https://github.com/dnth/x.infer
Framework agnostic computer vision inference. Run 1000+ models by changing only one line of code. Supports models from transformers, timm, ultralytics, vllm, ollama and your custom model.
https://github.com/dnth/x.infer
computer-vision inference-api ollama pytorch-image-models transformers ultralytics vllm
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Framework agnostic computer vision inference. Run 1000+ models by changing only one line of code. Supports models from transformers, timm, ultralytics, vllm, ollama and your custom model.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/dnth/x.infer
- Owner: dnth
- License: other
- Created: 2024-10-10T02:30:03.000Z (9 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-11-27T06:19:09.000Z (8 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-02T18:09:23.514Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: computer-vision, inference-api, ollama, pytorch-image-models, transformers, ultralytics, vllm
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage: https://dnth.github.io/x.infer
- Size: 44.6 MB
- Stars: 130
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 25
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: docs/contributing.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[python_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Python-3.10+-brightgreen?style=for-the-badge&logo=python&logoColor=white
[pypi_badge]: https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/xinfer.svg?style=for-the-badge&logo=pypi&logoColor=white&label=PyPI&color=blue
[downloads_badge]: https://img.shields.io/pepy/dt/xinfer.svg?style=for-the-badge&logo=pypi&logoColor=white&label=Downloads&color=purple
[license_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/License-Apache%202.0-green.svg?style=for-the-badge&logo=apache&logoColor=white
[transformers_badge]: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/huggingface/transformers?style=for-the-badge&logo=huggingface&label=Transformers%20⭐&color=yellow
[timm_badge]: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/huggingface/pytorch-image-models?style=for-the-badge&logo=pytorch&label=TIMM%20⭐&color=limegreen
[ultralytics_badge]: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/ultralytics/ultralytics?style=for-the-badge&logo=udacity&label=Ultralytics%20⭐&color=red
[vllm_badge]: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/vllm-project/vllm?style=for-the-badge&logo=v&label=vLLM%20⭐&color=purple
[ollama_badge]: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/ollama/ollama?style=for-the-badge&logo=ollama&label=Ollama%20⭐&color=darkgreen
[colab_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Open%20In-Colab-blue?style=for-the-badge&logo=google-colab
[kaggle_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Open%20In-Kaggle-blue?style=for-the-badge&logo=kaggle
[back_to_top_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Back_to_Top-↑-blue?style=for-the-badge
[image_classification_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Image%20Classification-6366f1?style=for-the-badge
[object_detection_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Object%20Detection-8b5cf6?style=for-the-badge
[image_captioning_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Image%20Captioning-a855f7?style=for-the-badge
[vqa_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Visual%20QA-d946ef?style=for-the-badge
[os_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Tested%20on-Linux%20%7C%20macOS%20%7C%20Windows-indigo?style=for-the-badge&logo=iterm2&logoColor=white&color=indigo
[pose_estimation_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Pose%20Estimation-ec4899?style=for-the-badge
[instance_segmentation_badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Instance%20Segmentation-f43f5e?style=for-the-badge
![Python][python_badge]
[![PyPI version][pypi_badge]](https://pypi.org/project/xinfer/)
[![Downloads][downloads_badge]](https://pypi.org/project/xinfer/)
![License][license_badge]
![OS Support][os_badge]
🌟 Features
🤔 Why x.infer?
🚀 Quickstart
📦 Installation
🛠️ Usage
🤖 Models
🤝 Contributing
⚠️ Disclaimer
## 🌟 Key Features
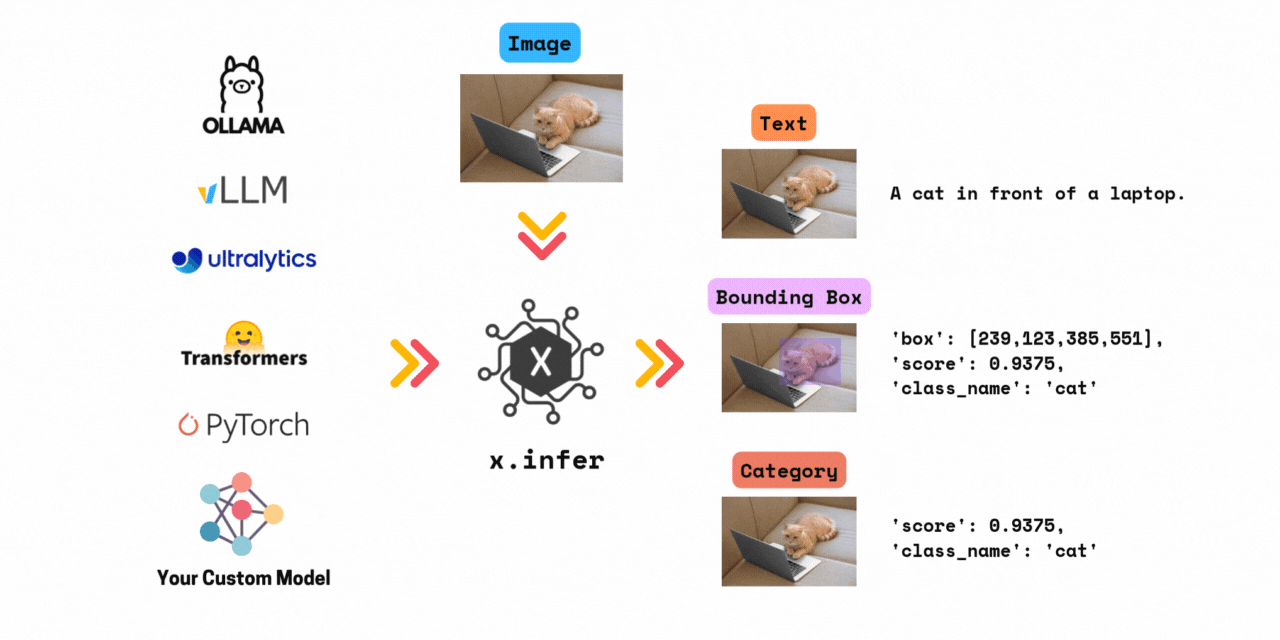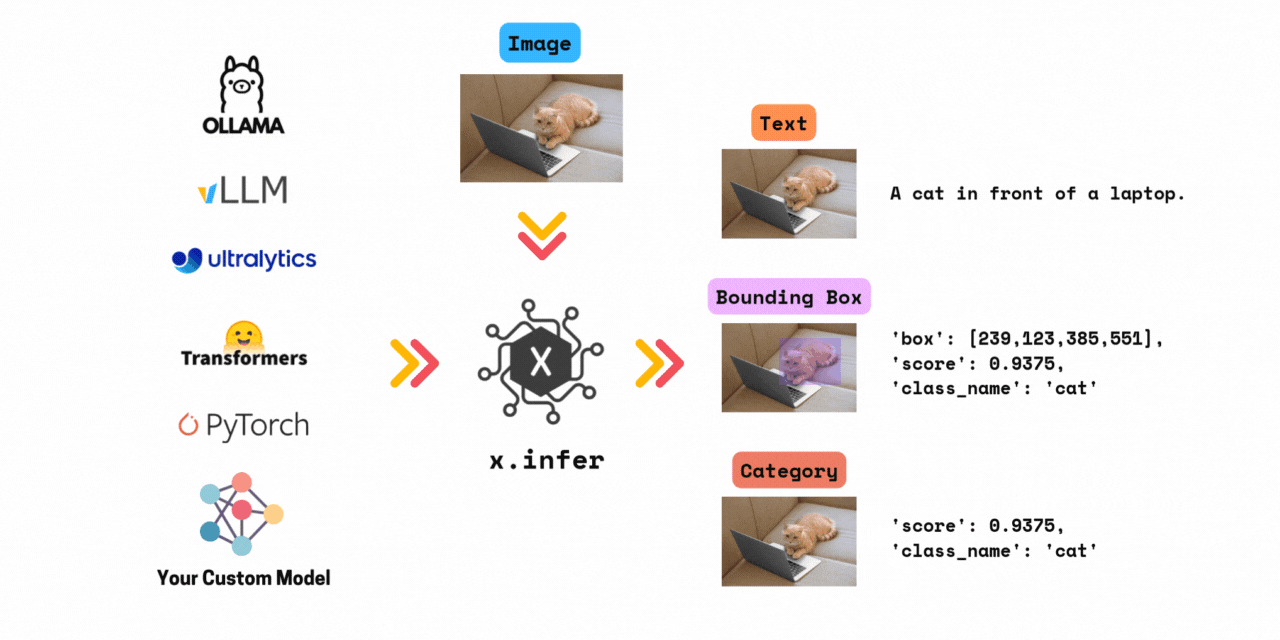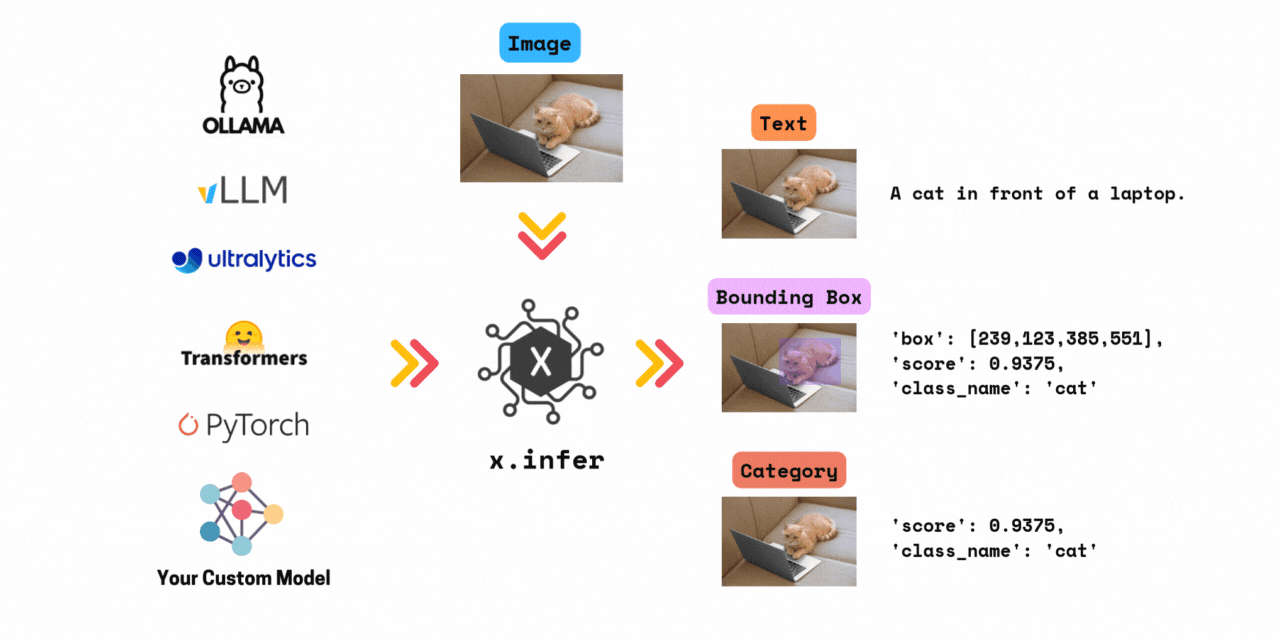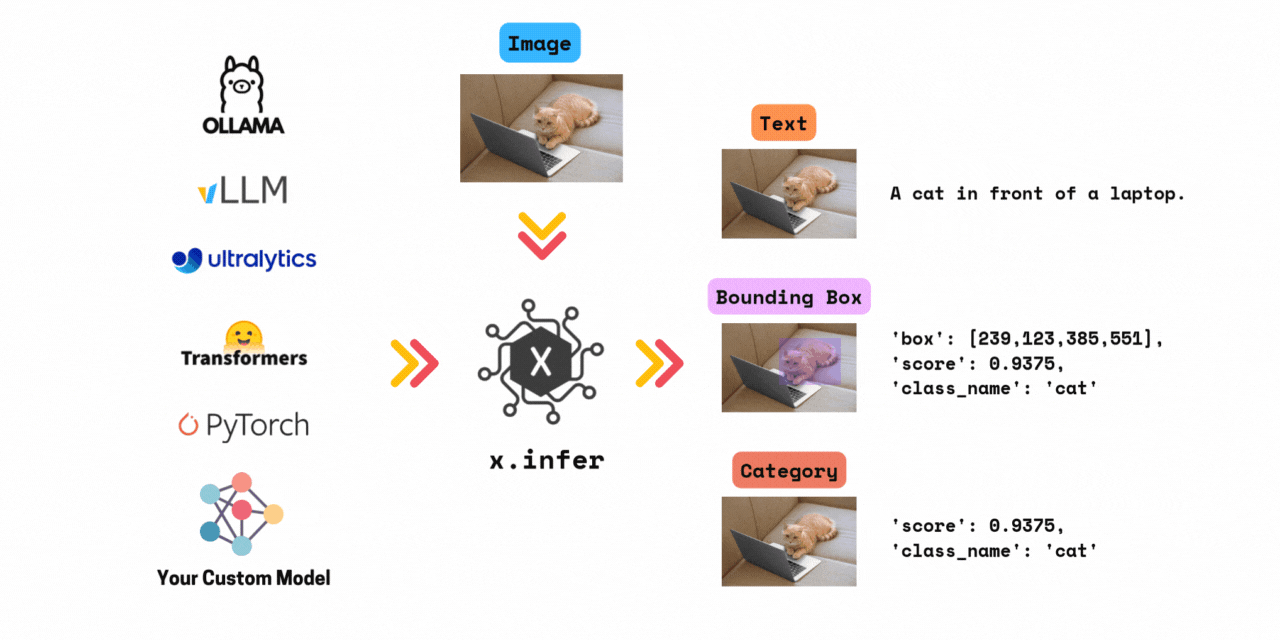
✅ Run inference with >1000+ models in 3 lines of code. \
✅ List and search models interactively. \
✅ Launch a Gradio interface to interact with a model. \
✅ Serve model as a REST API endpoint with Ray Serve and FastAPI. \
✅ OpenAI chat completions API compatible. \
✅ Customize and add your own models with minimal code changes.
Tasks supported:
![Image Classification][image_classification_badge]
![Object Detection][object_detection_badge]
![Image Captioning][image_captioning_badge]
![Visual QA][vqa_badge]
![Pose Estimation][pose_estimation_badge]
![Instance Segmentation][instance_segmentation_badge]
## 🤔 Why x.infer?
So, a new computer vision model just dropped last night. It's called `GPT-54o-mini-vision-pro-max-xxxl`. It's a super cool model, open-source, open-weights, open-data, all the good stuff.
You're excited. You want to try it out.
But it's written in a new framework, `TyPorch` that you know nothing about.
You don't want to spend a weekend learning `TyPorch` just to find out the model is not what you expected.
This is where x.infer comes in.
x.infer is a simple wrapper that allows you to run inference with any computer vision model in just a few lines of code. All in Python.
Out of the box, x.infer supports the following frameworks:
[![Transformers][transformers_badge]](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers)
[![TIMM][timm_badge]](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-image-models)
[![Ultralytics][ultralytics_badge]](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics)
[![vLLM][vllm_badge]](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm)
[![Ollama][ollama_badge]](https://github.com/ollama/ollama)
Combined, x.infer supports over 1000+ models from all the above frameworks.
Run any supported model using the following 4 lines of code:
```python
import xinfer
model = xinfer.create_model("vikhyatk/moondream2")
model.infer(image, prompt) # Run single inference
model.infer_batch(images, prompts) # Run batch inference
model.launch_gradio() # Launch Gradio interface
```
Have a custom model? Create a class that implements the `BaseXInferModel` interface and register it with x.infer. See [Add Your Own Model](#add-your-own-model) for more details.
## 🚀 Quickstart
Here's a quick example demonstrating how to use x.infer with a Transformers model:
[![Open In Colab][colab_badge]](https://colab.research.google.com/github/dnth/x.infer/blob/main/nbs/quickstart.ipynb)
[![Open In Kaggle][kaggle_badge]](https://kaggle.com/kernels/welcome?src=https://github.com/dnth/x.infer/blob/main/nbs/quickstart.ipynb)
```python
import xinfer
model = xinfer.create_model("vikhyatk/moondream2")
image = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dnth/x.infer/main/assets/demo/00aa2580828a9009.jpg"
prompt = "Describe this image. "
model.infer(image, prompt)
>>> 'A parade with a marching band and a flag-bearing figure passes through a town, with spectators lining the street and a church steeple visible in the background.'
```
## 📦 Installation
> [!IMPORTANT]
> You must have [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installed to use x.infer.
To install the barebones x.infer (without any optional dependencies), run:
```bash
pip install xinfer
```
x.infer can be used with multiple optional dependencies. You'll just need to install one or more of the following:
```bash
pip install "xinfer[transformers]"
pip install "xinfer[ultralytics]"
pip install "xinfer[timm]"
pip install "xinfer[vllm]"
pip install "xinfer[ollama]"
```
To install all optional dependencies, run:
```bash
pip install "xinfer[all]"
```
To install from a local directory, run:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/dnth/x.infer.git
cd x.infer
pip install -e .
```
## 🛠️ Usage
### List Models
```python
xinfer.list_models()
```
```
Available Models
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Implementation ┃ Model ID ┃ Input --> Output ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ timm │ timm/eva02_large_patch14_448.mim_m38m_ft_in22k_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_large_patch14_448.mim_m38m_ft_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_large_patch14_448.mim_in22k_ft_in22k_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_large_patch14_448.mim_in22k_ft_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_base_patch14_448.mim_in22k_ft_in22k_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_base_patch14_448.mim_in22k_ft_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_small_patch14_336.mim_in22k_ft_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ timm │ timm/eva02_tiny_patch14_336.mim_in22k_ft_in1k │ image --> categories │
│ transformers │ Salesforce/blip2-opt-6.7b-coco │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xxl │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ Salesforce/blip2-opt-6.7b │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ fancyfeast/llama-joycaption-alpha-two-hf-llava │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ vikhyatk/moondream2 │ image-text --> text │
│ transformers │ sashakunitsyn/vlrm-blip2-opt-2.7b │ image-text --> text │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8x │ image --> boxes │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8m │ image --> boxes │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8l │ image --> boxes │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8s │ image --> boxes │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8n │ image --> boxes │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8n-seg │ image --> masks │
│ ultralytics │ ultralytics/yolov8n-pose │ image --> poses │
│ ... │ ... │ ... │
│ ... │ ... │ ... │
└────────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────┘
```
If you're running in a Juypter Notebook environment, you can specify `interactive=True` to list and search supported models interactively.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/d51cf707-2001-478c-881a-ae27f690d1bc
### Gradio Interface
For all supported models, you can launch a Gradio interface to interact with the model. This is useful for quickly testing the model and visualizing the results.
Once the model is created, you can launch the Gradio interface with the following line of code:
```python
model.launch_gradio()
```
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/25ce31f3-c9e2-4934-b341-000a6d1b7dc4
If you'd like to launch a Gradio interface with all models available in a dropdown, you can use the following line of code:
```python
xinfer.launch_gradio_demo()
```
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/bd46f55a-573f-45b9-910f-e22bee27fd3d
See [Gradio Demo](./nbs/gradio_demo.ipynb) for more details.
### Serve Model
If you're happy with your model, you can serve it with x.infer.
```python
xinfer.serve_model("vikhyatk/moondream2")
```
This will start a FastAPI server at `http://localhost:8000` powered by [Ray Serve](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/serve/index.html), allowing you to interact with your model through a REST API.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/cd3925f8-ffcb-4890-8a34-13ee5f6884f1
You can also specify deployment options such as the number of replicas and GPU requirements and host/port.
```python
xinfer.serve_model(
"vikhyatk/moondream2",
device="cuda",
dtype="float16",
host="0.0.0.0",
port=8000,
deployment_kwargs={
"num_replicas": 1,
"ray_actor_options": {"num_gpus": 1}
}
)
```
### FastAPI Endpoint
You can now query the endpoint with an image and prompt.
```bash
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:8000/infer' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"image": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dnth/x.infer/main/assets/demo/00aa2580828a9009.jpg",
"infer_kwargs": {"text": "Caption this image"}
}'
```
Or in Python:
```python
import requests
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/infer"
headers = {
"accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"image": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dnth/x.infer/main/assets/demo/00aa2580828a9009.jpg",
"infer_kwargs": {
"text": "Caption this image"
}
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
print(response.json())
```
### OpenAI chat completions API
x.infer endpoint is also compatible with the OpenAI chat completions API format.
You'll have to install the `openai` package to use this feature.
```bash
pip install openai
```
```python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="dummy",
base_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1"
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="vikhyatk/moondream2",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dnth/x.infer/main/assets/demo/00aa2580828a9009.jpg"
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": "Caption this image"
}
]
}
]
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
```
### Add Your Own Model
+ **Step 1:** Create a new model class that implements the `BaseXInferModel` interface.
+ **Step 2:** Implement the required abstract methods `load_model`, `infer`, and `infer_batch`.
+ **Step 3:** Decorate your class with the `register_model` decorator, specifying the model ID, implementation, and input/output.
For example:
```python
@register_model("my-model", "custom", ModelInputOutput.IMAGE_TEXT_TO_TEXT)
class MyModel(BaseXInferModel):
def load_model(self):
# Load your model here
pass
def infer(self, image, prompt):
# Run single inference
pass
def infer_batch(self, images, prompts):
# Run batch inference here
pass
```
See an example implementation of the Molmo model [here](https://github.com/dnth/x.infer/blob/main/xinfer/vllm/molmo.py).
## 🤖 Supported Models
Transformers
Model
Usage
BLIP2 Series
xinfer.create_model("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
Moondream2
xinfer.create_model("vikhyatk/moondream2")
VLRM-BLIP2
xinfer.create_model("sashakunitsyn/vlrm-blip2-opt-2.7b")
JoyCaption
xinfer.create_model("fancyfeast/llama-joycaption-alpha-two-hf-llava")
Llama-3.2 Vision Series
xinfer.create_model("meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct")
Florence-2 Series
xinfer.create_model("microsoft/Florence-2-base-ft")
Qwen2-VL Series
xinfer.create_model("Qwen/Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct")
You can also load any [AutoModelForVision2Seq model](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/auto#transformers.AutoModelForVision2Seq)
from Transformers by using the `Vision2SeqModel` class.
```python
from xinfer.transformers import Vision2SeqModel
model = Vision2SeqModel("facebook/chameleon-7b")
model = xinfer.create_model(model)
```
TIMM
All models from [TIMM](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-image-models) fine-tuned for ImageNet 1k are supported.
For example load a `resnet18.a1_in1k` model:
```python
xinfer.create_model("timm/resnet18.a1_in1k")
```
You can also load any model (or a custom timm model) by using the `TIMMModel` class.
```python
from xinfer.timm import TimmModel
model = TimmModel("resnet18")
model = xinfer.create_model(model)
```
Ultralytics
Model
Usage
YOLOv8 Detection Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov8n")
YOLOv10 Detection Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov10x")
YOLOv11 Detection Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov11s")
YOLOv8 Classification Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov8n-cls")
YOLOv11 Classification Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov11s-cls")
YOLOv8 Segmentation Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov8n-seg")
YOLOv8 Pose Series
xinfer.create_model("ultralytics/yolov8n-pose")
You can also load any model from Ultralytics by using the `UltralyticsModel` class.
```python
from xinfer.ultralytics import UltralyticsModel
model = UltralyticsModel("yolov5n6u")
model = xinfer.create_model(model)
```
vLLM
Model
Usage
Molmo-72B
xinfer.create_model("vllm/allenai/Molmo-72B-0924")
Molmo-7B-D
xinfer.create_model("vllm/allenai/Molmo-7B-D-0924")
Molmo-7B-O
xinfer.create_model("vllm/allenai/Molmo-7B-O-0924")
Phi-3.5-vision-instruct
xinfer.create_model("vllm/microsoft/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct")
Phi-3-vision-128k-instruct
xinfer.create_model("vllm/microsoft/Phi-3-vision-128k-instruct")
Ollama
To use Ollama models, you'll need to install the Ollama on your machine. See [Ollama Installation Guide](https://ollama.com/download) for more details.
Model
Usage
LLaVA Phi3
xinfer.create_model("ollama/llava-phi3")
## 🤝 Contributing
If you'd like to contribute, here are some ways you can help:
1. **Add new models:** Implement new model classes following the steps in the [Adding New Models](#-adding-new-models) section.
2. **Improve documentation:** Help us enhance our documentation, including this README, inline code comments, and the [official docs](https://dnth.github.io/x.infer).
3. **Report bugs:** If you find a bug, please [open an issue](https://github.com/dnth/x.infer/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug_report.md) with a clear description and steps to reproduce.
4. **Suggest enhancements:** Have ideas for new features? [Open a feature request](https://github.com/dnth/x.infer/issues/new?assignees=&labels=Feature+Request&projects=&template=feature_request.md).
5. **Financial support:** Please consider sponsoring the project to support continued development.
Please also see the code of conduct [here](./CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
Thank you for helping make x.infer better!
## ⚠️ Disclaimer
x.infer is not affiliated with any of the libraries it supports. It is a simple wrapper that allows you to run inference with any of the supported models.
Although x.infer is Apache 2.0 licensed, the models it supports may have their own licenses. Please check the individual model repositories for more details.



