https://github.com/earthskyorg/scaffold-eth-nft-auction
Scaffold Ether NFT Auction
https://github.com/earthskyorg/scaffold-eth-nft-auction
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Scaffold Ether NFT Auction
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/earthskyorg/scaffold-eth-nft-auction
- Owner: earthskyorg
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-10-31T02:30:15.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-10-31T02:31:09.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-19T23:43:47.945Z (5 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 5.85 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# 🏦🏗 scaffold-eth - NFT Auction
> Discover how you can build your own NFT auction where the highest bid gets an NFT
Table of Contents
-
About The Project
-
Speed Run
-
Getting Started
- Exploring smart contracts
- Practice
- Additional resources
- Contact
## About The Project
This branch uses [buyer-mints-nft](https://github.com/austintgriffith/scaffold-eth/tree/buyer-mints-nft) as a starting point. Please refer to its own README for the context.
We will show you how a simple NFT auction can be built and also will demonstrate how you can spin it up locally as a playground.
## Speed Run
[](https://youtu.be/ws1bZ5VTolw)
## Getting Started
### Prerequisites
You have to know what is an ERC721 standard and what is NFT. Please refer to [this](http://erc721.org/) and [this](https://docs.openzeppelin.com/contracts/4.x/erc721) for more information if you are not familiar with these terms.
### Installation
Let's start our environment for tinkering and exploring how NFT auction would work.
1. Clone the repo first
```sh
git clone https://github.com/yingjingyang/nft-auction.git
```
2. Install dependencies
```bash
yarn install
```
3. Config environment variable
```shell
cd packages/hardhat
cp .env.example .env
## Then config privatekey in file .env
```
4. The ui currently depends on a json file so to generate that run
```bash
yarn upload
```
5. Deploy your smart contracts
Right now, we use Rinkeby as default testnet, so the contract will be deployed on Rinkeby.
```bash
yarn deploy
```
6. Start your React frontend
```bash
yarn start
```
## Smart contracts
Let's navigate to `packages/hardhat/contracts` folder and check out what contracts we have there.
We are mostly interested in `Auction.sol` smart contract which contains all the logic for NFT auction.
### Auction.sol
First of all, note how we are initializing our smart contract using this line.
```solidity
contract Auction is IERC721Receiver
```
We inherit from [IERC721Receiver](https://docs.openzeppelin.com/contracts/4.x/api/token/erc721#IERC721Receiver) which is an interface created by OpenZeppelin. Inheriting from this contract will allow us to receive transfer of NFT from another account to our contract.
Inheriting from this contract also requires us to paste the implementation of `onERC721Received` which you can find at the bottom of the contract.
The logic for creating an auction is in `createTokenAuction` function. It takes an address of NFT contract which in our case is an address of `YourCollectible.sol` deployed to our local chain, unique token ID which is going to be sold, minimum bid and duration in seconds.
```solidity
ERC721(_nft).safeTransferFrom(owner, address(this), _tokenId);
tokenToAuction[_nft][_tokenId] = _auction;
```
As you can see above, creating an auction means temporarily transfer an NFT to the Auction contract and also save information about auction to our Solidity mapping.
Users place bids by calling `bid` function which basically checks that the bid which is going to be made is currently the highest one. Note that we store the entire history of all bids made to allow us to return funds back to users who did not win an auction.
`executeSale` is a function used to complete the auction and identify the winner. It simply checks the last element of all bids placed and transfers NFT to the winner. If no bids were made, NFT is returned back to the initial owner.
`cancelAuction` allows to prematurely cancel the auction and lets the initial owner to get back his NFT.
## Practice
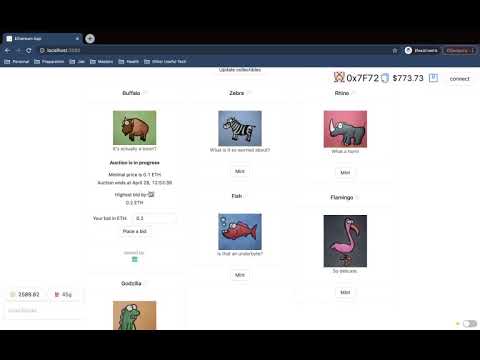
Firstly, let's get us some funds using local faucet and mint any NFT, so we become its owner.

You can now note that we have an option to Start auction because we are an owner of this newly minted NFT. Let's try to start an auction!

The minimal bid that users will be able to place is 0.1 ETH, and the total duration for our auction will be 5 minutes.

Auction is now in progress, and we can complete it or cancel it. No bids were made yet so there is no information about them yet. Let's try to put some bid now.
After you submit your bid, the information about auction will be updated if your bid is the highest at this point of time.

We placed a bid of 0.2 ETH and now we are the highest bidder. Yay!
Now let's try to open an incognito window and place a higher bid by a different user.

We placed 0.5 ETH big as a different user and now it's the highest bid. Now let's get back to our first account to complete an auction.

As you see, after we finished the auction, we are no longer an owner of the NFT. The account which placed 0.5 ETH is now a new owner. This is why we do not have an option to start an auction now.
## Additional resources
* [Dutch auction](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dutch_auction) - The idea behind auctions used in this contract
## Contact
Join the [telegram support chat 💬](https://t.me/joinchat/KByvmRe5wkR-8F_zz6AjpA) to ask questions and find others building with 🏗 scaffold-eth!