Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/facebookresearch/benchmarl
A collection of MARL benchmarks based on TorchRL
https://github.com/facebookresearch/benchmarl
benchmark machine-learning marl multi-agent multi-agent-reinforcement-learning pytorch reinforcement-learning rl robotics torch
Last synced: 7 days ago
JSON representation
A collection of MARL benchmarks based on TorchRL
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/facebookresearch/benchmarl
- Owner: facebookresearch
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-08-22T11:19:20.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-10T17:04:38.000Z (8 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-11T09:17:47.461Z (8 days ago)
- Topics: benchmark, machine-learning, marl, multi-agent, multi-agent-reinforcement-learning, pytorch, reinforcement-learning, rl, robotics, torch
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://benchmarl.readthedocs.io/
- Size: 474 KB
- Stars: 339
- Watchers: 13
- Forks: 53
- Open Issues: 10
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# BenchMARL
[](test)
[](https://benchmarl.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)

[](https://pepy.tech/project/benchmarl)
[](https://discord.gg/jEEWCn6T3p)
[](https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.01472)
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py algorithm=mappo task=vmas/balance
```
[](examples) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/facebookresearch/BenchMARL/blob/main/notebooks/run.ipynb)
[](https://wandb.ai/matteobettini/benchmarl-public/reportlist)
Watch the [talk on multi-agent simulation and learning in BenchMARL and TorchRL](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1tOIMgJf_VQ).
### What is BenchMARL 🧐?
BenchMARL is a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) training library created to enable reproducibility
and benchmarking across different MARL algorithms and environments.
Its mission is to present a standardized interface that allows easy integration of new algorithms and environments to
provide a fair comparison with existing solutions.
BenchMARL uses [TorchRL](https://github.com/pytorch/rl) as its backend, which grants it high performance
and state-of-the-art implementations.
It also uses [hydra](https://hydra.cc/docs/intro/) for flexible and modular configuration,
and its data reporting is compatible with [marl-eval](https://sites.google.com/view/marl-standard-protocol/home)
for standardised and statistically strong evaluations.
BenchMARL **core design tenets** are:
* _Reproducibility through systematical grounding and standardization of configuration_
* _Standardised and statistically-strong plotting and reporting_
* _Experiments that are independent of the algorithm, environment, and model choices_
* _Breadth over the MARL ecosystem_
* _Easy implementation of new algorithms, environments, and models_
* _Leveraging the know-how and infrastructure of [TorchRL](https://github.com/pytorch/rl), without reinventing the wheel_
### Why would I BenchMARL 🤔?
Why would you BenchMARL, I see you ask.
Well, you can BenchMARL to compare different algorithms, environments, models,
to check how your new research compares to existing ones, or if you just want to approach
the domain and want to easily take a picture of the landscape.
### Table of contents
- [BenchMARL](#benchmarl)
* [How to use](#how-to-use)
+ [Notebooks](#notebooks)
+ [Install](#install)
+ [Run](#run)
* [Concept](#concept)
* [Fine-tuned public benchmarks](#fine-tuned-public-benchmarks)
* [Reporting and plotting](#reporting-and-plotting)
* [Extending](#extending)
* [Configuring](#configuring)
+ [Experiment](#experiment)
+ [Algorithm](#algorithm)
+ [Task](#task)
+ [Model](#model)
* [Features](#features)
+ [Logging](#logging)
+ [Checkpointing](#checkpointing)
+ [Callbacks](#callbacks)
* [Citing BenchMARL](#citing-benchmarl)
## How to use
### Notebooks
- [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/facebookresearch/BenchMARL/blob/main/notebooks/run.ipynb) **Running BenchMARL experiments**.
- [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/proroklab/VectorizedMultiAgentSimulator/blob/main/notebooks/Simulation_and_training_in_VMAS_and_BenchMARL.ipynb) **Creating a VMAS scenario and training it in BenchMARL**. We will create a scenario where multiple robots with different embodiments need to navigate to their goals while avoiding each other (as well as obstacles) and train it using MAPPO and MLP/GNN policies.
### Install
#### Install TorchRL
You can install TorchRL from PyPi.
```bash
pip install torchrl
```
For more details, or for installing nightly versions, see the
[TorchRL installation guide](https://github.com/pytorch/rl#installation).
#### Install BenchMARL
You can just install it from github
```bash
pip install benchmarl
```
Or also clone it locally to access the configs and scripts
```bash
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/BenchMARL.git
pip install -e BenchMARL
```
#### Install environments
All enviornment dependencies are optional in BenchMARL and can be installed separately.
##### VMAS
```bash
pip install vmas
```
##### PettingZoo
```bash
pip install "pettingzoo[all]"
```
##### MeltingPot
```bash
pip install dm-meltingpot
```
##### MAgent2
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/Farama-Foundation/MAgent2
```
##### SMACv2
Follow the instructions on the environment [repository](https://github.com/oxwhirl/smacv2).
[Here](.github/unittest/install_smacv2.sh) is how we install it on linux.
### Run
Experiments are launched with a [default configuration](benchmarl/conf) that
can be overridden in many ways.
To learn how to customize and override configurations
please refer to the [configuring section](#configuring).
#### Command line
To launch an experiment from the command line you can do
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py algorithm=mappo task=vmas/balance
```
[](examples/running/run_experiment.sh)
Thanks to [hydra](https://hydra.cc/docs/intro/), you can run benchmarks as multi-runs like:
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py -m algorithm=mappo,qmix,masac task=vmas/balance,vmas/sampling seed=0,1
```
[](examples/running/run_benchmark.sh)
The default implementation for hydra multi-runs is sequential, but [parallel](https://hydra.cc/docs/plugins/joblib_launcher/)
and [slurm](https://hydra.cc/docs/plugins/submitit_launcher/) launchers are also available.
#### Script
You can also load and launch your experiments from within a script
```python
experiment = Experiment(
task=VmasTask.BALANCE.get_from_yaml(),
algorithm_config=MappoConfig.get_from_yaml(),
model_config=MlpConfig.get_from_yaml(),
critic_model_config=MlpConfig.get_from_yaml(),
seed=0,
config=ExperimentConfig.get_from_yaml(),
)
experiment.run()
```
[](examples/running/run_experiment.py)
You can also run multiple experiments in a `Benchmark`.
```python
benchmark = Benchmark(
algorithm_configs=[
MappoConfig.get_from_yaml(),
QmixConfig.get_from_yaml(),
MasacConfig.get_from_yaml(),
],
tasks=[
VmasTask.BALANCE.get_from_yaml(),
VmasTask.SAMPLING.get_from_yaml(),
],
seeds={0, 1},
experiment_config=ExperimentConfig.get_from_yaml(),
model_config=MlpConfig.get_from_yaml(),
critic_model_config=MlpConfig.get_from_yaml(),
)
benchmark.run_sequential()
```
[](examples/running/run_benchmark.py)
## Concept
The goal of BenchMARL is to bring different MARL environments and algorithms
under the same interfaces to enable fair and reproducible comparison and benchmarking.
BenchMARL is a full-pipline unified training library with the goal of enabling users to run
any comparison they want across our algorithms and tasks in just one line of code.
To achieve this, BenchMARL interconnects components from [TorchRL](https://github.com/pytorch/rl),
which provides an efficient and reliable backend.
The library has a [default configuration](benchmarl/conf) for each of its components.
While parts of this configuration are supposed to be changed (for example experiment configurations),
other parts (such as tasks) should not be changed to allow for reproducibility.
To aid in this, each version of BenchMARL is paired to a default configuration.
Let's now introduce each component in the library.
**Experiment**. An experiment is a training run in which an algorithm, a task, and a model are fixed.
Experiments are configured by passing these values alongside a seed and the experiment hyperparameters.
The experiment [hyperparameters](benchmarl/conf/experiment/base_experiment.yaml) cover both
on-policy and off-policy algorithms, discrete and continuous actions, and probabilistic and deterministic policies
(as they are agnostic of the algorithm or task used).
An experiment can be launched from the command line or from a script.
See the [run](#run) section for more information.
**Benchmark**. In the library we call `benchmark` a collection of experiments that can vary in tasks, algorithm, or model.
A benchmark shares the same experiment configuration across all of its experiments.
Benchmarks allow to compare different MARL components in a standardized way.
A benchmark can be launched from the command line or from a script.
See the [run](#run) section for more information.
**Algorithms**. Algorithms are an ensemble of components (e.g., losss, replay buffer) which
determine the training strategy. Here is a table with the currently implemented algorithms in BenchMARL.
| Name | On/Off policy | Actor-critic | Full-observability in critic | Action compatibility | Probabilistic actor |
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|--------------|------------------------------|-----------------------|---------------------|
| [MAPPO](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.01955) | On | Yes | Yes | Continuous + Discrete | Yes |
| [IPPO](https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.09533) | On | Yes | No | Continuous + Discrete | Yes |
| [MADDPG](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02275) | Off | Yes | Yes | Continuous | No |
| [IDDPG](benchmarl/algorithms/iddpg.py) | Off | Yes | No | Continuous | No |
| [MASAC](benchmarl/algorithms/masac.py) | Off | Yes | Yes | Continuous + Discrete | Yes |
| [ISAC](benchmarl/algorithms/isac.py) | Off | Yes | No | Continuous + Discrete | Yes |
| [QMIX](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.11485) | Off | No | NA | Discrete | No |
| [VDN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05296) | Off | No | NA | Discrete | No |
| [IQL](https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Multi-Agent-Reinforcement-Learning%3A-Independent-Tan/59de874c1e547399b695337bcff23070664fa66e) | Off | No | NA | Discrete | No |
**Tasks**. Tasks are scenarios from a specific environment which constitute the MARL
challenge to solve.
They differ based on many aspects, here is a table with the current environments in BenchMARL
| Environment | Tasks | Cooperation | Global state | Reward function | Action space | Vectorized |
|---------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|---------------------------|--------------|-------------------------------|-----------------------|:----------------:|
| [VMAS](https://github.com/proroklab/VectorizedMultiAgentSimulator) | [27](benchmarl/conf/task/vmas) | Cooperative + Competitive | No | Shared + Independent + Global | Continuous + Discrete | Yes |
| [SMACv2](https://github.com/oxwhirl/smacv2) | [15](benchmarl/conf/task/smacv2) | Cooperative | Yes | Global | Discrete | No |
| [MPE](https://github.com/openai/multiagent-particle-envs) | [8](benchmarl/conf/task/pettingzoo) | Cooperative + Competitive | Yes | Shared + Independent | Continuous + Discrete | No |
| [SISL](https://github.com/sisl/MADRL) | [2](benchmarl/conf/task/pettingzoo) | Cooperative | No | Shared | Continuous | No |
| [MeltingPot](https://github.com/google-deepmind/meltingpot) | [49](benchmarl/conf/task/meltingpot) | Cooperative + Competitive | Yes | Independent | Discrete | No |
| [MAgent2](https://github.com/Farama-Foundation/magent2) | [1](benchmarl/conf/task/magent) | Cooperative + Competitive | Yes | Global in groups | Discrete | No |
> [!NOTE]
> BenchMARL uses the [TorchRL MARL API](https://github.com/pytorch/rl/issues/1463) for grouping agents.
> In competitive environments like MPE, for example, teams will be in different groups. Each group has its own loss,
> models, buffers, and so on. Parameter sharing options refer to sharing within the group. See the example on [creating
> a custom algorithm](examples/extending/algorithm/algorithms/customalgorithm.py) for more info.
**Models**. Models are neural networks used to process data. They can be used as actors (policies) or,
when requested, as critics. We provide a set of base models (layers) and a SequenceModel to concatenate
different layers. All the models can be used with or without parameter sharing within an
agent group. Here is a table of the models implemented in BenchMARL
| Name | Decentralized | Centralized with local inputs | Centralized with global input |
|------------------------------------------|:-------------:|:-----------------------------:|:-----------------------------:|
| [MLP](benchmarl/models/mlp.py) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [GRU](benchmarl/models/gru.py) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [LSTM](benchmarl/models/lstm.py) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [GNN](benchmarl/models/gnn.py) | Yes | Yes | No |
| [CNN](benchmarl/models/cnn.py) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [Deepsets](benchmarl/models/deepsets.py) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
## Fine-tuned public benchmarks
> [!WARNING]
> This section is under a work in progress. We are constantly working on fine-tuning
> our experiments to enable our users to have access to state-of-the-art benchmarks.
> If you would like to collaborate in this effort, please reach out to us.
In the [fine_tuned](fine_tuned) folder we are collecting some tested hyperparameters for
specific environments to enable users to bootstrap their benchmarking.
You can just run the scripts in this folder to automatically use the proposed hyperparameters.
We will tune benchmarks for you and publish the config and benchmarking plots on
[Wandb](https://wandb.ai/matteobettini/benchmarl-public/reportlist) publicly
Currently available ones are:
- **VMAS**: [](fine_tuned/vmas/conf/config.yaml) [](https://api.wandb.ai/links/matteobettini/r5744vas)
In the following, we report a table of the results:
| **
Environment
** | **Sample efficiency curves (all tasks)
** | **Performance profile
** | **Aggregate scores
** |
|---------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| VMAS | 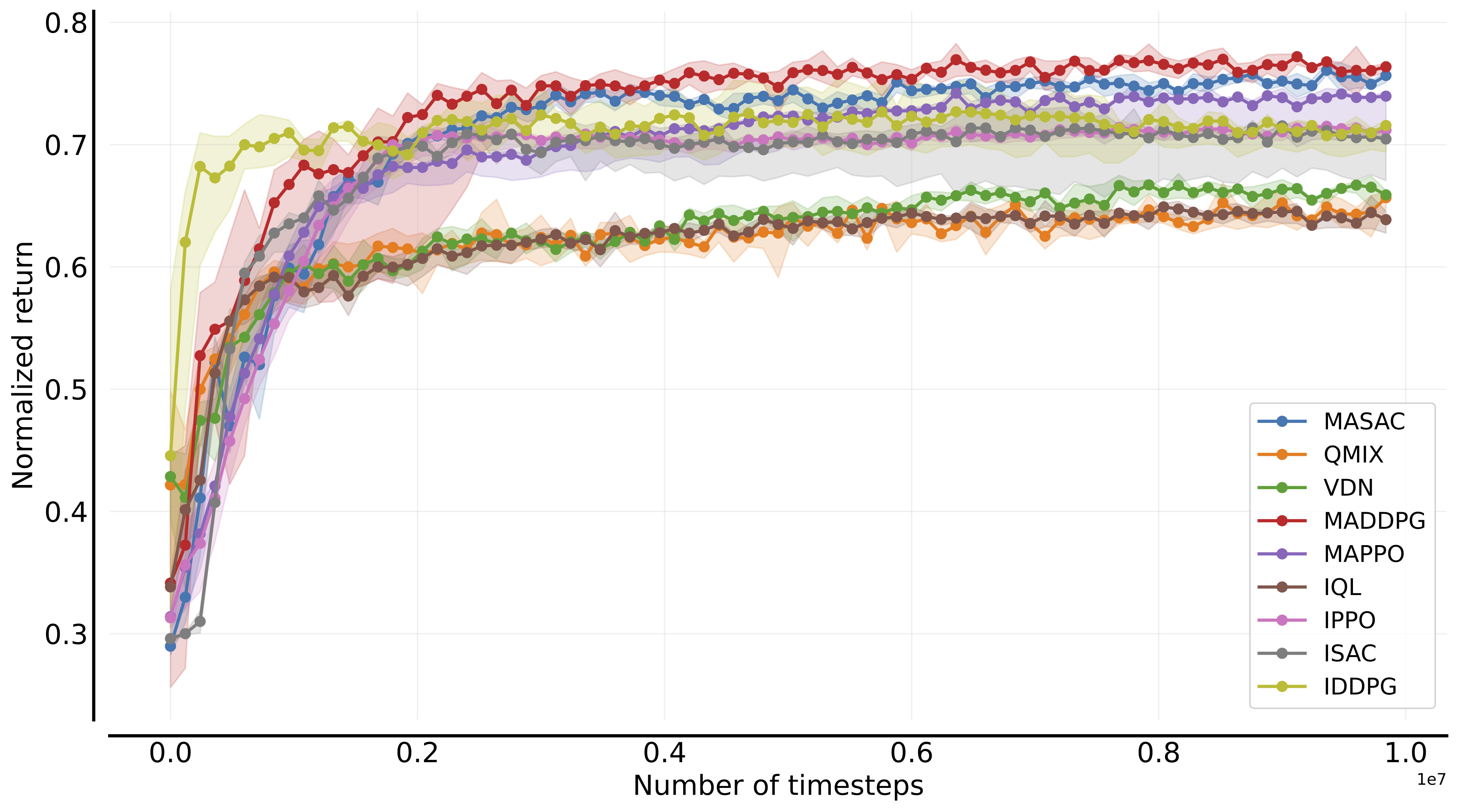 |
| 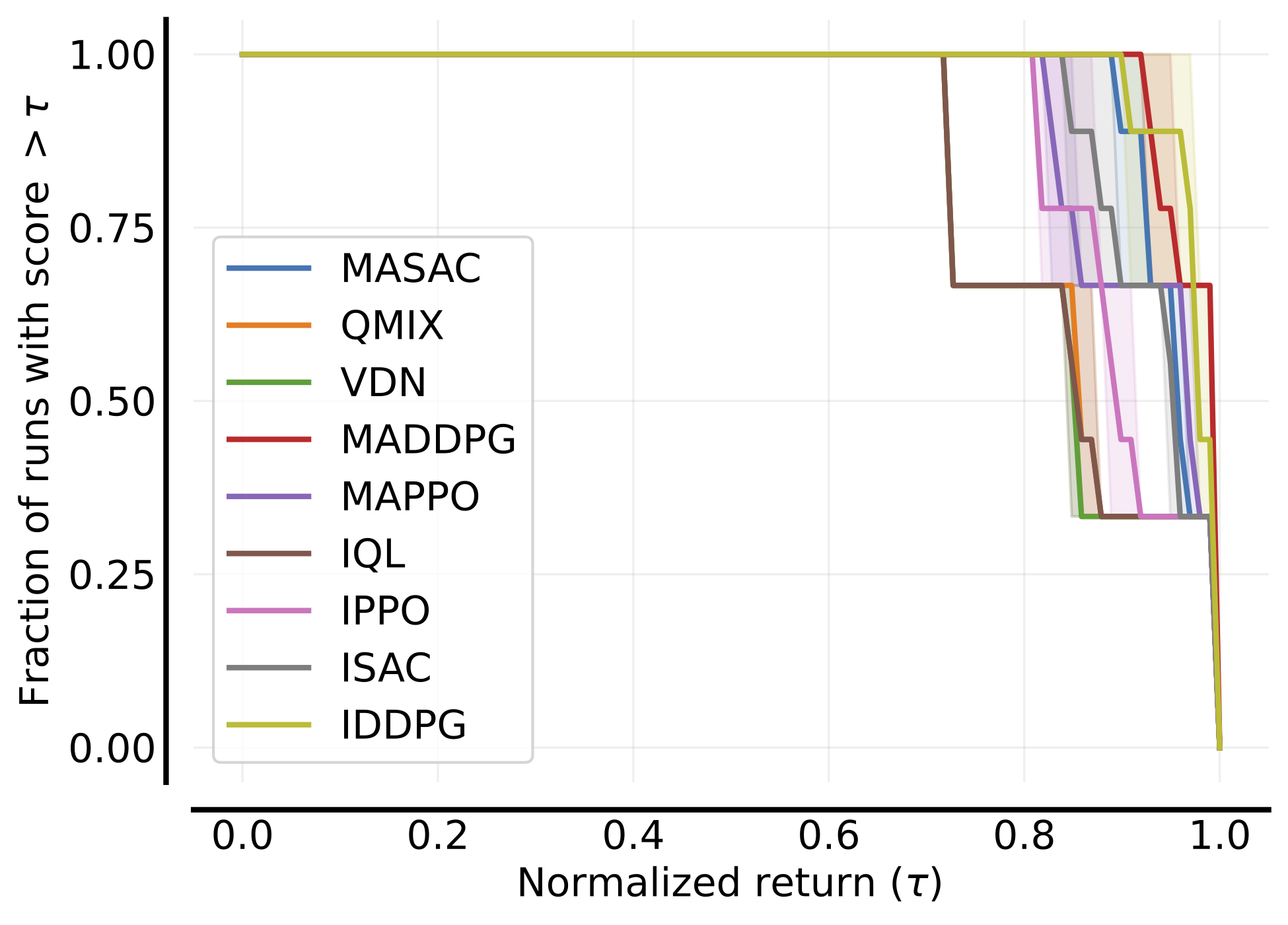 |
| 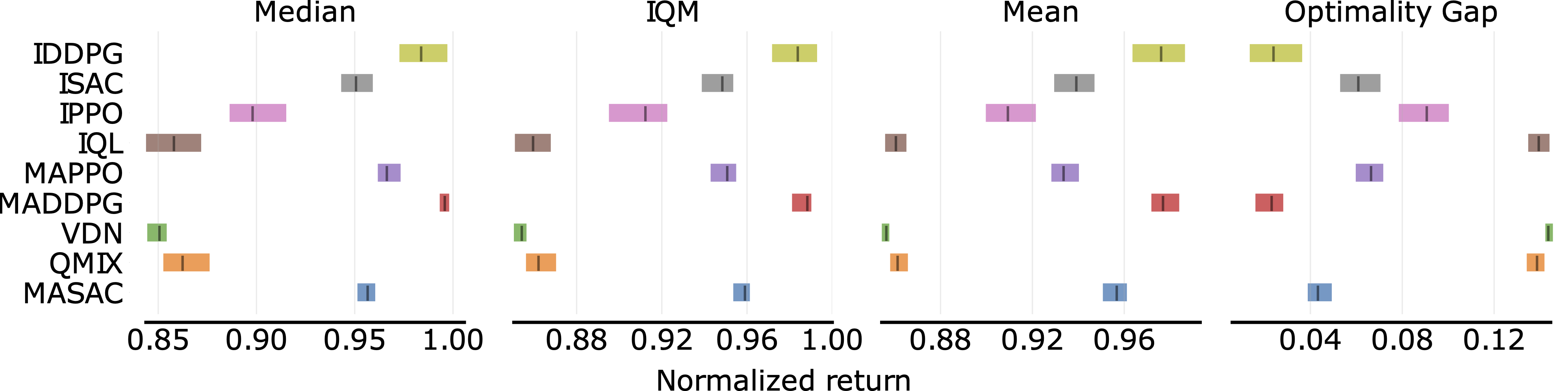 |
|
## Reporting and plotting
Reporting and plotting is compatible with [marl-eval](https://github.com/instadeepai/marl-eval).
If `experiment.create_json=True` (this is the default in the [experiment config](benchmarl/conf/experiment/base_experiment.yaml))
a file named `{experiment_name}.json` will be created in the experiment output folder with the format of [marl-eval](https://github.com/instadeepai/marl-eval).
You can load and merge these files using the utils in [eval_results](benchmarl/eval_results.py) to create beautiful plots of
your benchmarks. No more struggling with matplotlib and latex!
[](examples/plotting)



## Extending
One of the core tenets of BenchMARL is allowing users to leverage the existing algorithm
and tasks implementations to benchmark their newly proposed solution.
For this reason we expose standard interfaces with simple abstract methods
for [algorithms](benchmarl/algorithms/common.py), [tasks](benchmarl/environments/common.py) and [models](benchmarl/models/common.py).
To introduce your solution in the library, you just need to implement the abstract methods
exposed by these base classes which use objects from the [TorchRL](https://github.com/pytorch/rl) library.
Here is an example on how you can create a custom algorithm [](examples/extending/algorithm).
Here is an example on how you can create a custom task [](examples/extending/task).
Here is an example on how you can create a custom model [](examples/extending/model).
## Configuring
As highlighted in the [run](#run) section, the project can be configured either
in the script itself or via [hydra](https://hydra.cc/docs/intro/).
We suggest to read the hydra documentation
to get familiar with all its functionalities.
Each component in the project has a corresponding yaml configuration in the BenchMARL
[conf tree](benchmarl/conf).
Components' configurations are loaded from these files into python dataclasses that act
as schemas for validation of parameter names and types. That way we keep the best of
both words: separation of all configuration from code and strong typing for validation!
You can also directly load and validate configuration yaml files without using hydra from a script by calling
`ComponentConfig.get_from_yaml()`.
### Experiment
Experiment configurations are in [`benchmarl/conf/config.yaml`](benchmarl/conf/config.yaml).
Running custom experiments is extremely simplified by the [Hydra](https://hydra.cc/) configurations.
The default configuration for the library is contained in the [`benchmarl/conf`](benchmarl/conf) folder.
When running an experiment you can override its hyperparameters like so
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo experiment.lr=0.03 experiment.evaluation=true experiment.train_device="cpu"
```
Experiment hyperparameters are loaded from [`benchmarl/conf/experiment/base_experiment.yaml`](benchmarl/conf/experiment/base_experiment.yaml)
into a dataclass [`ExperimentConfig`](benchmarl/experiment/experiment.py) defining their domain.
This makes it so that all and only the parameters expected are loaded with the right types.
You can also directly load them from a script by calling `ExperimentConfig.get_from_yaml()`.
Here is an example of overriding experiment hyperparameters from hydra
[](examples/configuring/configuring_experiment.sh) or from
a script [](examples/configuring/configuring_experiment.py).
### Algorithm
You can override an algorithm configuration when launching BenchMARL.
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=masac algorithm.num_qvalue_nets=3 algorithm.target_entropy=auto algorithm.share_param_critic=true
```
Available algorithms and their default configs can be found at [`benchmarl/conf/algorithm`](benchmarl/conf/algorithm).
They are loaded into a dataclass [`AlgorithmConfig`](benchmarl/algorithms/common.py), present for each algorithm, defining their domain.
This makes it so that all and only the parameters expected are loaded with the right types.
You can also directly load them from a script by calling `YourAlgorithmConfig.get_from_yaml()`.
Here is an example of overriding algorithm hyperparameters from hydra
[](examples/configuring/configuring_algorithm.sh) or from
a script [](examples/configuring/configuring_algorithm.py).
### Task
You can override a task configuration when launching BenchMARL.
However this is not recommended for benchmarking as tasks should have fixed version and parameters for reproducibility.
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo task.n_agents=4
```
Available tasks and their default configs can be found at [`benchmarl/conf/task`](benchmarl/conf/task).
They are loaded into a dataclass [`TaskConfig`](benchmarl/environments/common.py), defining their domain.
Tasks are enumerations under the environment name. For example, `VmasTask.NAVIGATION` represents the navigation task in the
VMAS simulator. This allows autocompletion and seeing all available tasks at once.
You can also directly load them from a script by calling `YourEnvTask.TASK_NAME.get_from_yaml()`.
Here is an example of overriding task hyperparameters from hydra
[](examples/configuring/configuring_task.sh) or from
a script [](examples/configuring/configuring_task.py).
### Model
You can override the model configuration when launching BenchMARL.
By default an MLP model will be loaded with the default config.
You can change it like so:
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo model=layers/mlp model=layers/mlp model.layer_class="torch.nn.Linear" "model.num_cells=[32,32]" model.activation_class="torch.nn.ReLU"
```
Available models and their configs can be found at [`benchmarl/conf/model/layers`](benchmarl/conf/model/layers).
They are loaded into a dataclass [`ModelConfig`](benchmarl/models/common.py), defining their domain.
You can also directly load them from a script by calling `YourModelConfig.get_from_yaml()`.
Here is an example of overriding model hyperparameters from hydra
[](examples/configuring/configuring_model.sh) or from
a script [](examples/configuring/configuring_model.py).
#### Sequence model
You can compose layers into a sequence model.
Available layer names are in the [`benchmarl/conf/model/layers`](benchmarl/conf/model/layers) folder.
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo model=sequence "model.intermediate_sizes=[256]" "model/[email protected]=mlp" "model/[email protected]=mlp" "+model/[email protected]=mlp" "model.layers.l3.num_cells=[3]"
```
Add a layer with `"+model/[email protected]=mlp"`.
Remove a layer with `"~model.layers.l2"`.
Configure a layer with `"model.layers.l1.num_cells=[3]"`.
Here is an example of creating a sequence model from hydra
[](examples/configuring/configuring_sequence_model.sh) or from
a script [](examples/configuring/configuring_sequence_model.py).
## Features
BenchMARL has several features:
- A test CI with integration and training test routines that are run for all simulators and algorithms
- Integration in the official TorchRL ecosystem for dedicated support
- Possibility of using different algorithms and models for different agent groups (see [`examples/ensemble`](examples/ensemble))
### Logging
BenchMARL is compatible with the [TorchRL loggers](https://github.com/pytorch/rl/tree/main/torchrl/record/loggers).
A list of logger names can be provided in the [experiment config])(benchmarl/conf/experiment/base_experiment.yaml.
Example of available options are: `wandb`, `csv`, `mflow`, `tensorboard` or any other option available in TorchRL. You can specify the loggers
in the yaml config files or in the script arguments like so:
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py algorithm=mappo task=vmas/balance "experiment.loggers=[wandb]"
```
The wandb logger is fully compatible with experiment restoring and will automatically resume the run of
the loaded experiment.
### Checkpointing
Experiments can be checkpointed every `experiment.checkpoint_interval` collected frames.
Experiments will use an output folder for logging and checkpointing which can be specified in `experiment.save_folder`.
If this is left unspecified,
the default will be the hydra output folder (if using hydra) or (otherwise) the current directory
where the script is launched.
The output folder will contain a folder for each experiment with the corresponding experiment name.
Their checkpoints will be stored in a `"checkpoints"` folder within the experiment folder.
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo experiment.max_n_iters=3 experiment.on_policy_collected_frames_per_batch=100 experiment.checkpoint_interval=100
```
To load from a checkpoint, pass the absolute checkpoint file name to `experiment.restore_file`.
```bash
python benchmarl/run.py task=vmas/balance algorithm=mappo experiment.max_n_iters=6 experiment.on_policy_collected_frames_per_batch=100 experiment.restore_file="/hydra/experiment/folder/checkpoint/checkpoint_300.pt"
```
[](examples/checkpointing/reload_experiment.py)
There are also ways to **resume** and **evaluate** hydra experiments directly from the file
```bash
python benchmarl/evaluate.py ../outputs/2024-09-09/20-39-31/mappo_balance_mlp__cd977b69_24_09_09-20_39_31/checkpoints/checkpoint_100.pt
```
```bash
python benchmarl/resume.py ../outputs/2024-09-09/20-39-31/mappo_balance_mlp__cd977b69_24_09_09-20_39_31/checkpoints/checkpoint_100.pt
```
### Callbacks
Experiments optionally take a list of [`Callback`](benchmarl/experiment/callback.py) which have several methods
that you can implement to see what's going on during training such
as `on_batch_collected`, `on_train_end`, and `on_evaluation_end`.
[](examples/callback/custom_callback.py)
## Citing BenchMARL
If you use BenchMARL in your research please use the following BibTeX entry:
```BibTeX
@article{bettini2024benchmarl,
author = {Matteo Bettini and Amanda Prorok and Vincent Moens},
title = {BenchMARL: Benchmarking Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2024},
volume = {25},
number = {217},
pages = {1--10},
url = {http://jmlr.org/papers/v25/23-1612.html}
}
```
## License
BenchMARL is licensed under the MIT License. See [LICENSE](LICENSE) for details.