https://github.com/eldimious/slack-golang-gcf
Google cloud function which sends messages to slack via slack-webhook and triggered by http request
https://github.com/eldimious/slack-golang-gcf
gcf go golang google-cloud-functions slack slack-webhook
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
Google cloud function which sends messages to slack via slack-webhook and triggered by http request
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/eldimious/slack-golang-gcf
- Owner: eldimious
- Created: 2019-02-27T14:37:42.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-02-24T17:50:16.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-12T18:55:23.618Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: gcf, go, golang, google-cloud-functions, slack, slack-webhook
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 28.3 KB
- Stars: 2
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Serverless Slack messages dispatcher using Google Cloud Functions as FaaS.
When we say “serverless”, it doesn’t mean servers are no longer involved. It means that you no longer need to think about them.
Serverless is an approach that aims to eliminate the need to manage infrastructure by:
- Using a managed FaaS compute service such as AWS Lambda, Webtask, Google Cloud Functions, and IBM OpenWhisk to execute code,
- Leveraging third-party services and APIs, and
- Applying serverless architectures and patterns.
FaaS providers such as Gcf offers a new kind of platform that lets you deploy and invoke ephemeral (short-lived) function processes via events to handle individual requests. It provides a means to achieve the serverless dream allowing developers to execute code in response to events without building out or maintaining a complex infrastructure.
`slack-golang-gcf` is a serverless implementation of basic Stripe requests using Faas(Google Cloud Functions).
# Architecture Overview #
The app is designed to use a layered architecture. The architecture is heavily influenced by the Clean Architecture and Hexagonal Architecture. [Clean Architecture](https://8thlight.com/blog/uncle-bob/2012/08/13/the-clean-architecture.html) is an architecture where `the business rules can be tested without the UI, database, web server, or any external element`.
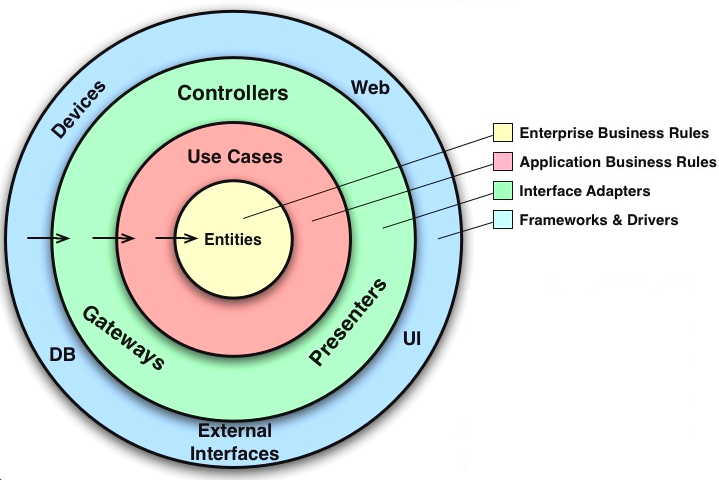
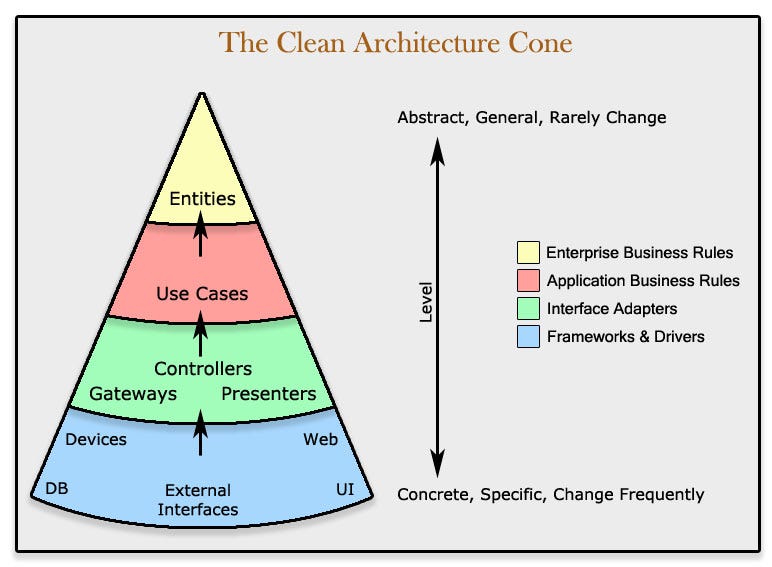
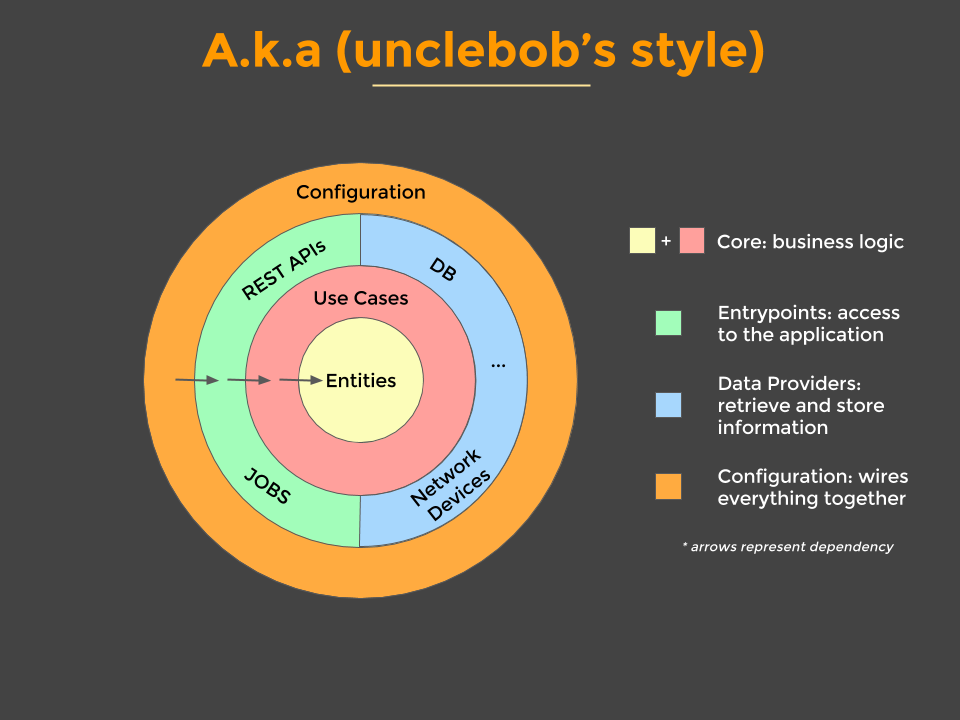

## Data Layer ##
The data layer is implemented using repositories, that hide the underlying data sources (BaaS, database, network, cache, etc), and provides an abstraction over them so other parts of the application that make use of the repositories, don't care about the origin of the data and are decoupled from the specific implementations used. Here, we use Stripe as a BaaS provider for both creating customers and payments and exporsure methods.This is important to enable the decoupling.
## Domain Layer ##
The domain layer is implemented using services. They depend on the repositories to get the exported methods and apply the *business rules* on them. They are not coupled to a specific BaaS implementation and can be reused if we change our Baas client from Stripe to another platform.
## Routes/Controller Layer ##
This layer is being used in the exported GCF and depends on the domain layer (services). Here we define the middleware where we specify some validation rules for the requests.
## Entry point ##
The entry point for the applications is the fn.go file, where we specify all google cloud functions that we will deploy.
# Quick start #
### Prerequisites ###
Create an .env.yaml file in project root to register the following required environment variable(we need the slack WEBHOOK_URL):
- `WEBHOOK_URL: "xxxxxxxxxxxx"`
### Deployment ###
In order to deploy your functions to gcloud just use gcloud cli, e.g. in order to deploy `SendNotification` use this cmd:
```shell
gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID && gcloud beta functions deploy sendNotification --entry-point SendNotification --runtime go111 --trigger-http --env-vars-file .env.yaml
```
where `--env-vars-file .env.yaml` flag reads and sets the env vars from your.env.yaml as function's scope.
For more info about enviroment variables in gcf you can take a look at this [link](https://cloud.google.com/functions/docs/env-var#using_environment_variables)
Also you can take a look how we deploy a gcf at this [link](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/functions/deploy)
### Usage ###
After you deploy the function in google cloud, you can use them by a HTTP request to their URL. E.g. to trigger `sendNotification` gcf we should:
```shell
curl "https://REGION-PROJECT_ID.cloudfunctions.net/sendNotification"
```
where:
- REGION is the region where your function is deployed. This is visible in your terminal when your function finishes deploying.
- PROJECT_ID is your Cloud project ID. This is visible in your terminal when your function finishes deploying.
## Support Me
[](https://ko-fi.com/Y8Y797KCA)
## Show your support
Give a ⭐️ if this project helped you!