https://github.com/fboender/multi-git-status
Show uncommitted, untracked and unpushed changes for multiple Git repos
https://github.com/fboender/multi-git-status
git overview scans status uncommited unpushed-changes untracked-files
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Show uncommitted, untracked and unpushed changes for multiple Git repos
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/fboender/multi-git-status
- Owner: fboender
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-12-07T15:01:47.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-10-31T13:10:52.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-14T18:17:23.284Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: git, overview, scans, status, uncommited, unpushed-changes, untracked-files
- Language: Shell
- Size: 192 KB
- Stars: 491
- Watchers: 16
- Forks: 72
- Open Issues: 14
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-starred - multi-git-status - Show uncommitted, untracked and unpushed changes for multiple Git repos (Shell)
- awesome-devop-tools - multi-git-status
README
mgitstatus
==========
Show uncommitted, untracked and unpushed changes in multiple Git
repositories. Scan for .git dirs up to **DEPTH** directories deep.
The default is 2. If **DEPTH** is 0, the scan is infinitely deep.
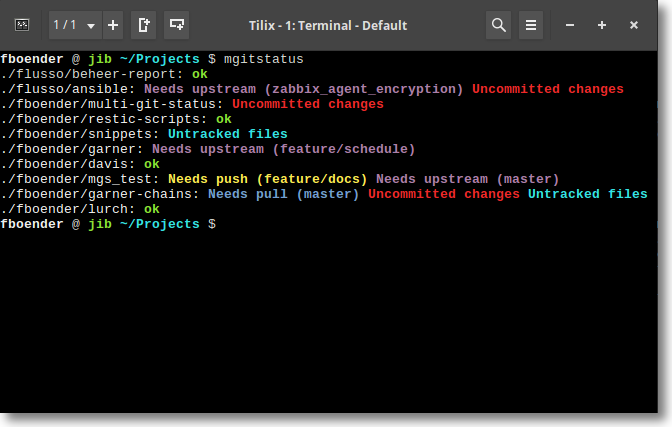
mgitstatus shows:
* **Uncommitted changes** if there are unstaged or uncommitted changes on the
checked out branch.
* **Untracked files** if there are untracked files which are not ignored.
* **Needs push (BRANCH)** if the branch is tracking a (remote) branch which is
behind.
* **Needs upstream (BRANCH)** if a branch does not have a local or remote
upstream branch configured. Changes in the branch may otherwise never be
pushed or merged.
* **Needs pull (BRANCH)** if the branch is tracking a (remote) branch which is
ahead. This requires that the local git repo already knows about the remote
changes (i.e. you've done a `fetch`), or that you specify the `-f` option.
mgitstatus does NOT contact the remote by default.
* **X stashes** if there are stashes.
Since there are a lot of different states a git repository can be in,
mgitstatus makes no guarantees that *all* states are taken into account.
mgitstatus can also list dirs that are not a repo, if given the `-w`
switch. To ignore certain repos, set the `mgitstatus.ignore` git config flag
for that repo to `true`. (See "usage" below for an example).
# Usage
Usage: mgitstatus [--version] [-w] [-e] [-f] [--throttle SEC] [-c] [-d/--depth=2] [--no-depth] [--flatten] [--no-X] [DIR [DIR]...]
mgitstatus shows uncommitted, untracked and unpushed changes in multiple Git
repositories. By default, mgitstatus scans two directories deep. This can be
changed with the -d (--depth) option. If DEPTH is 0, the scan is infinitely
deep.
--version Show version
-w Warn about dirs that are not Git repositories
-e Exclude repos that are 'ok'
-f Do a 'git fetch' on each repo (slow for many repos)
--throttle SEC Wait SEC seconds between each 'git fetch' (-f option)
-c Force color output (preserve colors when using pipes)
-d, --depth=2 Scan this many directories deep
--no-depth Do not recurse into directories (incompatible with -d)
--flatten Show only one status per line
You can limit output with the following options:
--no-push
--no-pull
--no-upstream
--no-uncommitted
--no-untracked
--no-stashes
--no-ok (same as -e)
The following example scans all directories under the current dir, with a
depth of 2. That means the current dir and all directories directly under it.
~/Projects/fboender $ mgitstatus
./mgitstatus: ok
./mdpreview: ok
./snippets: ok
./boxes: ok
./ansible-cmdb: Uncommitted changes Untracked files
./scriptform: Uncommitted changes
For more examples, see the [manual page](mgitstatus.1.md).
# Installation
mgitstatus requires make.
The following steps will install mgitstatus:
# Clone the repo
$ git clone https://github.com/fboender/multi-git-status.git
$ cd multi-git-status
# Install globally (all users)
$ sudo make install
# Install locally (only your user)
$ PREFIX=~/.local make install
# License
Copyright 2016-2022, Ferry Boender (et al).
Licensed under the MIT license. For more information, see the LICENSE.txt file.