Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/emcrisostomo/Time-Machine-Cleanup
Zsh script to clean up Time Machine backups and reduce its size
https://github.com/emcrisostomo/Time-Machine-Cleanup
time-machine
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Zsh script to clean up Time Machine backups and reduce its size
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/emcrisostomo/Time-Machine-Cleanup
- Owner: emcrisostomo
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2015-05-02T11:28:27.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-12T18:40:42.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-14T06:51:52.737Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: time-machine
- Language: Shell
- Homepage:
- Size: 284 KB
- Stars: 138
- Watchers: 17
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: ChangeLog
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Time Machine Cleanup
====================
`tm-cleanup.sh` is a Zsh script to clean up Time Machine backups and reduce its
size. `tm-cleanup.sh` provides two interfaces:
* A command-line interface.
* An interactive, dialog-based interface.
`tm-cleanup.sh` requires super-user privileges, so it's normally executed using
`sudo`.
tm-cleanup.sh
-------------
`tm-cleanup.sh` is a Zsh script that lists the completed Time Machine snapshots
and deletes those that satisfy the specified criteria. Two types of deletion
criteria exist:
* By date: snapshots that are older than a specified number of days are
deleted. The default threshold is 30 days.
* By number: a maximum number of snapshots is retained and oldest snapshots
are deleted.
Only one deletion criteria can be specified.
The syntax of `tm-cleanup.sh` is the following:
$ tm-cleanup.sh (-d days | -n number) [-f] [-x]
$ tm-cleanup.sh [-h]
where
* If `-d` is specified, backups older than the specified number of days will
be deleted. `days` is a positive integer number.
* `-n` specifies the number of backups to retain. `number` is a positive
integer number.
* By default, `tm-cleanup.sh` exits and prints an error message if a Time
Machine backup is currently in progress. `-f` forces the backup deletion
concurrently.
* `-h` prints the help message and exits the program.
* `-x` performs a dry clean: it will print the list of operations that will
be performed without actually performing any.
This script *never* deletes the latest snapshot, no matter the value of the `-d`
or `-n` options.
Interactive Interface
---------------------
`tm-cleanup.sh` also provides an interactive interface which is useful if the
user wishes to pick which backups to delete using a dialog-based interface. The
interactive interface can be launched by passing no arguments to the script:
$ tm-cleanup.sh
The interactive interface starts with a menu showing the available operations a
user can perform:
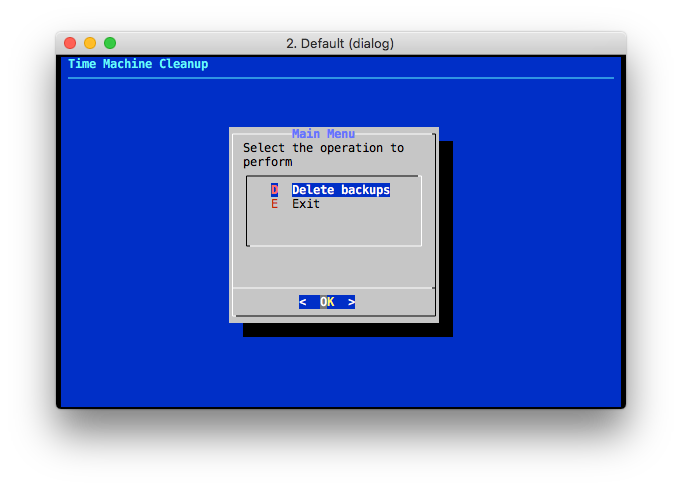
The _Delete backups_ operation brings the user to a dialog where the backups to
delete can be selected. By default, backups are shown in reverse chronological
order (i.e.: latest first) and all except the first are selected.
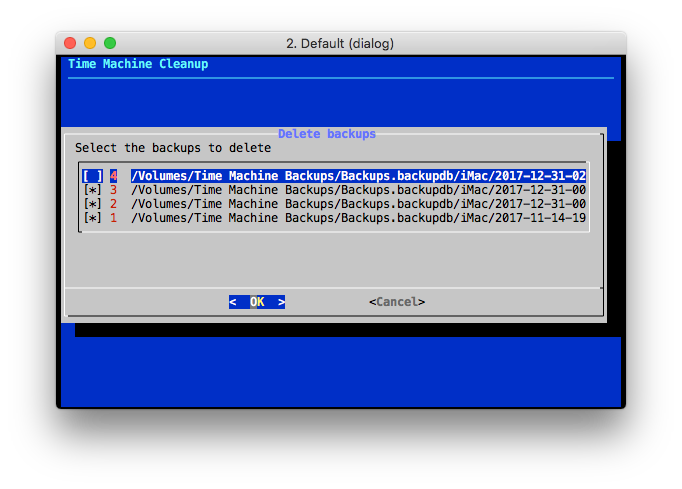
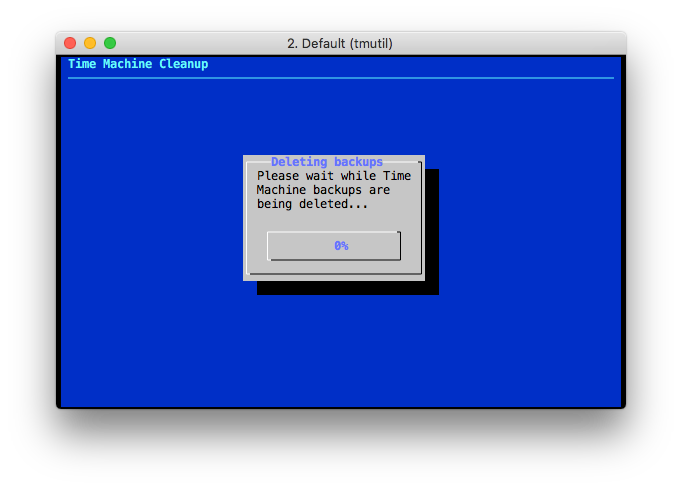
The backups deletion may take a long time to complete, during which a progress
dialog is shown.
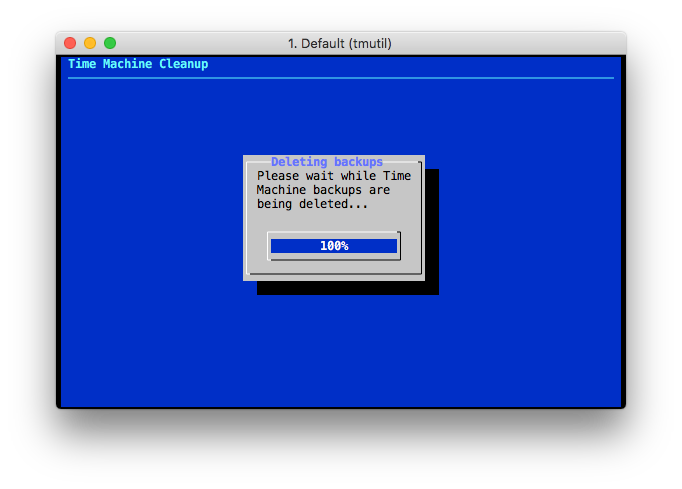
At the end of the deletion, a confirmation is shown to the user.
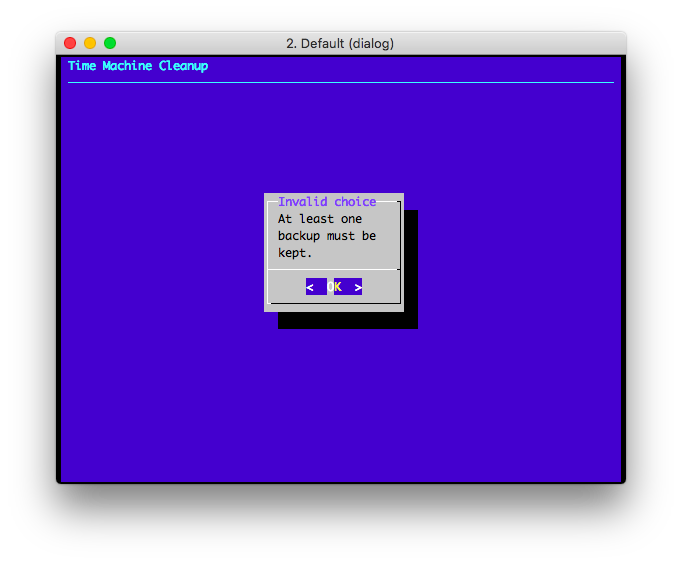
The script prevents users to delete all the backups. If all the backups are
selected, an error message is shown.
Installation
------------
This package is configured using the GNU Autotools. For this reason, users who
just wish to use this software have to download a release tarball. Release
tarball are attached to each release. The [latest] release of this package can
always be found using the [latest] tag.
[latest]: https://github.com/emcrisostomo/Time-Machine-Cleanup/releases/latest
Once a release tarball has been downloaded and uncompressed, this package can be
installed using the following commands:
$ ./configure
$ sudo make install
Please, refer to the Autotools documentation if you'd like to customise the
installation procedure.
The package can then be uninstalled using the following command:
$ sudo make uninstall
To make path changes visibile in an existing Zsh session, execute the `rehash`
command:
$ rehash
Requirements
------------
Since a compatible version of Zsh is bundled with OS X, the command-line
interface of this script has no other requirements. To use the dialog-based
interface, `dialog` is required.
Bug Reports
-----------
Bug reports can be sent directly to the authors.
-----
Copyright (C) 2015-2017 Enrico M. Crisostomo
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 3, or (at your option)
any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see .