https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics
Demo application to create maps with routes in order to find out the best way to deliver products.
https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics
angularjs aws bootstrap docker dockerfile javaee jenkinsfile mongodb rest-api sonarqube swagger togglz vagrantfile
Last synced: 3 days ago
JSON representation
Demo application to create maps with routes in order to find out the best way to deliver products.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics
- Owner: esign-consulting
- License: mit
- Created: 2015-09-27T03:30:39.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-10-23T18:20:20.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-10-23T19:35:03.262Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: angularjs, aws, bootstrap, docker, dockerfile, javaee, jenkinsfile, mongodb, rest-api, sonarqube, swagger, togglz, vagrantfile
- Language: Java
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.01 MB
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Logistics
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=esign-consulting_logistics)
[](https://snyk.io/test/github/esign-consulting/logistics)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/esignbr/logistics/builds)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/esignbr/logistics)
[](http://www.esign.com.br/logistics)
The goal of the Logistcs application is find out the best route between two places within a map. Once created, add routes to the map, as following:
Origin | Destination | Distance (Km)
------ | ----------- | -------------
A | B | 10
B | D | 15
A | C | 20
C | D | 30
B | E | 50
D | E | 30
The best route is the cheapest one, considering the truck autonomy (Km/l) and the fuel price (l). Based on the routes above, if the truck has to go from **place A** to **place D**, its autonomy is **10 Km/l** and the litre of the fuel cost **$2.50**, the best route will be **A -> B -> D**, because it's the cheapest one: **$6.25**.
## Quality Assurance
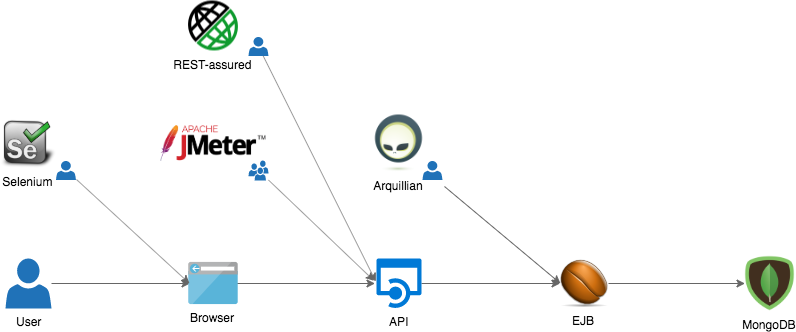
The Logistics application has quality in its core. Beyond unit tests, the following projects were developed in order to validate the whole solution:
Project | Test type | Build status
------- | --------- | ------------
[logistics-test-arquillian](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-arquillian) | Integration test | [](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-arquillian/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Java+CI%22)
[logistics-test-restassured](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-restassured) | API test | [](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-restassured/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Java+CI%22)
[logistics-test-selenium](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-selenium) | UI test | [](https://travis-ci.org/esign-consulting/logistics-test-selenium)
[logistics-test-jmeter](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-jmeter) | Load test | [](https://github.com/esign-consulting/logistics-test-jmeter/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Java+CI%22)
### Static code analysis
The application code quality is evaluated with [SonarQube](https://www.sonarqube.org). If you want to run the [SonarScanner for Maven](https://docs.sonarqube.org/latest/analysis/scan/sonarscanner-for-maven) in order to take a look at the [static code analisys](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_program_analysis)' results, firstly execute (requires [Docker](https://www.docker.com)):
`docker run --name sonarqube -p 9000:9000 -d sonarqube:8.4.1-community`
And then, execute (requires [JDK 11](https://openjdk.java.net/projects/jdk/11) and [Maven](https://maven.apache.org)):
`mvn clean install sonar:sonar`
After running the analysis, the Logistics application dashboard will be available in .
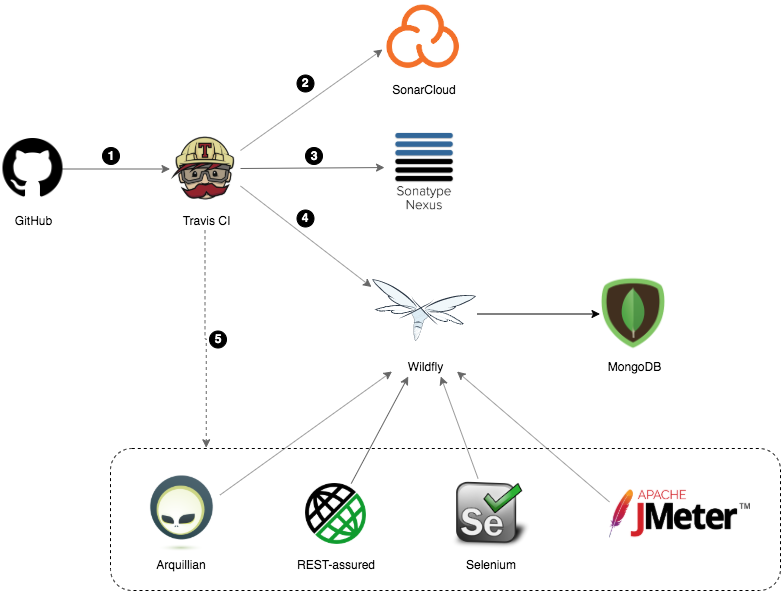
## The CI/CD Pipeline
Each push to this repository triggers the pipeline below:
1. Travis CI clones this GitHub repository;
2. After compiling and performing several unit tests in the application source code, Maven triggers the SonarQube static code analisys, and the results are sent to [SonarCloud](https://sonarcloud.io);
3. Once generated the Java artifacts, they are deployed to [Sonatype OSSRH](https://oss.sonatype.org), a Nexus Repository Manager instance Sonatype uses to provide repository hosting service to open source projects binaries;
4. The application EAR file is deployed in a Wildfly instance avaliable at [esign.com.br](http://www.esign.com.br). From there, the Logistics application connects to a MongoDB instance hosted by [MongoDB Atlas](https://www.mongodb.com/cloud/atlas);
5. Several tests are triggered asynchronously. Each one is performed against the Wildfly instance where the latest version of application was deployed.
## Running with Docker
You can run the application as a [Docker](https://www.docker.com) container. Install [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/install) and then run:
`docker run --name logistics -p 8080:8080 -e MONGODB_URI=mongodb://username:password@host:port/logistics -d esignbr/logistics`
The environment variable **MONGODB_URI** is mandatory and must set the [MongoDB connection URI](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/connection-string). Remember to replace *username* and *password* with your MongoDB credentials as well as *host* and *port* with the appropriate values, according with where your MongoDB instance is avaliable on.
The Logistics application can also be executed along with MongoDB by using [Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose). If you've already installed [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/install) and [Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install), clone the repository and then run:
`docker-compose up -d`
The application will be available through the URL in your browser.
## Deploying to a local VM
Alternatively, you can deploy both the application and the database to a local VM, by using the [Ansible playbook](playbook.yml). If you want to know how it works, first install [Ansible](https://www.ansible.com), [VirtualBox](https://www.virtualbox.org) and [Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com), and then run:
`vagrant up`
Vagrant will download the [codeyourinfra](https://app.vagrantup.com/codeyourinfra)/[docker](https://app.vagrantup.com/codeyourinfra/boxes/docker) [Vagrant box](https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/boxes.html) (if it was not done yet), then will bootstrap the local VM and at the end will trigger the Ansible playbook execution.
Once the local VM is up, open the URL in your browser, and give the Logistics application a try.
Finally, if you want to cleanup everything, execute the command:
`vagrant destroy -f && rm -rf .vagrant/`
## Deploying to AWS
In order to deploy Logistics into an [EC2 instance](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2), execute the command below with your [AWS credentials](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws-sec-cred-types.html#access-keys-and-secret-access-keys):
```bash
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/ansible:/ansible \
-e ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/ansible/ansible.cfg \
-e AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID= \
-e AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY= \
codeyourinfra/myansible ansible-playbook /ansible/deploy-to-aws.yml
```
After deploying, check the output to find out what is the EC2 instance public IP address. You can get the IP from the *inventory.yml* file as well. Then, open the Logistics' URL in your browser, replacing the IP with the one you've just got. Finally, if you want to undo everything, just run:
```bash
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/ansible:/ansible \
-e ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/ansible/ansible.cfg \
-e AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID= \
-e AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY= \
codeyourinfra/myansible ansible-playbook /ansible/undeploy-from-aws.yml
```
## Deploying to Azure
In order to deploy Logistics into an [Azure virtual machine](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/virtual-machines), execute the command below with your [Azure service principal](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/create-an-azure-service-principal-azure-cli):
```bash
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/ansible:/ansible \
-e ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/ansible/ansible.cfg \
-e AZURE_CLIENT_ID= \
-e AZURE_SECRET= \
-e AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID= \
-e AZURE_TENANT= \
codeyourinfra/myansible ansible-playbook /ansible/deploy-to-azure.yml
```
After deploying, check the output to find out what is the Azure VM public IP address. You can get the IP from the *inventory.yml* file as well. Then, open the Logistics' URL in your browser, replacing the IP with the one you've just got. Finally, if you want to undo everything, just run:
```bash
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/ansible:/ansible \
-e ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/ansible/ansible.cfg \
-e AZURE_CLIENT_ID= \
-e AZURE_SECRET= \
-e AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID= \
-e AZURE_TENANT= \
codeyourinfra/myansible ansible-playbook /ansible/undeploy-from-azure.yml
```
## Logistics API
The Logistics API documentation is generated through [Swagger](https://swagger.io) and can be checked by accessing the `/logistics/docs` endpoint, after deploying the application. In the [Esign Consulting website](http://www.esign.com.br), for example, the Logistics API documentation is available on .
## Feature toggles
The Logistics application has a [feature toggles](https://www.martinfowler.com/articles/feature-toggles.html) admin console that comes with [Togglz](https://www.togglz.org). The console can be accessed through the `/logistics/togglz` endpoint, after deploying the application. In the [Esign Consulting website](http://www.esign.com.br), for example, the Logistics Feature Flags console is available on .