (a direct if somewhat
wasteful representation for sparse models) or as an array of 3D coordinates
(more memory-efficient for large and sparse models).
[Binvox](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~min/binvox/) is a neat little program to
convert 3D models into binary voxel format. The `.binvox` file format is a
simple run length encoding format described
[here](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~min/binvox/binvox.html).
## Code example
Suppose you have a voxelized chair model, `chair.binvox` (you can try it on the
one in the repo). Here's how it looks in
[`viewvox`](http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~min/viewvox/):
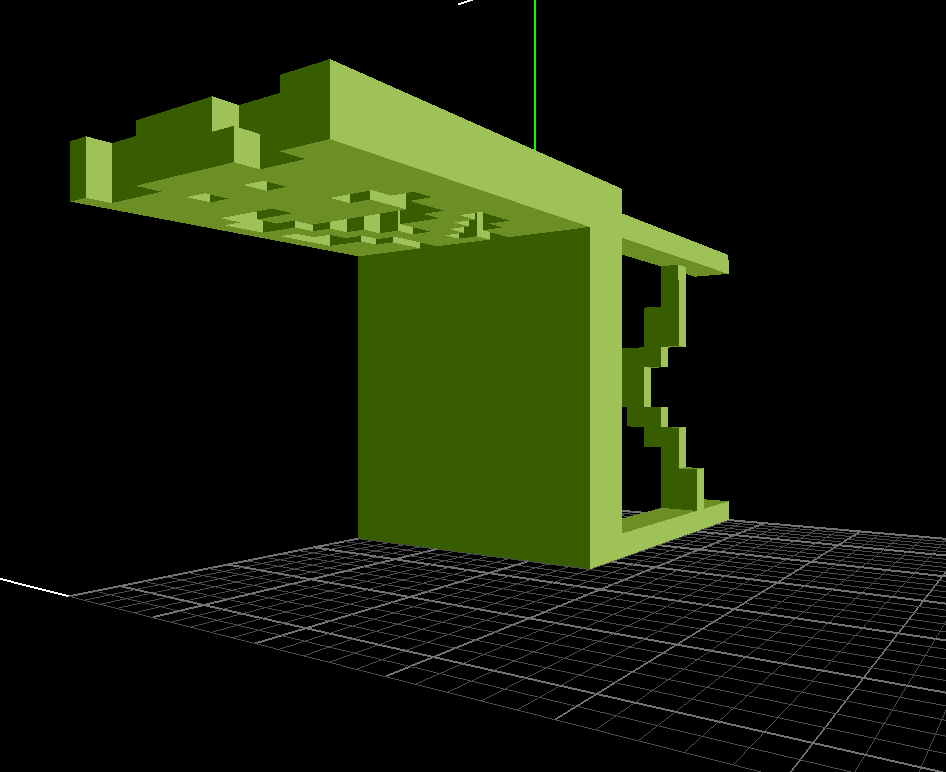
Then
>>> import binvox_rw
>>> with open('chair.binvox', 'rb') as f:
... model = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array(f)
...
>>> model.dims
[32, 32, 32]
>>> model.scale
41.133000000000003
>>> model.translate
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
>>> model.data
array([[[ True, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[ True, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[ True, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
...,
[[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
...,
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False]]], dtype=bool)
You get the idea. `model.data` has the boolean 3D array. You can then
manipulate however you wish. For example, here we dilate it with
`scipy.ndimage` and write the dilated version to disk:
>>> import scipy.ndimage
>>> scipy.ndimage.binary_dilation(model.data.copy(), output=model.data)
>>> model.write('dilated.binvox')
Then we get a fat chair:
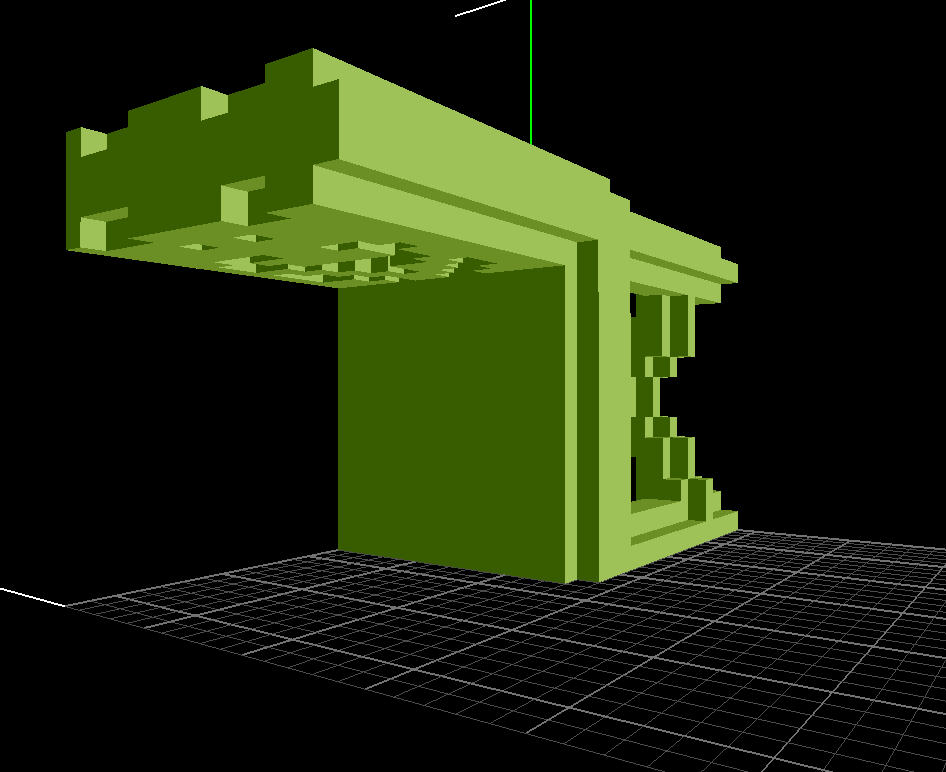
## Sparse representation
To get the data as an array of coordinates, look at `binvox_rw.read_coords`.
## Installation
This is a really simple, 200-line module. You should just stick into whatever
project you're using. Or copy it to `/usr/share/lib/pythonX.Y/site-packages`
if you really want a system-wide installation.
---
Daniel Maturana
`[email protected]`