Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/ephantus-wambui/sars-cov-2-genome-assembly
https://github.com/ephantus-wambui/sars-cov-2-genome-assembly
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ephantus-wambui/sars-cov-2-genome-assembly
- Owner: Ephantus-Wambui
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2023-02-03T07:32:53.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-11-11T07:17:46.000Z (about 2 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-11T08:19:09.434Z (about 2 months ago)
- Size: 24.4 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Sars-CoV-2-Genome-assembly
# Introduction
After first case of Sars-CoV-2 virus was reported in Kenya, the Ministry of Health under the government of Kenya, in conjuction with the World Health Organization, took measures to curb the spread of the virus in the country. Such measures included, equipping and building ultra modern labs for testing and research purposes. One of the labs given this mandate by the government was Covid-19 Testing and Reaserch Center at the Institute of Primate Research. The lab was tasked to test using Real Time PCR machine, for diagnosis of Covid-19 disease, and for tracking the variants bioinformatics skills were utilised to track the spread and emergence of the variants in the country.
# Scope
For identification of various clades, and variants we will use actual raw dataset from EMBL-ENA to create a consensus genome and run the various consensus genome through [Nextclade](https://https://clades.nextstrain.org/) to find out our clades and mutations present.
# Dataset
You can download the dataset, using the wget command on your terminal. The dataset is in fastq format, and you can download it by using the following commands.
```
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/048/SRR11479148/SRR11479148_2.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/048/SRR11479148/SRR11479148_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/050/SRR11479150/SRR11479150_2.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/050/SRR11479150/SRR11479150_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/049/SRR11479149/SRR11479149_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR114/049/SRR11479149/SRR11479149_2.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR134/071/SRR13495171/SRR13495171_2.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR134/071/SRR13495171/SRR13495171_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR211/056/SRR21139656/SRR21139656_2.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR211/056/SRR21139656/SRR21139656_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR211/089/SRR21139689/SRR21139689_1.fastq.gz
wget -nc ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR211/089/SRR21139689/SRR21139689_2.fastq.gz
```
# Prerequisite
This read me assumes familiriaty with Linux commands, and you have already installed all the necessary tools required for the next steps to begin. If you have not installed the tools, you can install them by following the instructions below.
Install Miniconda
```
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
```
Then create a conda environment called cov-analysis
```
conda create -n cov-analysis
```
Activate the environment
```
conda activate cov-analysis
```
Install the necessary tools
```
conda install -c bioconda fastqc
conda install -c bioconda bwa
conda install -c bioconda samtools
conda install -c bioconda ivar
conda install -c bioconda trimmomatic
```
Download the reference genome
```
wget https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sars-cov-2/reference-sequences/fasta/nc_045512.2.fasta
```
Download the bed file
```
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/artic-network/artic-ncov2019/master/primer_schemes/nCoV-2019/V3/nCoV-2019.bed
```
## Analysis
1. We will begin by first activating our environment.
```
conda activate cov-analysis
```
2. First let us view the quality of our data. We do this by using the command
```
fastqc *fastq.gz
```
This creates a html file that you can view it by opening it to the browser. Example of such result can be seen down below.
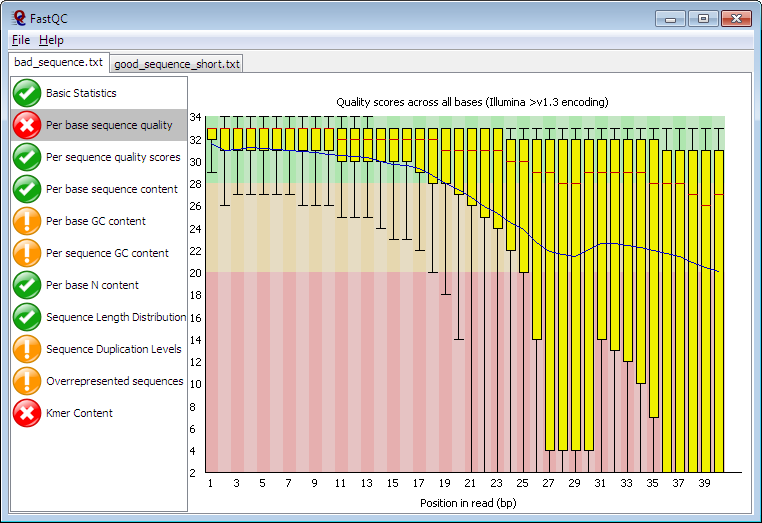
3. After determining the quality of our sequences, next we proceed to trimming adapters and low quality sequences (sequences that have a score of less than 30), and we remain with clean data that can undergo further down stream processes. Since our data is from illumina sequencer, we will use trimmomatic tool to cut illumina adapters together with other bad sequences.
```
trimmomatic PE -threads 4 raw_data/R1.fastq.gz R2.fastq.gz raw_data/R1_pair.fastq R1_unpair.fastq R2_pair.fastq R2_unpair.fastq ILLUMINACLIP:/path to our adapters.fa:2:30:10 LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15 MINLEN:70
```
After trimming you can view the result of the trimmed data, by using the fastqc command.
4. Next after trimming we need to map our reads to our reference genome.
To achieve this we use the Burrow-Wheeler Aligner Maximal Exact Match algorithm or bwa mem in short, to map our trimmed fastq files against our reference Sars-CoV-2 genome. The output is then piped into samtools as input to sort the alignments, which are then output as bam files. But before aligning our reads, we need to index our reference genome. This is done by using the following command;
```
bwa index reference_genome.fasta
```
After indexing our reference genome, we can now align our reads to the reference genome.
```
bwa mem -t 4 reference_genome.fasta *R1_pair.fastq *R2_pair.fastq | samtools sort | samtools view -F 4 -o *.sorted.bam
```
5. Removing primers
In this step we will use ivar, which is a computational package that contains functions broadly useful for viral amplicon-based sequencing. This tools is used to remove primers from our alignment map.
```
ivar trim -e -i *.sorted.bam -b ARTIC-V3.bed -p *.sorted.bam.primer.trim
```
6. Sorting bams
Before calling our consensus sequences, we have to sort our bams. It is achieved by using this command;
```
samtools sort *.primertrim.bam -o *.primertrim.bam.sorted
```
7. Calling the consensus sequence
Finally we create our consensus genome by using samtools. Samtools creates the read pileups which ivar uses to call consensus at a minimum depth quality of 10.
```
samtools mpileup -A -d 1000 -B -Q 0 --reference reference_genome.fasta *.primertrim.bam.sorted | ivar consensus -p *.consensus -n N -m 10
```
Note after building your consensus genome. You can use nextclade to Nexclade to classify your genome according to clades and pango lineages, as well as catalogue the nucleotide and amino acid mutations in your consensus genome compared to your reference genome.