https://github.com/edinburgh-genome-foundry/dnachisel
:pencil2: A versatile DNA sequence optimizer
https://github.com/edinburgh-genome-foundry/dnachisel
bioinformatics codon-optimization dna-optimization sequence-design synbio synthetic-biology
Last synced: 10 days ago
JSON representation
:pencil2: A versatile DNA sequence optimizer
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/edinburgh-genome-foundry/dnachisel
- Owner: Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-09-07T16:37:36.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-04T08:56:58.000Z (19 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-06T15:03:31.155Z (17 days ago)
- Topics: bioinformatics, codon-optimization, dna-optimization, sequence-design, synbio, synthetic-biology
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://edinburgh-genome-foundry.github.io/DnaChisel/
- Size: 9.29 MB
- Stars: 232
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 47
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.rst
- Changelog: changes.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
.. raw:: html

DNA Chisel - a versatile sequence optimizer
===========================================
.. image:: https://github.com/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/DnaChisel/actions/workflows/build.yml/badge.svg
:target: https://github.com/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/DnaChisel/actions/workflows/build.yml
:alt: GitHub CI build status
.. image:: https://coveralls.io/repos/github/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/DnaChisel/badge.svg?branch=master
:target: https://coveralls.io/github/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/DnaChisel?branch=master
DNA Chisel (complete documentation `here `_)
is a Python library for optimizing DNA sequences with respect to a set of
constraints and optimization objectives. It can also be used via a command-line
interface, or a `web application `_.
The library comes with over 15 classes of sequence specifications which can be
composed to, for instance, codon-optimize genes, meet the constraints of a
commercial DNA provider, avoid homologies between sequences, tune GC content,
or all of this at once! Users can also define their own specifications using
Python, making the library suitable for a large range of automated sequence
design applications, and complex custom design projects. A specification can be
either a hard constraint, which must be satisfied in the final sequence, or an
optimization objective, whose score must be maximized.
For more information, please see the publication.
Citation
--------
DNA Chisel, a versatile sequence optimizer, *Valentin Zulkower, Susan Rosser.* `Bioinformatics `_ (2020) 36, 16, 4508–4509
Usage
-----
Defining a problem via scripts
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The example below will generate a random sequence and optimize it so that:
- It will be rid of BsaI sites (on both strands).
- GC content will be between 30% and 70% on every 50bp window.
- The reading frame at position 500-1400 will be codon-optimized for *E. coli*.
.. code:: python
from dnachisel import *
# DEFINE THE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM
problem = DnaOptimizationProblem(
sequence=random_dna_sequence(10000),
constraints=[
AvoidPattern("BsaI_site"),
EnforceGCContent(mini=0.3, maxi=0.7, window=50),
EnforceTranslation(location=(500, 1400))
],
objectives=[CodonOptimize(species='e_coli', location=(500, 1400))]
) # Note: always use a codon optimisation specification with EnforceTranslation
# SOLVE THE CONSTRAINTS, OPTIMIZE WITH RESPECT TO THE OBJECTIVE
problem.resolve_constraints()
problem.optimize()
# PRINT SUMMARIES TO CHECK THAT CONSTRAINTS PASS
print(problem.constraints_text_summary())
print(problem.objectives_text_summary())
# GET THE FINAL SEQUENCE (AS STRING OR ANNOTATED BIOPYTHON RECORDS)
final_sequence = problem.sequence # string
final_record = problem.to_record(with_sequence_edits=True)
Defining a problem via Genbank features
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
You can also define a problem by annotating directly a Genbank as follows:
.. raw:: html
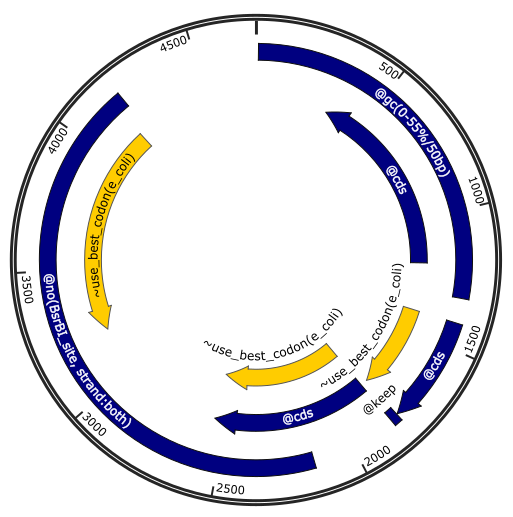
Note that constraints (colored in blue in the illustration) are features of type
``misc_feature`` with a prefix ``@`` followed by the name of the constraints
and its parameters, which are the same as in python scripts. Optimization
objectives (colored in yellow in the illustration) use prefix ``~``. See
`the Genbank API documentation `_
for more details.
Genbank files with specification annotations can be directly fed to the
`web application `_
or processed via the command line interface:
.. code:: bash
# Output the result to "optimized_record.gb"
dnachisel annotated_record.gb optimized_record.gb
Or via a Python script:
.. code:: python
from dnachisel import DnaOptimizationProblem
problem = DnaOptimizationProblem.from_record("my_record.gb")
problem.optimize_with_report(target="report.zip")
By default, only the built-in specifications of DNA Chisel can be used in the
annotations, however it is easy to add your own specifications to the Genbank
parser, and build applications supporting custom specifications on top of
DNA Chisel.
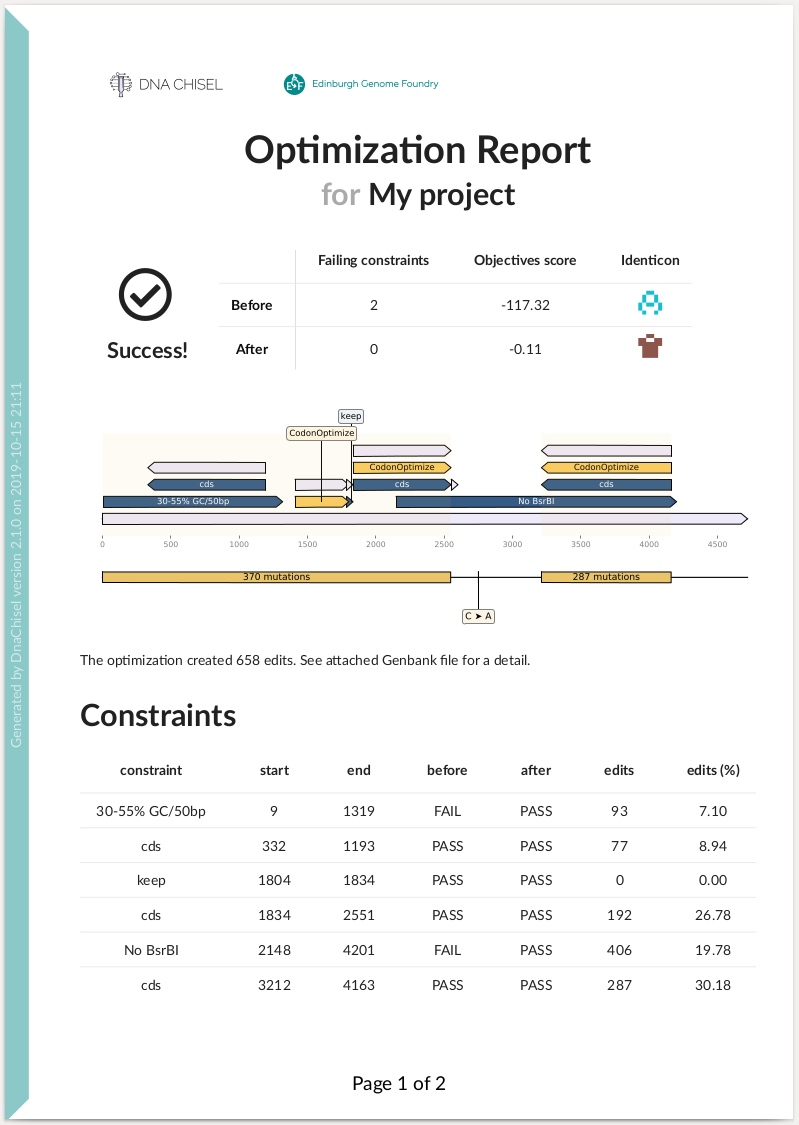
Reports
~~~~~~~
DNA Chisel also implements features for verification and troubleshooting. For
instance by generating optimization reports:
.. code:: python
problem = DnaOptimizationProblem(...)
problem.optimize_with_report(target="report.zip")
Here is an example of summary report:
.. raw:: html
How it works
------------
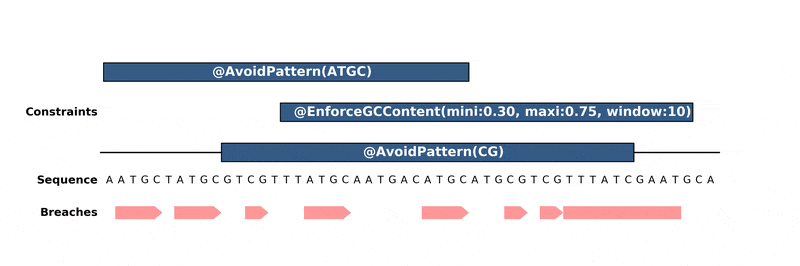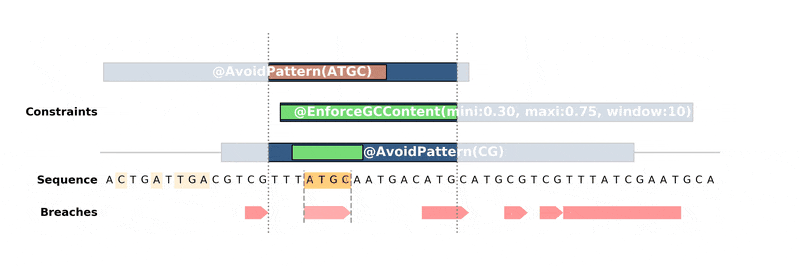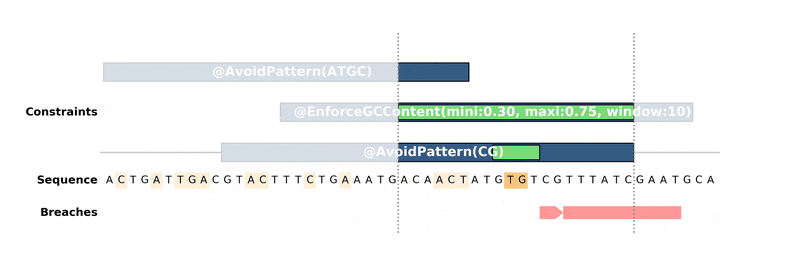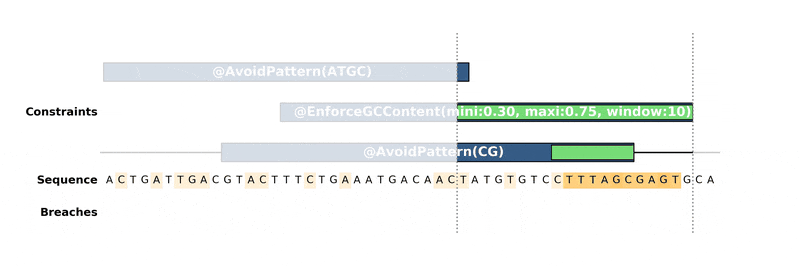
DNA Chisel hunts down every constraint breach and suboptimal region by
recreating local version of the problem around these regions. Each type of
constraint can be locally *reduced* and solved in its own way, to ensure fast
and reliable resolution.
Below is an animation of the algorithm in action:
.. raw:: html
Installation
------------
DNA Chisel requires Python 3, and can be installed via a pip command:
.. code::
pip install dnachisel # <= minimal install without reports support
pip install 'dnachisel[reports]' # <= full install with all dependencies
The full installation using ``dnachisel[reports]`` downloads heavier libraries
(Matplotlib, PDF reports, sequenticon) for report generation, but is highly
recommended to use DNA Chisel interactively via Python scripts. Also install
`GeneBlocks `_ and its
dependencies if you wish to include a plot of sequence edits in the report.
Optionally, also install Bowtie to be able to use ``AvoidMatches`` (which
removes short homologies with existing genomes). On Ubuntu:
.. code::
sudo apt-get install bowtie
License = MIT
-------------
DNA Chisel is an open-source software originally written at the `Edinburgh Genome Foundry
`_ by `Zulko `_
and `released on Github `_ under the MIT licence (Copyright 2017 Edinburgh Genome Foundry, University of Edinburgh). Everyone is welcome to contribute!
More biology software
---------------------
.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry/Edinburgh-Genome-Foundry.github.io/master/static/imgs/logos/egf-codon-horizontal.png
:target: https://edinburgh-genome-foundry.github.io/
DNA Chisel is part of the `EGF Codons `_ synthetic biology software suite for DNA design, manufacturing and validation.
Related projects
----------------
(If you would like to see a DNA Chisel-related project advertized here, please open
an issue or propose a PR)
- `Benchling `_ uses DNA Chisel as part of its sequence
optimization pipeline according to `this webinar video `_.
- `dnachisel-dtailor-mode `_ brings
features from `D-tailor `_
to DNA Chisel, in particular for the generation of large collection of sequences
covering the objectives fitness landscape (i.e. with sequences with are good at
some objectives and bad at others, and vice versa).