https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus
A library for differentiable nonlinear optimization
https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus
bilevel-optimization computer-vision deep-learning differentiable-optimization embodied-ai gauss-newton implicit-differentiation levenberg-marquardt nonlinear-least-squares pytorch robotics
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
A library for differentiable nonlinear optimization
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus
- Owner: facebookresearch
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-11-18T20:28:27.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-16T17:47:06.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-28T11:52:42.738Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: bilevel-optimization, computer-vision, deep-learning, differentiable-optimization, embodied-ai, gauss-newton, implicit-differentiation, levenberg-marquardt, nonlinear-least-squares, pytorch, robotics
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 11.3 MB
- Stars: 1,877
- Watchers: 32
- Forks: 133
- Open Issues: 78
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-robotics-projects - facebookresearch/theseus - A library for differentiable nonlinear optimization (Library, Framework, SDK / ML & Vision)
README

A library for differentiable nonlinear optimization
Paper •
Video •
Twitter •
Webpage •
Tutorials
Theseus is an efficient application-agnostic library for building custom nonlinear optimization layers in PyTorch to support constructing various problems in robotics and vision as end-to-end differentiable architectures.
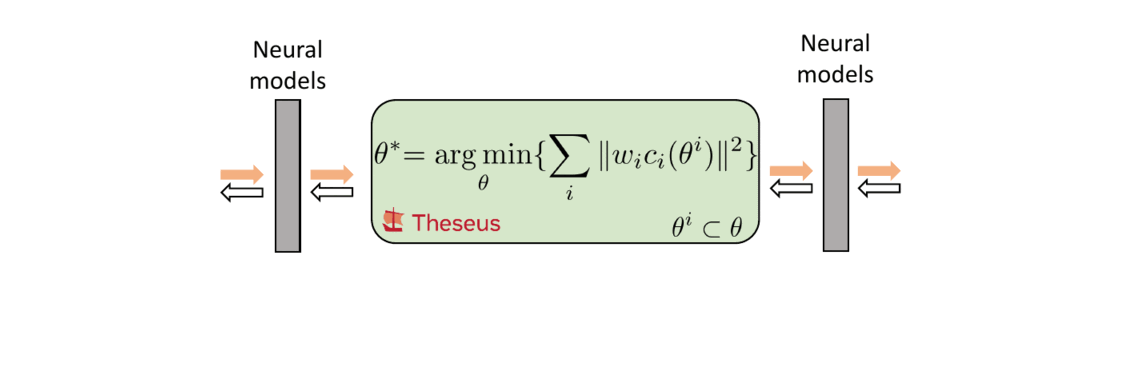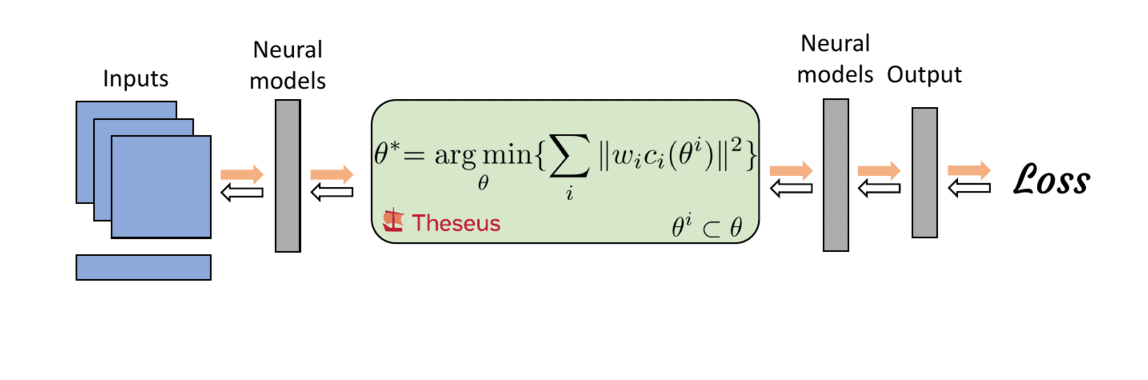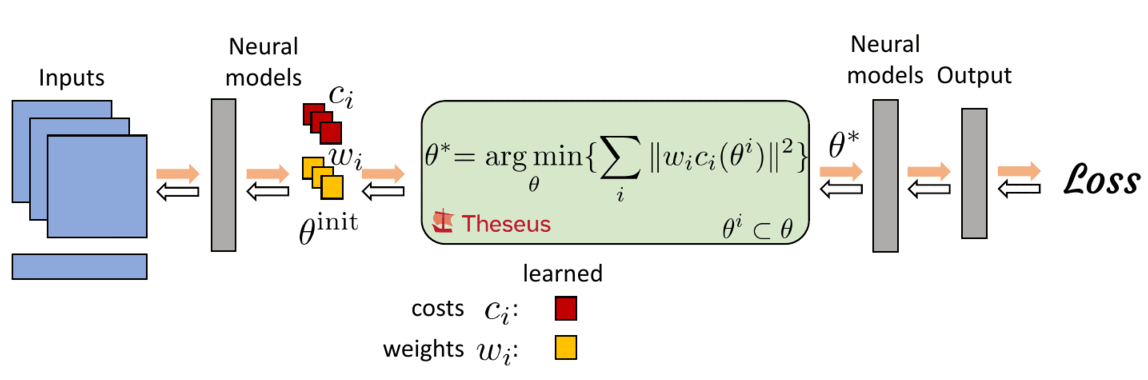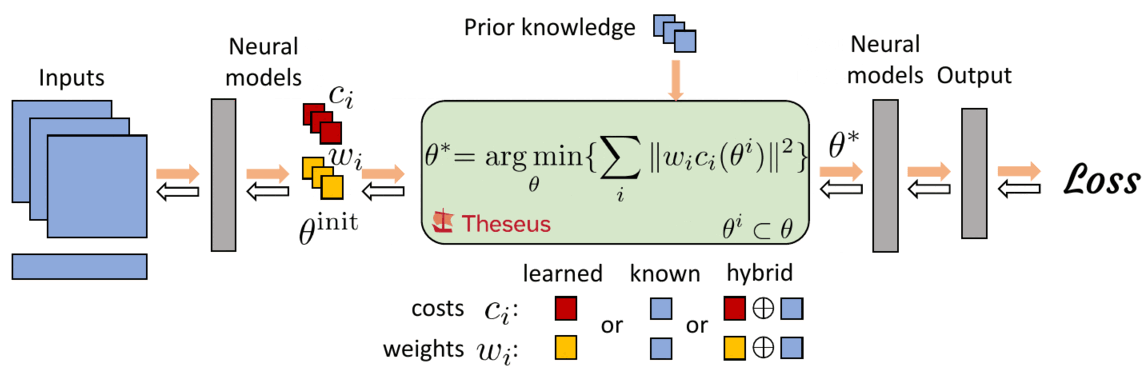
Differentiable nonlinear optimization provides a general scheme to encode inductive priors, as the objective function can be partly parameterized by neural models and partly with expert domain-specific differentiable models. The ability to compute gradients end-to-end is retained by differentiating through the optimizer which allows neural models to train on the final task loss, while also taking advantage of priors captured by the optimizer.
See [list of papers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/papers.md) published using Theseus for examples across various application domains.
-----
## Current Features
### Application agnostic interface
Our implementation provides an easy to use interface to build custom optimization layers and plug them into any neural architecture. Following differentiable features are currently available:
- [Second-order nonlinear optimizers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/optimizer/nonlinear)
- Gauss-Newton (GN), Levenberg–Marquardt (LM), Trust Region, Dogleg
- [Other nonlinear optimizers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/optimizer/nonlinear)
- Cross Entropy Method (CEM)
- [Linear solvers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/optimizer/linear)
- Dense: Cholesky, LU; Sparse: CHOLMOD, LU (GPU-only), [BaSpaCho](https://github.com/facebookresearch/baspacho)
- [Commonly used costs](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/embodied), [AutoDiffCostFunction](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/core/cost_function.py), [RobustCostFunction](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/core/robust_cost_function.py)
- [Lie groups](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/geometry) based on [torchlie](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/torchlie)
- [Robot kinematics](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/embodied/kinematics) based on [torchkin](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/torchkin)
### Efficiency based design
We support several features that improve computation times and memory consumption:
- [Sparse linear solvers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/optimizer/linear)
- Batching and GPU acceleration
- [Automatic vectorization](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/core/vectorizer.py)
- [Backward modes](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/optimizer/nonlinear/nonlinear_optimizer.py)
- Implicit, Truncated, Direct Loss Minimization ([DLM](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/theseus/theseus_layer.py)), Sampling ([LEO](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/examples/state_estimation_2d.py))
## Getting Started
### Prerequisites
- We *strongly* recommend you install Theseus in a venv or conda environment with Python 3.8-3.10.
- Theseus requires `torch` installation. To install for your particular CPU/CUDA configuration, follow the instructions in the PyTorch [website](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/).
- For GPU support, Theseus requires [nvcc](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-compiler-driver-nvcc/index.html) to compile custom CUDA operations. Make sure it matches the version used to compile pytorch with `nvcc --version`. If not, install it and ensure its location is on your system's `$PATH` variable.
- Theseus also requires [`suitesparse`](https://people.engr.tamu.edu/davis/suitesparse.html), which you can install via:
- `sudo apt-get install libsuitesparse-dev` (Ubuntu).
- `conda install -c conda-forge suitesparse` (Mac).
### Installing
- **pypi**
```bash
pip install theseus-ai
```
We currently provide wheels with our CUDA extensions compiled using CUDA 11.6 and Python 3.10.
For other CUDA versions, consider installing from source or using our
[build script](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/build_scripts/build_wheel.sh).
Note that `pypi` installation doesn't include our experimental [Theseus Labs](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/theseus/labs).
For this, please install from source.
- #### **From source**
The simplest way to install Theseus from source is by running the following (see further below to also include BaSpaCho)
```bash
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus.git && cd theseus
pip install -e .
```
If you are interested in contributing to Theseus, instead install
```bash
pip install -e ".[dev]"
pre-commit install
```
and follow the more detailed instructions in [CONTRIBUTING](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).
- **Installing BaSpaCho extensions from source**
By default, installing from source doesn't include our BaSpaCho sparse solver extension. For this, follow these steps:
1. Compile BaSpaCho from source following instructions [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/baspacho). We recommend using flags `-DBLA_STATIC=ON -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=OFF`.
2. Run
```bash
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus.git && cd theseus
BASPACHO_ROOT_DIR= pip install -e .
```
where the BaSpaCho root dir must have the binaries in the subdirectory `build`.
### Running unit tests (requires `dev` installation)
```bash
python -m pytest tests
```
By default, unit tests include tests for our CUDA extensions. You can add the option `-m "not cudaext"`
to skip them when installing without CUDA support. Additionally, the tests for sparse solver BaSpaCho are automatically
skipped when its extlib is not compiled.
## Examples
[Simple example](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/examples/simple_example.py). This example is fitting the curve $y$ to a dataset of $N$ observations $(x,y) \sim D$. This is modeled as an `Objective` with a single `CostFunction` that computes the residual $y - v e^x$. The `Objective` and the `GaussNewton` optimizer are encapsulated into a `TheseusLayer`. With `Adam` and MSE loss, $x$ is learned by differentiating through the `TheseusLayer`.
```python
import torch
import theseus as th
x_true, y_true, v_true = read_data() # shapes (1, N), (1, N), (1, 1)
x = th.Variable(torch.randn_like(x_true), name="x")
y = th.Variable(y_true, name="y")
v = th.Vector(1, name="v") # a manifold subclass of Variable for optim_vars
def error_fn(optim_vars, aux_vars): # returns y - v * exp(x)
x, y = aux_vars
return y.tensor - optim_vars[0].tensor * torch.exp(x.tensor)
objective = th.Objective()
cost_function = th.AutoDiffCostFunction(
[v], error_fn, y_true.shape[1], aux_vars=[x, y],
cost_weight=th.ScaleCostWeight(1.0))
objective.add(cost_function)
layer = th.TheseusLayer(th.GaussNewton(objective, max_iterations=10))
phi = torch.nn.Parameter(x_true + 0.1 * torch.ones_like(x_true))
outer_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([phi], lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(10):
solution, info = layer.forward(
input_tensors={"x": phi.clone(), "v": torch.ones(1, 1)},
optimizer_kwargs={"backward_mode": "implicit"})
outer_loss = torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(solution["v"], v_true)
outer_loss.backward()
outer_optimizer.step()
```
See [tutorials](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/tutorials/), and robotics and vision [examples](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/tree/main/examples) to learn about the API and usage.
## Citing Theseus
If you use Theseus in your work, please cite the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.09442) with the BibTeX below.
```bibtex
@article{pineda2022theseus,
title = {{Theseus: A Library for Differentiable Nonlinear Optimization}},
author = {Luis Pineda and Taosha Fan and Maurizio Monge and Shobha Venkataraman and Paloma Sodhi and Ricky TQ Chen and Joseph Ortiz and Daniel DeTone and Austin Wang and Stuart Anderson and Jing Dong and Brandon Amos and Mustafa Mukadam},
journal = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
year = {2022}
}
```
## License
Theseus is MIT licensed. See the [LICENSE](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/LICENSE) for details.
## Additional Information
- Join the community on [Github Discussions](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/discussions) for questions and sugesstions.
- Use [Github Issues](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/issues/new/choose) for bugs and features.
- See [CONTRIBUTING](https://github.com/facebookresearch/theseus/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) if interested in helping out.
Theseus is made possible by the following contributors:
Made with [contrib.rocks](https://contrib.rocks).
