https://github.com/esafirm/universal-router
↩️ Router for every occasions
https://github.com/esafirm/universal-router
android-navigation hacktoberfest modular navigation router
Last synced: 15 days ago
JSON representation
↩️ Router for every occasions
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/esafirm/universal-router
- Owner: esafirm
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-05-19T06:52:00.000Z (almost 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-23T18:02:56.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-07T21:05:57.322Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: android-navigation, hacktoberfest, modular, navigation, router
- Language: Kotlin
- Homepage:
- Size: 819 KB
- Stars: 76
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 11
- Open Issues: 13
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-list - esafirm/universal-router - ↩️ Router for every occasions (Kotlin)
README
# Universal Router

> Router for every ocassion ~
Universal router comes with two flavor, the core module which basically a link router that can convert your URI to whatever you need. And the Android module which more opinionated to how you can use it to help you solve your navigation problem
## Download
Add this to your project `build.gradle`
```groovy
allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url "https://jitpack.io" }
}
}
```
And add this to your module `build.gradle`
```groovy
dependencies {
implementation "com.github.esafirm.universal-router:core:$routerVersion"
implementation "com.github.esafirm.universal-router:android:$routerVersion"
}
```
## Core
It basically consist of two router
1. `SimpleRouter` which route `Any` type of object to anything you need
2. `UrlRouter` which takes URI instead of object
### Some Examples
```kotlin
// Define router
class StringRouter : UrlRouter() {
init {
addEntry("nolambda://test/{a}/{b}", "https://test/{a}/{b}") { _, param ->
val first = param["a"]
val second = param["b"]
"$second came to the wrong neighborhood $first"
}
}
}
// Call router
// This will return string "you can to the wrong neighborhood yo"
StringRouter().resolve("nolambda://test/yo/you")
```
> For more sample, plese look at the `samples` directory.
## Android
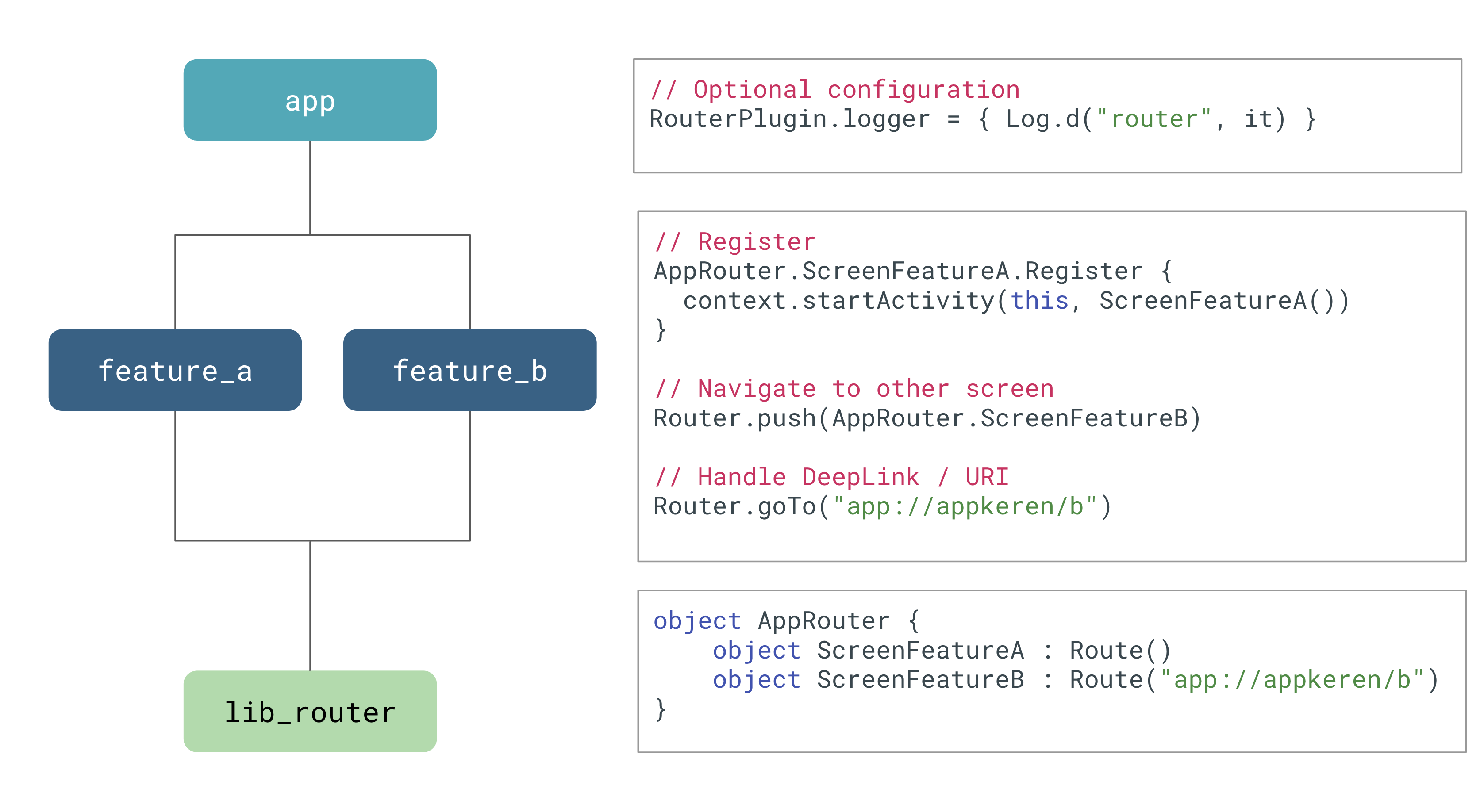
Basically with just the `core` module you already can have a navigation system in your modular structured application (think dynamic module use case). The easiest way would be creating a `Singleton` router in your "core" module and then add entries in every other module, but this can get quite messy sometimes, this is when the android router module comes in.
First let's define our project structure:
```kotlin
project
│
├── app // Android app module, depends to all modules
│
├── cart // Feature cart, only depends to router
│
├── product // Feature product, only depends to router
│
└── approuter // Router libs that every module depends
```
> In dynamic module use case the `cart` and `product` module would be depends the `app` module
Next what you want to create is the list of the routes in the "router" module, in this case `approuter`
```kotlin
object AppRouter {
// Simplest form of Route
object Home : Route()
// Route support deeplink navigation
object Cart : Route("https://bukatoko.com/cart")
// Route also support navigation with parameter
object Product : RouteWithParam(
paths = arrayOf("https://bukatoko.com/{product_id}", "app://product/{id}"),
) {
data class ProductParam(
val productId: String
)
}
}
```
After that, you have to register your navigation logic to the `Route`
```kotlin
AppRouter.Cart.Register {
context.startActivity(Intent(context, CartScreen::class.java))
}
```
If you want to initiate this in startup and your module doesn't have the access to `Application` class you can use the initializer
```kotlin
class CartRouterInitializer : RouterInitializer {
override fun onInit(appContext: Context) {
... // do as above
}
}
```
Don't forget to register this on manifest
```xml
```
This is actually it if your navigation logic nature is "fire and forget", but in case you have to get something back (like `Fragment`) and use it in other place you can use the `RouteProcessor`
```kotlin
// Processor only process return that has the same type as passed class
// In this case it will only process router that return Fragment
Router.addProcessor {
supportManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.container, it)
.commit()
}
```
After that you can use the `Router` to navigate your app
```kotlin
// This will trigger Cart register lambda
Router.push(AppRouter.Cart)
// You can use the registered deeplink too
Router.goTo("https://bukatoko.com/cart")
```
And that's it you got yourself a navigation system.
> I can't stress enough that you should check `samples` for better understanding of the library
## What's Next
- Navigation type (push, replace, pop)
- Annotation auto register (It's partially working now)
## License
MIT @ Esa Firman