https://github.com/erikdrobne/swiftuicoordinator
SwiftUICoordinator is a package that seamlessly integrates the Coordinator pattern into the SwiftUI framework.
https://github.com/erikdrobne/swiftuicoordinator
app-architecture coordinator-pattern ios navigation swift swiftui xcode
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
SwiftUICoordinator is a package that seamlessly integrates the Coordinator pattern into the SwiftUI framework.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/erikdrobne/swiftuicoordinator
- Owner: erikdrobne
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-03-10T12:10:54.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-27T20:10:19.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-05T02:03:48.065Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: app-architecture, coordinator-pattern, ios, navigation, swift, swiftui, xcode
- Language: Swift
- Homepage:
- Size: 341 KB
- Stars: 169
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# SwiftUICoordinator

[](https://github.com/erikdrobne/SwiftUICoordinator/blob/main/LICENSE.md)

## Introduction
SwiftUICoordinator is a powerful implementation of the Coordinator pattern specifically designed for SwiftUI applications. It provides a robust solution for managing navigation flows while maintaining clean architecture principles and separation of concerns.
## Features
- 🏗️ **Modular Architecture**: Clear separation between navigation logic and view presentation
- 🔄 **Flexible Navigation**: Support for stack-based, modal, and tab bar navigation
- 🔗 **Deep Linking**: Built-in support for handling deep links
- 🎨 **Custom Transitions**: Extensible transition system
- 📱 **iOS 15+ Support**
## Installation
### Requirements
`iOS 15.0+`
### Swift Package Manager
```Swift
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/erikdrobne/SwiftUICoordinator")
]
```
## 🏃 Core Components
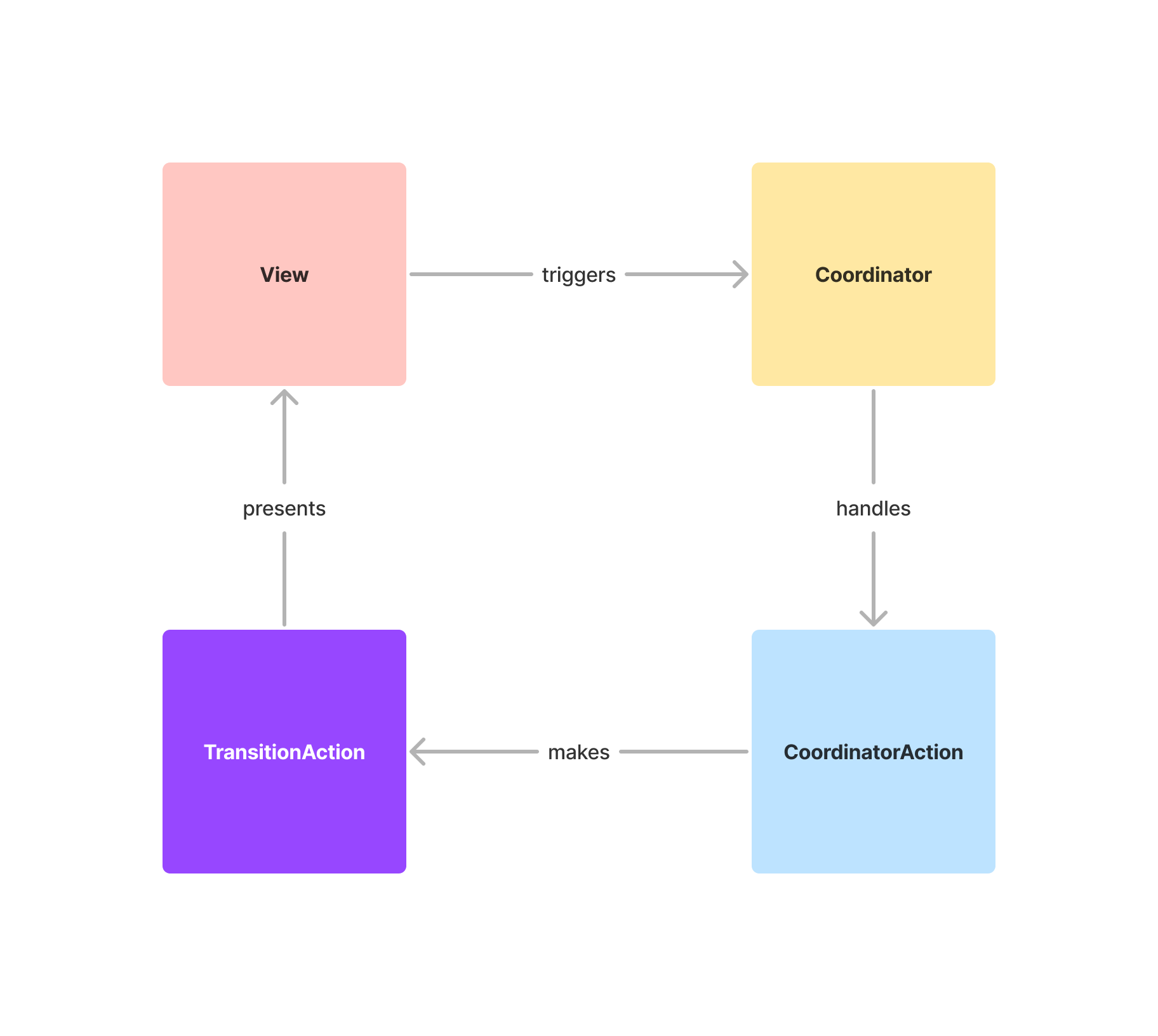
### Coordinator Protocol
The foundation of navigation flow management:
```swift
@MainActor
protocol Coordinator: AnyObject {
var parent: Coordinator? { get }
var childCoordinators: [Coordinator] { get set }
var name: String { get }
func handle(_ action: CoordinatorAction)
func add(child: Coordinator)
func remove(coordinator: Coordinator)
}
```
### Navigator Protocol
Manages the navigation stack and view presentation:
```swift
@MainActor
public protocol Navigator: ObservableObject {
associatedtype Route: StackNavigationRoute
var navigationController: UINavigationController { get }
var startRoute: Route { get }
func start()
func show(route: Route)
func set(routes: [Route], animated: Bool)
func append(routes: [Route], animated: Bool)
func pop(animated: Bool)
func popToRoot(animated: Bool)
func dismiss(animated: Bool)
}
// Combine Navigator and Coordinator
public typealias Routing = Coordinator & Navigator
```
### Navigation Routes
Define your navigation paths:
```swift
protocol NavigationRoute {
var title: String? { get }
var appearance: RouteAppearance? { get }
var hidesNavigationBar: Bool? { get }
}
protocol StackNavigationRoute: NavigationRoute {
var action: TransitionAction { get }
var hidesBackButton: Bool? { get }
}
// Example Implementation
enum AuthRoute: StackNavigationRoute {
case login
case signup
case resetPassword
var action: TransitionAction {
return .push(animated: true)
}
}
```
### CoordinatorAction
Defines the available actions for the coordinator. Views should exclusively interact with the coordinator through actions, ensuring a unidirectional flow of communication.
```swift
protocol CoordinatorAction {
var name: String { get }
}
// Example Implementation
enum AuthAction: CoordinatorAction {
case didLogin
case didSignup
case showSignup
case showLogin
case showResetPassword
}
```
### RouterViewFactory
Connect routes to views:
```swift
@MainActor
protocol RouterViewFactory {
associatedtype V: View
associatedtype Route: NavigationRoute
@ViewBuilder
func view(for route: Route) -> V
}
```
## 🔧 Usage
```Swift
import SwiftUICoordinator
```
### Create Route
Start by creating an enum with all the available routes for a particular coordinator flow.
```Swift
enum AuthRoute: StackNavigationRoute {
case login
case signup
case resetPassword
var action: TransitionAction {
return .push(animated: true)
}
}
```
### Create Action
Specify custom actions that can be sent from coordinated objects to their coordinators.
```Swift
enum AuthAction: CoordinatorAction {
case didLogin
case didSignup
case showLogin
case showSignup
case showResetPassword
}
```
### Create Coordinator
The coordinator has to conform to the `Routing` protocol.
```Swift
final class AuthCoordinator: Routing {
weak var parent: Coordinator?
var childCoordinators = [Coordinator]()
let navigationController: UINavigationController
let startRoute: AuthRoute
init(
parent: Coordinator?,
navigationController: NavigationController,
startRoute: AuthRoute = .login
) {
self.parent = parent
self.navigationController = navigationController
self.startRoute = startRoute
}
func handle(_ action: CoordinatorAction) {
switch action {
case AuthAction.didLogin:
parent?.handle(Action.done(self))
case AuthAction.showSignup:
show(route: .signup)
case AuthAction.showLogin:
pop()
default:
parent?.handle(action)
}
}
}
// Connect views to routes
extension AuthCoordinator: RouterViewFactory {
@ViewBuilder
func view(for route: AuthRoute) -> some View {
switch route {
case .login:
LoginView(viewModel: LoginViewModel(coordinator: self))
case .signup:
SignupView(viewModel: SignupViewModel(coordinator: self))
case .resetPassword:
ResetPasswordView(viewModel: ResetPasswordViewModel(coordinator: self))
}
}
}
```
### Custom transitions
SwiftUICoordinator also supports creating custom transitions.
```Swift
final class FadeTransition: NSObject, Transitionable {
func isEligible(
from fromRoute: NavigationRoute,
to toRoute: NavigationRoute,
operation: NavigationOperation
) -> Bool {
// Define when this transition should be used
return true
}
func animateTransition(using context: UIViewControllerContextTransitioning) {
guard let toView = context.view(forKey: .to) else {
context.completeTransition(false)
return
}
let containerView = context.containerView
toView.alpha = 0.0
containerView.addSubview(toView)
UIView.animate(
withDuration: transitionDuration(using: context),
animations: {
toView.alpha = 1.0
},
completion: { _ in
context.completeTransition(!context.transitionWasCancelled)
}
)
}
}
// Register transitions
let factory = NavigationControllerFactory()
let transitions = [FadeTransition()]
lazy var delegate = factory.makeTransitionDelegate(transitions)
lazy var navigationController = factory.makeNavigationController(delegate: self.delegate)
```
#### Modal transitions
First, define a transition delegate object that conforms to the `UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate` protocol.
```Swift
final class SlideTransitionDelegate: NSObject, UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate {
func animationController(forPresented presented: UIViewController, presenting: UIViewController, source: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
return SlideTransition(isPresenting: true)
}
func animationController(forDismissed dismissed: UIViewController) -> UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning? {
return SlideTransition(isPresenting: false)
}
}
```
In this example, `SlideTransition` is a custom class that conforms to the `UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning` protocol and handles the actual animation logic.
Pass the `SlideTransitionDelegate` instance to the specific action where you wish to apply your modal transition.
```Swift
var action: TransitionAction? {
switch self {
case .rect:
return .present(delegate: SlideTransitionDelegate())
default:
return .push(animated: true)
}
}
```
### Handling deep links
In your application, you can handle deep links by creating a `DeepLinkHandler` that conforms to the `DeepLinkHandling` protocol. This handler will specify the URL scheme and the supported deep links that your app can recognize.
```Swift
class DeepLinkHandler: DeepLinkHandling {
static let shared = DeepLinkHandler()
let scheme = "coordinatorexample"
let links: Set = [
DeepLink(action: "cart", route: CatalogRoute.cart)
]
private init() {}
}
```
To handle incoming deep links in your app, you can implement the `scene(_:openURLContexts:)` method in your scene delegate.
```Swift
func scene(_ scene: UIScene, openURLContexts URLContexts: Set) {
guard
let url = URLContexts.first?.url,
let deepLink = try? dependencyContainer.deepLinkHandler.link(for: url),
let params = try? dependencyContainer.deepLinkHandler.params(for: url, and: deepLink.params)
else {
return
}
dependencyContainer.appCoordinator?.handle(deepLink, with: params)
}
```
## Example project
For better understanding, I recommend that you check the example project located in the `SwiftUICoordinatorExample` directory.
## 🤝 Contributions
Contributions are welcome to help improve and grow this project!
### Reporting bugs
If you come across a bug, kindly open an issue on GitHub, providing a detailed description of the problem.
Include the following information:
- steps to reproduce the bug
- expected behavior
- actual behavior
- environment details
### Requesting features
For feature requests, please open an issue on GitHub. Clearly describe the new functionality you'd like to see and provide any relevant details or use cases.
### Submitting pull requests
To submit a pull request:
1. Fork the repository.
2. Create a new branch for your changes.
3. Make your changes and test thoroughly.
4. Open a pull request, clearly describing the changes you've made.
Thank you for contributing to SwiftUICoordinator! 🚀
**If you appreciate this project, kindly give it a ⭐️ to help others discover the repository.**