https://github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache
The First Redis Cache Library To Ensure Eventual Consistency And Strong Consistency With DB.
https://github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache
cache consistency distributed redis
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
The First Redis Cache Library To Ensure Eventual Consistency And Strong Consistency With DB.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache
- Owner: dtm-labs
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2022-04-28T03:26:53.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-29T12:21:05.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-08T14:07:54.517Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: cache, consistency, distributed, redis
- Language: Go
- Homepage: http://d.dtm.pub/app/cache.html
- Size: 83 KB
- Stars: 556
- Watchers: 18
- Forks: 69
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README


[](https://codecov.io/gh/dtm-labs/rockscache)
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache)
[](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache)
English | [简体中文](https://github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache/blob/main/helper/README-cn.md)
# RocksCache
The first Redis cache library to ensure eventual consistency and strong consistency with DB.
## Features
- Eventual Consistency: ensures eventual consistency of cache even in extreme cases
- Strong consistency: provides strong consistent access to applications
- Anti-breakdown: a better solution for cache breakdown
- Anti-penetration
- Anti-avalanche
- Batch Query
## Usage
This cache repository uses the most common `update DB and then delete cache` cache management policy
### Read cache
``` Go
import "github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache"
// new a client for rockscache using the default options
rc := rockscache.NewClient(redisClient, NewDefaultOptions())
// use Fetch to fetch data
// 1. the first parameter is the key of the data
// 2. the second parameter is the data expiration time
// 3. the third parameter is the data fetch function which is called when the cache does not exist
v, err := rc.Fetch("key1", 300 * time.Second, func()(string, error) {
// fetch data from database or other sources
return "value1", nil
})
```
### Delete the cache
``` Go
rc.TagAsDeleted(key)
```
## Batch usage
### Batch read cache
``` Go
import "github.com/dtm-labs/rockscache"
// new a client for rockscache using the default options
rc := rockscache.NewClient(redisClient, NewDefaultOptions())
// use FetchBatch to fetch data
// 1. the first parameter is the keys list of the data
// 2. the second parameter is the data expiration time
// 3. the third parameter is the batch data fetch function which is called when the cache does not exist
// the parameter of the batch data fetch function is the index list of those keys
// missing in cache, which can be used to form a batch query for missing data.
// the return value of the batch data fetch function is a map, with key of the
// index and value of the corresponding data in form of string
v, err := rc.FetchBatch([]string{"key1", "key2", "key3"}, 300, func(idxs []int) (map[int]string, error) {
// fetch data from database or other sources
values := make(map[int]string)
for _, i := range idxs {
values[i] = fmt.Sprintf("value%d", i)
}
return values, nil
})
```
### Batch delete cache
``` Go
rc.TagAsDeletedBatch(keys)
```
## Eventual consistency
With the introduction of caching, consistency problems in a distributed system show up, as the data is stored in two places at the same time: the database and Redis. For background on this consistency problem, and an introduction to popular Redis caching solutions, see.
- [https://yunpengn.github.io/blog/2019/05/04/consistent-redis-sql/](https://yunpengn.github.io/blog/2019/05/04/consistent-redis-sql/)
But all the caching solutions we've seen so far, without introducing versioning at the application level, fail to address the following data inconsistency scenario.

Even if you use lock to do the updating, there are still corner cases that can cause inconsistency.
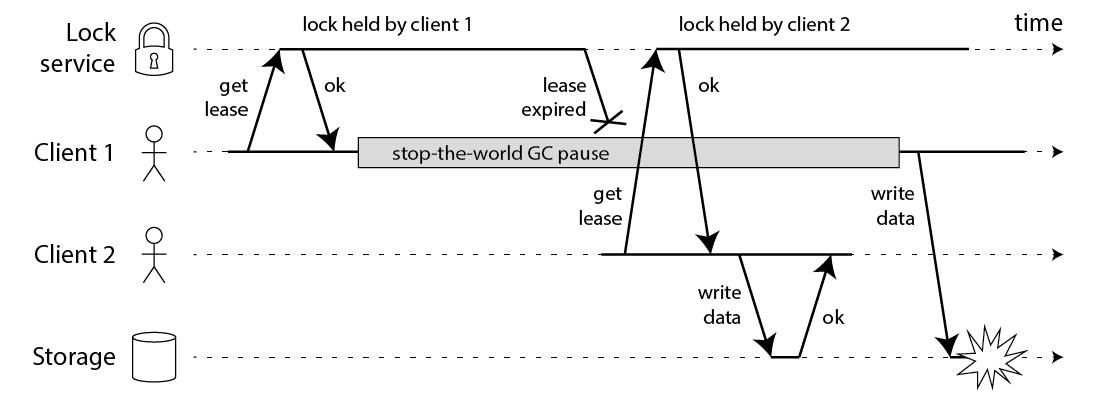
### Solution
This project brings you a brand new solution that guarantee data consistency between the cache and the database, without introducing version. This solution is the first of its kind and has been patented and is now open sourced for everyone to use.
When the developer calls `Fetch` when reading the data, and makes sure to call `TagAsDeleted` after updating the database, then the cache can guarentee the eventual consistency. When step 5 in the diagram above is writing to v1, the write in this solution will eventually be ignored.
- See [Atomicity of DB and cache operations](https://en.dtm.pub/app/cache.html#atomic) for how to ensure that TagAsDeleted is called after updating the database.
- See [Cache consistency](https://en.dtm.pub/app/cache.html) for why data writes are ignored when step 5 is writing v1 to cache.
For a full runnable example, see [dtm-cases/cache](https://github.com/dtm-labs/dtm-cases/tree/main/cache)
## Strongly consistent access
If your application needs to use caching and requires strong consistency rather than eventual consistency, then this can be supported by turning on the option `StrongConsisteny`, with the access method remaining the same
``` Go
rc.Options.StrongConsisteny = true
```
Refer to [cache consistency](https://en.dtm.pub/app/cache.html) for detailed principles and [dtm-cases/cache](https://github.com/dtm-labs/dtm-cases/tree/main/cache) for examples
## Downgrading and strong consistency
The library supports downgrading. The downgrade switch is divided into
- `DisableCacheRead`: turns off cache reads, default `false`; if on, then Fetch does not read from the cache, but calls fn directly to fetch the data
- `DisableCacheDelete`: disables cache delete, default false; if on, then TagAsDeleted does nothing and returns directly
When Redis has a problem and needs to be downgraded, you can control this with these two switches. If you need to maintain strong consistent access even during a downgrade, rockscache also supports
Refer to [cache-consistency](https://en.dtm.pub/app/cache.html) for detailed principles and [dtm-cases/cache](https://github.com/dtm-labs/dtm-cases/tree/main/cache) for examples
## Anti-Breakdown
The use of cache through this library comes with an anti-breakdown feature. On the one hand `Fetch` will use `singleflight` within the process to avoid multiple requests being sent to Redis within a process, and on the other hand distributed locks will be used in the Redis layer to avoid multiple requests being sent to the DB from multiple processes at the same time, ensuring that only one data query request ends up at the DB.
The project's anti-breakdown provides a faster response time when hot cached data is deleted. If a hot cache data takes 3s to compute, a normal anti-breakdown solution would cause all requests for this hot data to wait 3s for this time, whereas this project's solution returns it immediately.
## Anti-Penetration
The use of caching through this library comes with anti-penetration features. When `fn` in `Fetch` returns an empty string, this is considered an empty result and the expiry time is set to `EmptyExpire` in the rockscache option.
`EmptyExpire` defaults to 60s, if set to 0 then anti-penetration is turned off and no empty results are saved
## Anti-Avalanche
The cache is used with this library and comes with an anti-avalanche. `RandomExpireAdjustment` in rockscache defaults to 0.1, if set to an expiry time of 600 then the expiry time will be set to a random number in the middle of `540s - 600s` to avoid data expiring at the same time
## Contact us
## Chat Group
Join the chat via [https://discord.gg/dV9jS5Rb33](https://discord.gg/dV9jS5Rb33).
## Give a star! ⭐
If you think this project is interesting, or helpful to you, please give a star!