Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/euonymus/baryon
Baryon is a react component that allows you to inspect neo4j graph in a simple and intuitive manner. This enables users to explore further relations from one node to another.
https://github.com/euonymus/baryon
baryon graph-database javascript neo4j react react-component
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Baryon is a react component that allows you to inspect neo4j graph in a simple and intuitive manner. This enables users to explore further relations from one node to another.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/euonymus/baryon
- Owner: euonymus
- Created: 2019-09-23T06:49:19.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-04T11:14:07.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-03-24T01:50:55.328Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Topics: baryon, graph-database, javascript, neo4j, react, react-component
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 124 MB
- Stars: 7
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 21
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
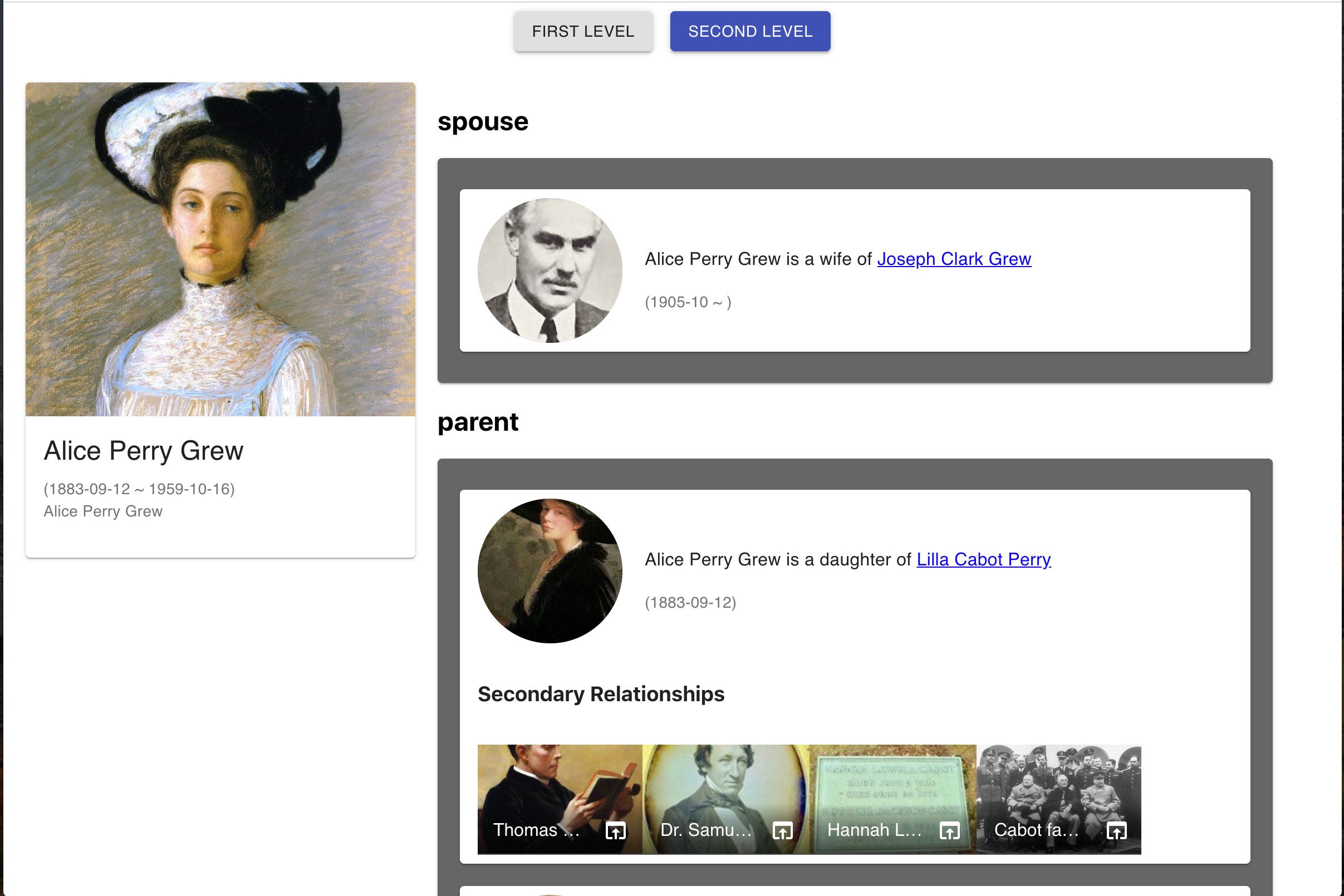
Baryon is a react component to compose organized ui view for your neo4j graph that allows you to inspect simply and intuitively.
This enables users to explore further relations from one node to another.
-> [Link to Youtube Video](https://youtu.be/1yNPHG9HTWs)
## Features
* Baryon provides you a simple ui to inspect neo4j graph data
* Subject node appears in the main area
* Relationships appear in a list
* Each relationship is expressed in sentence powered by RDF triple
* Each node or relationship can have start-date and end-date
* Relationships are sorted by start-date of relationships, then start-date of nodes
* Secondary relationships on each connected node is listed below the node
* Secondary relationship list can be configured to be On / Off
* Each node-label has their node-label-properties
* Relations are categorized depending on relationship-types
* Each node-label-property is a collection of relationship-types
* ex: Both BROTHER_OF and SISTER_OF go into sibling node-label-property
* URL path to Baryon ui on your app can be configured
## Steps to Run sample app
1. Create your [neo4j sandbox](https://neo4j.com/sandbox-v2/)
2. Import [sampledata.txt](https://github.com/euonymus/baryon/blob/master/sampledata.txt) into your neo4j sandbox
3. git clone this project
```
$ git clone [email protected]:euonymus/baryon.git
$ cd baryon
```
4. Setup your neo4j connection in .env.local
sample .env.local settings
```
# neo4j connection
REACT_APP_NEO4J_URI=bolt://100.26.232.160:38283
REACT_APP_NEO4J_USER=neo4j
REACT_APP_NEO4J_PASSWORD=measurement-intakes-bells
```
5. Install node modules
```
$ npm install
```
6. Start npm project
```
$ npm start
```
## How to Use sample app
* Open [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000) in your browser.
* Enter "**The Matrix**" in the form. (In the case of you used [sampledata.txt](https://github.com/euonymus/baryon/blob/master/sampledata.txt))
* Go explore
## How to implement Baryon into your React Application
Install Baryon as a node_module
```bash
# Configuring Bit as a scoped registry for NPM
$ npm config set '@bit:registry' https://node.bit.dev
# Install Baryon
$ npm i --save @bit/euonymus.baryon.baryon
```
In your React Application, call Baryon in JSX
```js
import Baryon from '@bit/euonymus.baryon.baryon';
function App() {
return (
);
}
```
## Configurations
### On and Off secondary relationship list
Set boolean ***hasSecondLevel*** props when you call Baryon Component in your JSX
```js
function App() {
return (
);
}
```
**hasSecondLevel** props configuration
|hasSecondLevel props| Secondary Relationships|
|---|---|
|true| Secondary Relationships are shown |
|false| No Secondary Relationships |
### Set URL path to baryon ui on your app
You can configure the path to the baryon ui by setting graphPath props.
for example, if you set graphPath like this
```js
function App() {
return (
);
}
```
Each link to other node in baryon component will point to following path
```
/graph/{node-name}
```
**graphPath** props configuration
|graphPath props|URL|
|---|---|
|false|No URL change|
|string| /{path to string}/{node-name}|
|empty string| /{node-name} |
## Data Structure
### Actionable node properties
|property|explanation|example|
|---|---|---|
|name|Japanese node name|ピコ太郎|
|en_name|English node name|Pikotaro|
|description|Japanese Explanation|ピコ太郎は日本のコメディアン|
|en_description|English Explanation|Pikotaro is a Japanese comedian, television personality and entertainer|
|image_path|Image URL|[https://ilyricsbuzz.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Pen-Pineapple-Apple-Pen.jpeg](https://ilyricsbuzz.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Pen-Pineapple-Apple-Pen.jpeg)|
|start|Start date of the node|1973-07-17|
|end|End date of the node|2080-07-17|
|start_accuracy|year / month / null are allowed|month|
|end_accuracy|year / month / null are allowed|year|
|is_momentary|Flag of if the node lifetime is momentary|false|
|url|Official URL of the Node|[https://avex-management.jp/artists/talent/TKDMA](https://avex-management.jp/artists/talent/TKDMA)|
Sorry for the inconvenience caused by property name and en_name.
The reason why I did this was, I needed to deal with my pre-existed Japanese data at first.
### Actionable relationship properties
|property|explanation|example|
|---|---|---|
|relation|Relation between nodes|was created by|
|start|Start date of the node|1973-07-17|
|end|End date of the node|2080-07-17|
|start_accuracy|year / month / null are allowed|month|
|end_accuracy|year / month / null are allowed|year|
|is_momentary|Flag of if the node lifetime is momentary|false|