https://github.com/edgerun/faas-sim
A framework for trace-driven simulation of serverless Function-as-a-Service platforms
https://github.com/edgerun/faas-sim
edge-computing python serverless-computing simpy simulation
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
A framework for trace-driven simulation of serverless Function-as-a-Service platforms
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/edgerun/faas-sim
- Owner: edgerun
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-06-08T16:07:24.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-30T18:44:57.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-30T19:38:11.990Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: edge-computing, python, serverless-computing, simpy, simulation
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://edgerun.github.io/faas-sim/
- Size: 10.2 MB
- Stars: 68
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 8
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Authors: AUTHORS
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-edge-computing - faas-sim - sim is a powerful (Uncategorized / Uncategorized)
README
faas-sim: A trace-driven Function-as-a-Service simulator
========================================================
Faas-sim is a powerful trace-driven simulation framework to simulate container-based function-as-a-service platforms.
It can be used to develop, and evaluate the performance of operational strategies for such systems, like scheduling, autoscaling, load balancing, and others.
faas-sim was developed at the [Distributed Systems Group](https://dsg.tuwien.ac.at) at TU Wien as part of a larger research effort surrounding serverless edge computing systems.
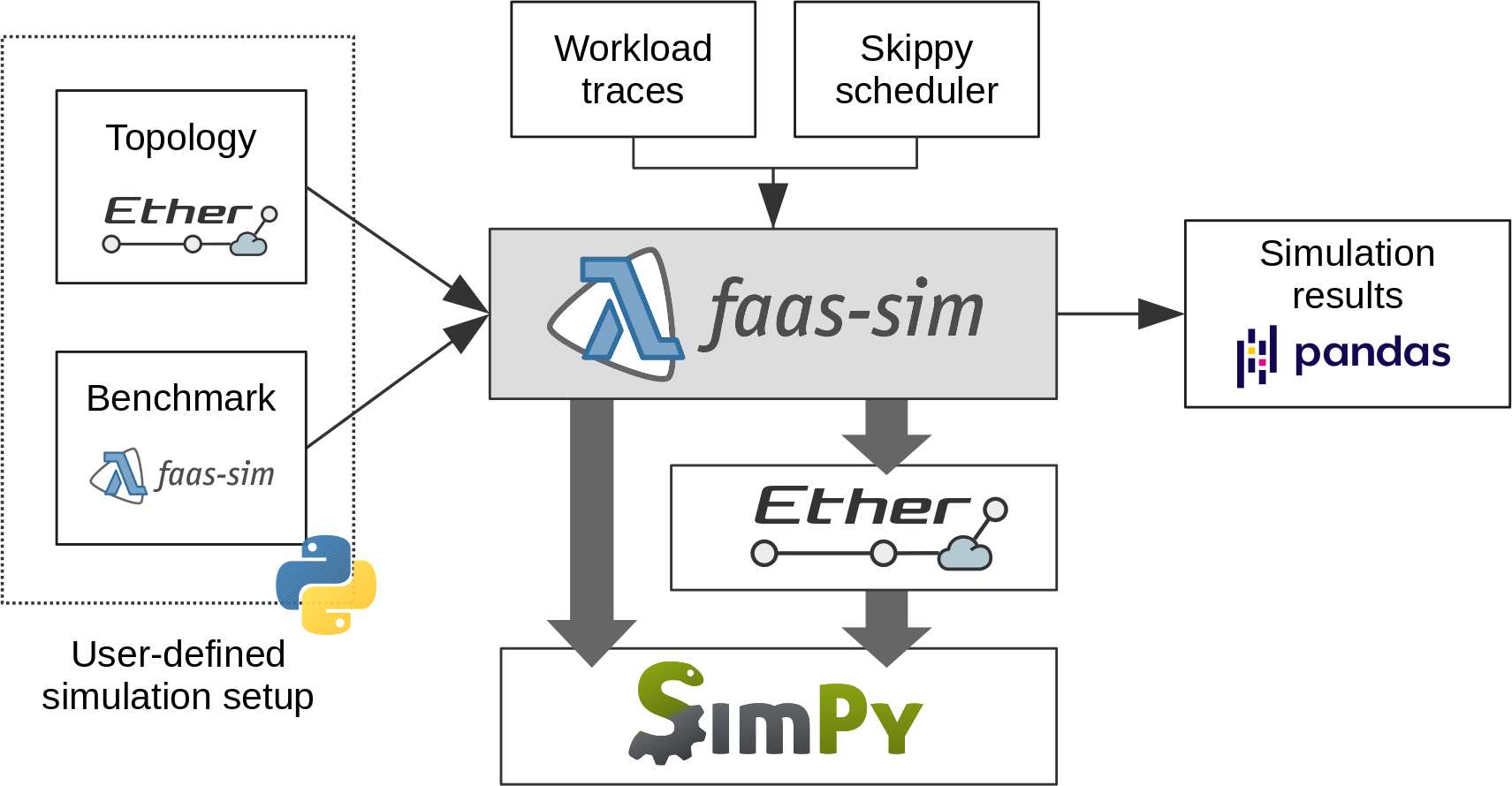
High-level architecture
-----------------------
faas-sim is based on the [SimPy](https://simpy.readthedocs.io) discrete-event simulation framework.
It uses [Ether](https://github.com/edgerun/ether) as network simulation layer, and to create cluster configurations and network topologies.
By default, it uses the [Skippy](https://github.com/edgerun/skippy-core) scheduling system for resource scheduling,
but schedulers, autoscalers, and load-balancers can be plugged in by the user.
faas-sim is trace-driven, and relies on profiling data from workloads and devices to simulate function execution.
It comes pre-packaged with traces from several common computing devices and representative cluster workloads.
The following figure shows a high-level overview:
Run examples
------------
You can run the examples we provide in https://github.com/edgerun/faas-sim/tree/master/examples by first creating a virtual environment and installing the necessary dependencies.
make venv
source .venv/bin/activate
python -m examples..main
Where example refers to the specific example package.
Check out the examples [README](https://github.com/edgerun/faas-sim/tree/master/examples/README.md) for more information.
Run notebooks
-------------
Notebooks are located in `notebooks`.
You need to install `faas-sim` in editable state to run the notebooks.
Inside `notebooks` import modules from `sim`.
To install the project (assuming you already created and activated a virtual environment via `make venv`):
pip install -e .
jupyter notebook
Documentation
-------------
You can find the documentation at https://edgerun.github.io/faas-sim/
Maintainers
------------
* [Thomas Rausch](https://github.com/thrau)
* [Philipp Raith](https://github.com/phip123)
Development
-----------
The simulator has seen a major refactoring in the branch `/feature/adapt-to-galileo-faas` and aims to be compatible with the other galileo projects.
Only this branch is in active development.
Related publications
--------------------
1. Raith, P., Rausch, T., Furutanpey, A., & Dustdar, S. (2023).
**faas‐sim: A trace‐driven simulation framework for serverless edge computing platforms.**
In *Software: Practice and Experience*. Wiley Online Library.
[[Paper](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/spe.3277)]
1. Raith, P. (2021)
Container Scheduling on Heterogeneous Clusters using Machine Learning-based Workload Characterization.
*Diploma Thesis*. TU Wien.
[[Thesis](https://repositum.tuwien.at/handle/20.500.12708/16871)]
1. Rausch, T., Lachner, C., Frangoudis, P. A., Raith, P., & Dustdar, S. (2020).
Synthesizing Plausible Infrastructure Configurations for Evaluating Edge Computing Systems.
In *3rd USENIX Workshop on Hot Topics in Edge Computing (HotEdge 20)*. USENIX Association.
[[Paper](https://www.usenix.org/conference/hotedge20/presentation/rausch)]
1. Rausch, T., Rashed, A., & Dustdar, S. (2020)
Optimized container scheduling for data-intensive serverless edge computing.
In *Future Generation Computer Systems.*.
[[Paper](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X2030399X)]
1. Rashed, A. (2020)
Optimized Container Scheduling for Serverless Edge Computing.
*Diploma Thesis*. TU Wien.
[[Thesis](http://repositum.tuwien.ac.at/obvutwhs/content/titleinfo/4671607)]