https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u
CRAN as Ubuntu Binaries
https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u
cran lts packages r ubuntu
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
CRAN as Ubuntu Binaries
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u
- Owner: eddelbuettel
- Created: 2022-04-10T22:36:12.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-26T14:39:49.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-10T01:10:37.194Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: cran, lts, packages, r, ubuntu
- Language: R
- Homepage: https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u
- Size: 14.6 MB
- Stars: 276
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 17
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: ChangeLog
Awesome Lists containing this project
- jimsghstars - eddelbuettel/r2u - CRAN as Ubuntu Binaries (R)
README
## r2u: CRAN as Ubuntu Binaries
### Key features
- **Full integration with `apt`** as every binary resolves _all_ its dependencies: No more
installations (of pre-built archives) only to discover that a shared library is missing. No more
surprises.
- **Full integration with `apt`** so that an update of a system library cannot break an R package:
if a (shared) library is used by a CRAN, the package manager knows, and will not remove it. No
more (R package) breakage from (system) library updates.
- **Simpler and lighter** than some alternatives as only _run-time_ library packages are installed as
dependencies (instead of generally heavier _development_ packages).
- **Installations are fast, automated and reversible** thanks to the package management layer.
- **Fast and well-connected mirror** at
[r2u.stat.illinois.edu](https://r2u.stat.illinois.edu) on the [Internet2](https://internet2.edu/)
- **Complete coverage** with (currently, using 22.04) ~ 24491 CRAN packages (and 435 from
BioConductor) using **current versions**: We use R 4.4.*, and BioConductor 3.20.
- Complete support for **Ubuntu 20.04 ("focal")**, **22.04 ("jammy")** and **24.04 ("noble")** on
amd64, as well as (initial) **24.04 ("noble")** support on arm64.
- Optional (but recommended) [bspm](https://cloud.r-project.org/package=bspm) use
**automagically connects R functions like `install.packages()` to `apt`** for access to binaries
_and_ dependencies.
- **Docker containers** `rocker/r2u` from the [Rocker Project](https://rocker-project.org/) for both
'focal', 'jammy' and 'noble'.
- **GitHub Actions support** to set up on Ubuntu 'latest' or via container.
### Brief Demo
The gif below shows how _one `install.packages("tidyverse")` command_ on an Ubuntu
20.04 system _installs all packages and dependencies as binaries in 18 seconds_ (by passing the
R package installation to `apt` using [bspm](https://cloud.r-project.org/package=bspm)).
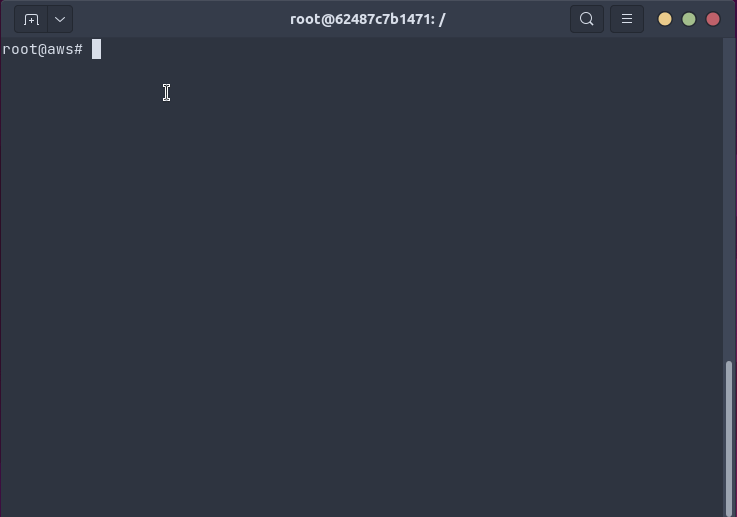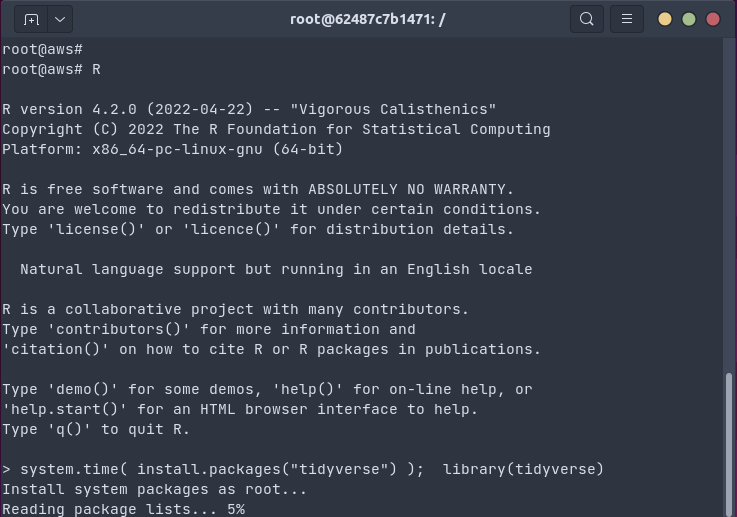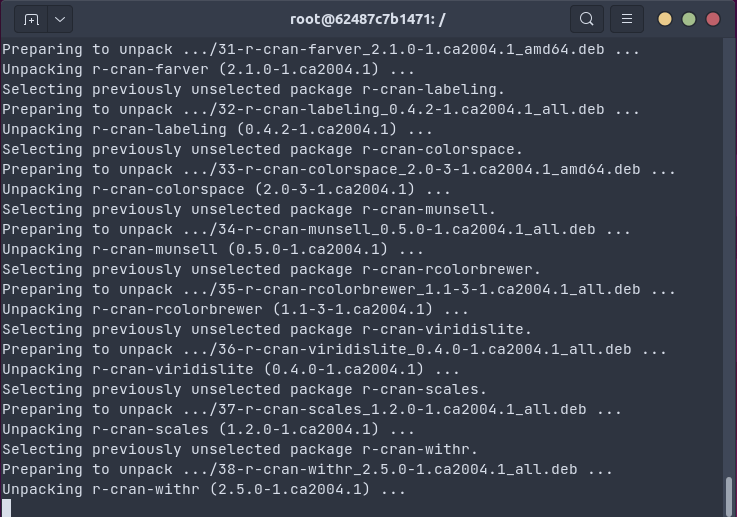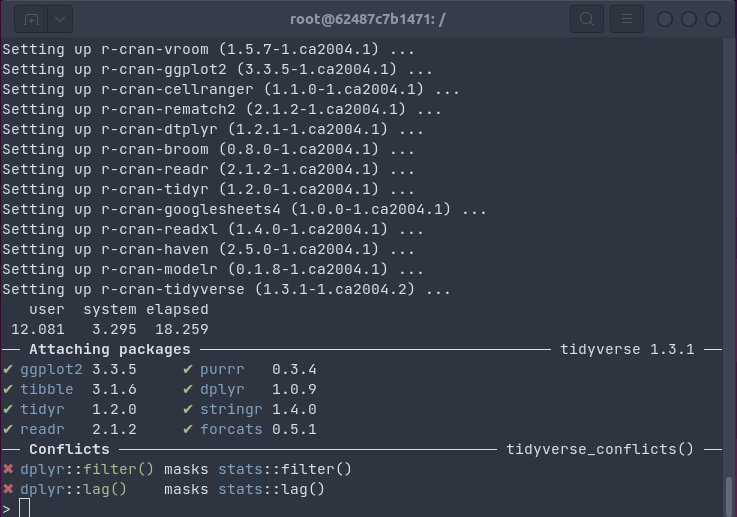
This uses the Docker container referenced below, which has been set up with
the five easy setup steps detailed here.
### What is Covered ?
We generally support amd64 (_i.e._ standard 64-bit Intel/AMD cpus, sometimes also called x86_64) for
the current Ubuntu LTS release and its predecessor release (more on this
[here](https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/vignettes/FAQ/#what-about-other-architectures-besides-x86_64)).
We use 'r-release' just like CRAN. So currently the 'focal' 20.04 LTS, 'jammy' 22.04 LTS and 'noble'
24.04 releases are fully supported. We are now also starting to support arm64 on 'noble' 24.04 taking
advantage of arm64-based runners at GitHub Actions.
Support for additional cpu architectures is certainly possible but somewhat unlikely due to a lack of
(additional hardware) resources and time. Support for other distributions is possible but unlikely
right now (due to a lack of resources and time). P3M/PPM/RSPM now appears to also support Debian which
could be added at some later point.
Current versions are based on R 4.4.*, and BioConductor release 3.20 packages are provided when
required by CRAN packages. Binaries are generally R 4.4.* based. Some older packages released when
we used R 4.2.* or 4.3.* may have been built with R 4.2.* or R 4.3.*, they will still work the same
with R 4.4.* as R is generally forward-compatible.
### What is Selected ?
Everything :)
Initially, we started from [cran-logs](https://cran-logs.rstudio.com/) by picking the _N_
most-downloaded packages, along with their dependencies from BioConductor. (It should be noted that
for example the first 100 packages already account for approximately half the total downloads: it is
a very skewed distribution.) We iterated, and fairly soon arrived of full coverage of CRAN.
So we now cover
- *all CRAN packages* (modulo at best a handful of blacklisted ones) including all packages needing
compilation
- all BioConductor packages implied by these plus a 'healthy subset' of the highest
[scoring](https://bioconductor.org/packages/stats/bioc/bioc_pkg_scores.tab) BioConductor
packages (also covering _e.g._ all BioConductor packages in the Debian and Ubuntu distributions)
This currently results in 24797, 24717, 22376 binary packages from CRAN in "focal", "jammy", and
"noble", respectively, and 429, 437, and 451 BioConductor packages, respectively, from the 3.20
releases. (See this
[FAQ](https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/vignettes/FAQ/#why-does-it-have-more-packages-than-cran)
about why this number is higher than CRAN, and variable between releases.)
The sole exception are packages we cannot build (as we do not have the required commercial software
it accessess, or do not have the required more recent toolchain component) plus a handful or so of
'odd builds' that fail and are skipped.
### What is it Based On?
For the CRAN binaries we either repackage
[P3M/RSPM/PPM](https://packagemanager.rstudio.com/client/#/repos/2/packages/) builds (where
available) or build natively. All selected BioConductor packages are built natively. For all of
these, full dependency resolution and integration with the system is a key feature.
Everything is provided as `.deb` binary files with proper dependency
resolution by using a proper `apt` repo which also has a signed Release file.
### Usage and Setup
(Note that you could use one of the scripts
[`add_cranapt_noble.sh`](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/blob/master/inst/scripts/add_cranapt_noble.sh)
(for Ubuntu 24.04), or
[`add_cranapt_jammy.sh`](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/blob/master/inst/scripts/add_cranapt_jammy.sh)
(for Ubuntu 22.04), or
[`add_cranapt_focal.sh`](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/blob/master/inst/scripts/add_cranapt_focal.sh)
(for the older Ubuntu 20.04) to facilitate the setup. They are tested on 'empty' Ubuntu containers
of the corresponding release. However, you may prefer to execute the steps outlined here by hand.)
You can use `lsb_release -cs` to generate your release name: "focal", "jammy", and "noble" are
supported and you could swap "focal" or "noble" in below (or use one of the scripts).
Here, we show the setup step by step for 'jammy' aka Ubuntu 22.04 (as it is still the most-widely
used distribution per our logs, though we may update this to 24.04 soon). You should run all these
commands as `root` to carefully review each one. If you prefer the newer Ubuntu 24.04, please see
the
[`add_cranapt_noble.sh`](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/blob/master/inst/scripts/add_cranapt_noble.sh)
script which also avoids the now-deprecated `apt-key` command).
**Step 1: Update apt, install tools, fetch key**
First add the repository key so that `apt` knows it (this is optional but recommended)
```sh
apt update -qq && apt install --yes --no-install-recommends wget \
ca-certificates gnupg
wget -q -O- https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/assets/dirk_eddelbuettel_key.asc \
| tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cranapt_key.asc
```
**Step 2: Add the apt repo**
Second, add the repository to the `apt` registry. We recommend the well-connected main mirror
provide at University of Illinois:
```sh
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://r2u.stat.illinois.edu/ubuntu jammy main" \
> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cranapt.list
apt update -qq
```
Use `arch=arm64` for arm64 support (currently only available for noble).
**Step 3: Ensure you have current R binaries (optional)**
Third, and optionally, if you do not yet have the current R version, run these two lines (or
use the [standard CRAN repo setup](https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/))
```sh
wget -q -O- https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/marutter_pubkey.asc \
| tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cran_ubuntu_key.asc
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu jammy-cran40/" \
> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cran_r.list
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys \
67C2D66C4B1D4339 51716619E084DAB9
apt update -qq
DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt install --yes --no-install-recommends \
r-base-core
```
Use `arch=arm64` for arm64 support (currently only available for noble).
**Step 4: Use pinning for the r2u repo (optional)**
Fourth, add repository 'pinning' as `apt` might get confused by some older
packages (in the Ubuntu distro) which accidentally appear with a higher
version number. See the next section for a short discussion how it ensures 'CRANapt'
sorts highest.
```sh
echo "Package: *" > /etc/apt/preferences.d/99cranapt
echo "Pin: release o=CRAN-Apt Project" >> /etc/apt/preferences.d/99cranapt
echo "Pin: release l=CRAN-Apt Packages" >> /etc/apt/preferences.d/99cranapt
echo "Pin-Priority: 700" >> /etc/apt/preferences.d/99cranapt
```
After that the package are known (under their `r-cran-*` and `r-bioc-*`
names). You can install them on the command-line using `apt` and `apt-get`,
via `aptitude` as well as other front-ends.
**Step 5: Use `bspm` (optional)**
Fifth, and also optional, install and enable the [bspm](https://cloud.r-project.org/package=bspm)
package so that the r2u (or CRANapt) as well as other R packages (available as `r-*.deb` binaries)
become available via `install.packages()` and `update.packages()`. Note that you may need to install
it directly from source via `sudo Rscript -e 'install.packages("bspm")'` to ensure it integrates
correctly with the packaging system. You should also install Python components used internally by
[bspm](https://cloud.r-project.org/package=bspm) via the `sudo apt-get install
python3-{dbus,gi,apt}` command.
```sh
apt install --yes --no-install-recommends python3-{dbus,gi,apt}
## Then install bspm (as root) and enable it, and enable a speed optimization
Rscript -e 'install.packages("bspm")'
RHOME=$(R RHOME)
echo "suppressMessages(bspm::enable())" >> ${RHOME}/etc/Rprofile.site
echo "options(bspm.version.check=FALSE)" >> ${RHOME}/etc/Rprofile.site
```
That's it! Now try it out!
### About Pinning
Packages can be found in different repositories, and _generally_ the highest available version is
the one we what---and `apt` picks it for us. Now, because we let `apt` (and related tools) pick the
packages based on versions, we may want to ensure that the CRANapt repo sorts higher than the
default repo as (older) package builds in the distribution itself may appear (to `apt`) to be newer
via a quirk in the sorting algorithm. A case in point was package `gtable` whose version in Ubuntu
was `0.3.0+dfsg-1` which accidentally sorts higher than the rebuild we made under a newer and more
consistent version number `0.3.0-1.ca2004.1`.
For this issue, one possible and popular fix is to use 'apt pinning'. It can give 'higher weight'
to packages from a particular repositor or tag. In the suggested example above, we
give the r2u / cranapt repo a weight of 700 which is higher than the package default value of
500.
### Docker
**Core r2u Containers**
There are also Docker containers for Ubuntu 20.04 'focal', 22.04 'jammy', and 24.04 'noble',
respectively. Initially published as
[eddelbuettel/r2u](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/eddelbuettel/r2u), these are now also
available also as [rocker/r2u](https://github.com/rocker-org/r2u). They all have the features
detailed above, including pinning and [bspm](https://cran.r-project.org/package=bspm) support,
already set up.
Each of the Ubuntu LTS flavors, _i.e._, 'focal' and 'jammy' is also available as an identical image
using the release version, _i.e._, '20.04', '22.04', and '24.04', respectively.
Note that with some builds of Docker (and possibly related to Ubuntu hosts) you may have to add
the `--security-opt seccomp=unconfined` option to your Docker invocation to take advantage of bspm
and the full system integration inside the container.
This is also documented in the [FAQ](https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/vignettes/FAQ/).
**Contributed Containers**
We are now starting to see derived containers:
- [BioConductor](https://www.bioconductor.org/) has an (alpha release) project
[bioc2u](https://github.com/Bioconductor/bioc2u) providing (internal ?) BioConductor builds
- [Jeffrey Girard](https://github.com/jmgirard) created
[rstudio2u](https://github.com/jmgirard/rstudio2u) which adds RStudio to the
base layer provided by r2u.
It is encouraging to see such specialisations based off r2u itself.
### GitHub Actions
There are two basic ways to take advantage of *r2u* in a GitHub Actions. The first, and simplest,
is to switch to using the Docker container (see previous section). This is as simple as adding the
`container:` statement after `runs-on:` in `jobs:` section:
```
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: rocker/r2u:22.04
```
A complete example is provided in [this R package
repo](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/RcppInt64/blob/master/.github/workflows/r2u.yaml). The key
advantage of this approach is that everything is already set up.
A second approach consists of adding *r2u* as a step via [the `r2u-setup` GitHub
Action](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/github-actions):
```
- name: Setup r2u
uses: eddelbuettel/github-actions/r2u-setup@master
```
A complete example is provided [in this
repo](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/spotifytop50us/blob/master/.github/workflows/update.yaml)
where we use it because using the Docker container approach makes committing back via `git` a little
harder.
### Try It
**Via codespaces**
See the vignette [Codespaces](https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/vignettes/Codespaces/) about how to
launch a 'Codespace' directly in your browser, launched from the gitrepo within minutes.
This also works from your [vscode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) installation as a remote
codespace.
The vignette has more details.
**Via gitpod.io**
Use this link below (after possibly signing up for
[gitpod.io](https://gitpod.io/) first)
[](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u)
and run [one of the three example
scripts](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/tree/master/inst/examples), or
just start R in the terminal window.
The gif below display running one such example to install
[brms](https://github.com/paul-buerkner/brms) from binaries in a few seconds. Using this requires
only (free) [GitHub](https://github.com) and [GitPod](https://gitpod.io) accounts.
### Usage Statistics
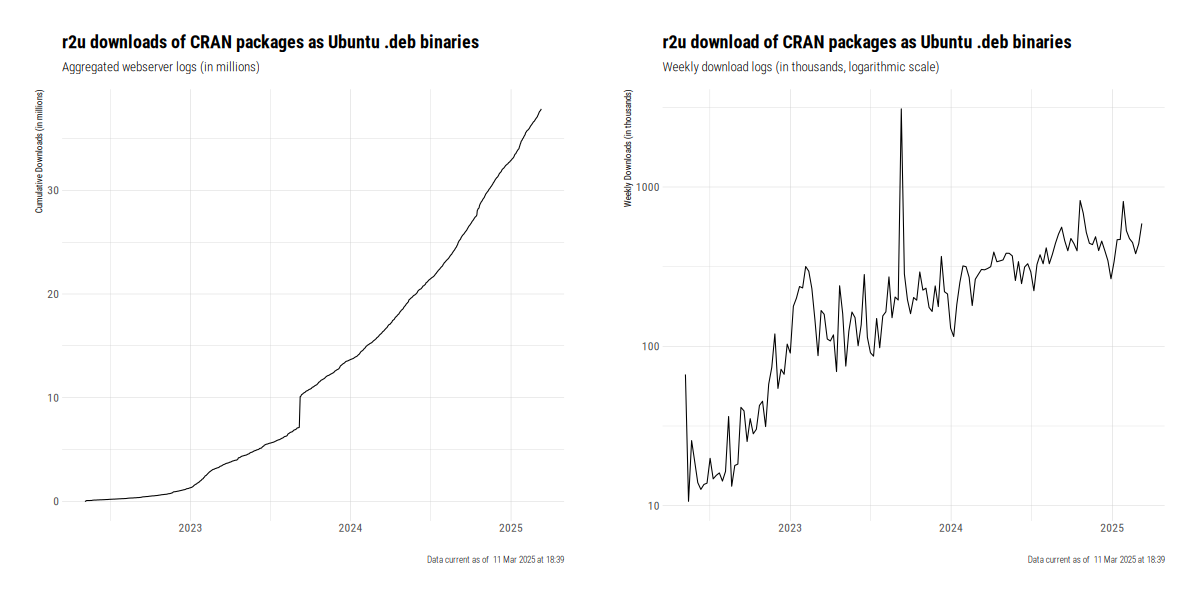
Usage is vibrant. As of March 2025, over 400,000 packages are shipped per week, with a total of
now over thirty seven million packages shipped. Early September 2023 also had the most recent and
dramatic spike of _over three million packages in two days_. The following chart gives a summary of
cumulative and average weekly downloads (the latter one on a log scale) as of August.
### Support
Please file issues at the [GitHub issues for r2u](https://github.com/eddelbuettel/r2u/issues).
### Frequently Asked Questions
Please also see the [FAQ](https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/vignettes/FAQ/) for answers to
_Frequently Asked Questions_.
### Known Issues
- The littler package reflects build-time configuration, the RSPM/PPM binary is then expecting a
different R location so it needs a binary rebuild. Added a 'force' flag, may need a list similar
to the blacklist to always compiled.
- A small number of packages do not build for lack required components; examples are ROracle and
Rcplex. They, and their reverse dependencies, are blacklisted and not built.
- r2u is an `apt` repo, which via `bspm` becomes used "automagically" via standard R calls of
`install.packages()` and alike. That last part is important: package installations that do not use
`install.packages()` (such as `renv`, `rig`, ...) do not benefit from
`install.packages()` calling `apt` for you, and cannot take advantage of r2u via `bspm`.
- `bspm` traces calls to `install.packages()` and maps them system-wide installation via `apt`. By
choice, it does not map the `remove.packages()` for package removal, see [this
issue](https://github.com/Enchufa2/bspm/issues/43) for more discussion. Packages can be uninstalled
via the system package manager using, respectively, `apt`, `dpkg` or one of graphical frontends as
well as via the R function `bspm::remove_sys()`.
### Author
Dirk Eddelbuettel
### License
The repository-building code in this package is released under the GPL (>= 2).
All CRAN and BioConductor packages are released under their respective licenses.
### Acknowledgment
This was made possible by the generous support of endless coffee thanks to my
[GitHub Sponsors](https://github.com/sponsors/eddelbuettel).