https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl
Fast and simple music and audio analysis using RNN in Python 🕵️♀️ 🥁
https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl
analysis audio audio-features beat-detection beats data feature-extraction machine-learning mir ml music music-information-retrieval pip pypi python rnn sample-rate tempo
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Fast and simple music and audio analysis using RNN in Python 🕵️♀️ 🥁
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl
- Owner: dodiku
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-04-16T23:42:13.000Z (almost 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-06-20T10:42:51.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-07T19:11:09.996Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: analysis, audio, audio-features, beat-detection, beats, data, feature-extraction, machine-learning, mir, ml, music, music-information-retrieval, pip, pypi, python, rnn, sample-rate, tempo
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 89.8 KB
- Stars: 289
- Watchers: 9
- Forks: 21
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-python-audio - AudioOwl
- awesome-rainmana - dodiku/AudioOwl - Fast and simple music and audio analysis using RNN in Python 🕵️♀️ 🥁 (Python)
README
[](https://github.com/Naereen/StrapDown.js/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](http://makeapullrequest.com)
# AudioOwl
AudioOwl is using [librosa](https://librosa.github.io/librosa/index.html) and [RNN models](http://madmom.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html) to run fast analysis of music files 🎸.
**Jump to:**
- [Quickstart](https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl#quickstart)
- [Installation](https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl#installation)
- [Usage](https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl#usage)
- [Output data explained](https://github.com/dodiku/AudioOwl#output-data-explained)
> Mix your music automatically with [MixingBear](https://github.com/dodiku/MixingBear) - Automatic beat-mixing of music files 🎚

# Quickstart
Analyze a WAV audio file -
```python
import audioowl
data = audioowl.analyze_file(path='my_music_file.wav', sr=22050)
print (data)
==> {'sample_rate': 22050,
'duration': 36.096009070294784,
'beat_samples': [12794, 40148, 66179, 93092, ...,
'notes': [2,2,2,2,3,3,3,1,1,...]
...}
```
or an MP3 file -
```python
data = audioowl.analyze_file(path='my_music_file.mp3', sr=22050)
```
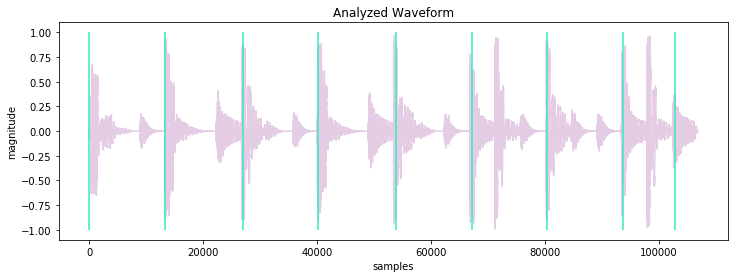
Get beat times in samples (``data['beat_samples']``) -
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
waveform = audioowl.get_waveform('drums.mp3', sr=22050)
data = audioowl.analyze_file('drums.mp3', sr=22050)
plt.figure()
plt.vlines(data['beat_samples'], -1.0, 1.0)
plt.plot(waveform)
plt.show()
```
# Installation
> Tested on Python 3.6 or later
> ⚠️ AudioOwl needs **ffmpeg** to be installed on your machine.
> The easiest way to install ffmpeg (at least on a Mac) is using homebrew. [See instructions here](https://gist.github.com/clayton/6196167).
The latest stable release is available on PyPI.
Install it using the following command -
```bash
$ pip install audioowl
```
# Usage
Given an audio file, AudioOwl generates an objects with many useful information about your file 💪.
## ``audioowl.get_waveform()``
Returns a numpy array that contains that audio file time series.
Supported keyword arguments for ``audioowl.get_waveform()``:
- ``path`` - Local path to the audio file.
- ``sr`` *[optional]* - Requested sample rate for the analyzed file. This does not have to be the actual sample rate of the file, but the sample rate that will be used for the analysis. default = 22050.
## ``audioowl.analyze_file()``
Returns an object (dictionary) with the analysis results.
The ``audioowl.analyze_file()`` function allows you to use the path to the audio file.
Supported keyword arguments for ``audioowl.analyze_file()``:
- ``path`` - Local path to the audio file.
- ``sr`` *[optional]* - Requested sample rate for the analyzed file. This does not have to be the actual sample rate of the file, but the sample rate that will be used for the analysis. default = 22050.
## ``audioowl.analyze_samples()``
Returns a numpy array that contains that audio file time series.
The ``audioowl.analyze_samples()`` function allows you to use an audio time series (as numpy array).
Example -
```python
import audioowl
time_series = audioowl.get_waveform('my_music_file.wav')
data = audioowl.analyze_samples(y=time_series, sr=44100)
```
Supported keyword arguments for ``audioowl.analyze_samples()``:
- ``y`` - Time series. Must be a numpy array, with shape (1,) for mono, and (2,) for stereo.
- ``sr`` - Requested sample rate for the analyzed file. This does not have to be the actual sample rate of the file, but the sample rate that will be used for the analysis.
## Output data explained
The return value of all function is a an object (dictionary) with the analysis results.
In case where the return value is stored in ``data``:
```python
import audioowl
data = audioowl.analyze_file(path='my_music_file.wav', sr=22050)
```
The ``data`` object will include the following properties:
```python
data['sample_rate'] # [int] sample rate
data['duration'] # [float] file duration
data['beat_samples'] # [list] beat location in samples
data['number_of_beats'] # [list] number of detected beats
data['tempo_float'] # [float] detected tempo as a float
data['tempo_int'] # [int] detected tempo as an int
data['zero_crossing'] # [list] detected zero level crossing, in samples detected
data['noisiness_median'] # [float] nosiness value as a median, across the file
data['noisiness_sum'] # [float] nosiness value as a sum, across the file
data['notes'] # [list] notes across the file, based on chromagram of hop_length=512 samples.
# notes legend:
# 0 c
# 1 c#
# 2 d
# 3 d#
# 4 e
# 5 f
# 6 f#
# 7 g
# 8 g#
# 9 a
# 10 a#
# 11 b
data['dominant_note'] # [int] most dominant (frequent) note across the file
```